The primary equipment used for calcination is a high-temperature reactor known as a calciner. This is a specialized, cylindrical apparatus designed to heat materials to a specific temperature in a controlled atmosphere to cause thermal decomposition or phase transition. In simpler applications or on a smaller scale, a high-temperature furnace may also be used.
While various types of furnaces and kilns can perform calcination, the core decision is not just about reaching a high temperature. It's about selecting a system that provides the precise control over heat transfer, atmosphere, and material handling required for the final product's specific chemical and physical properties.
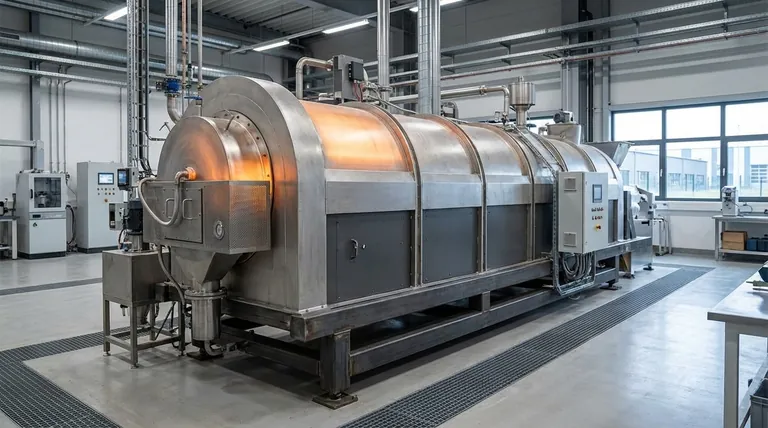

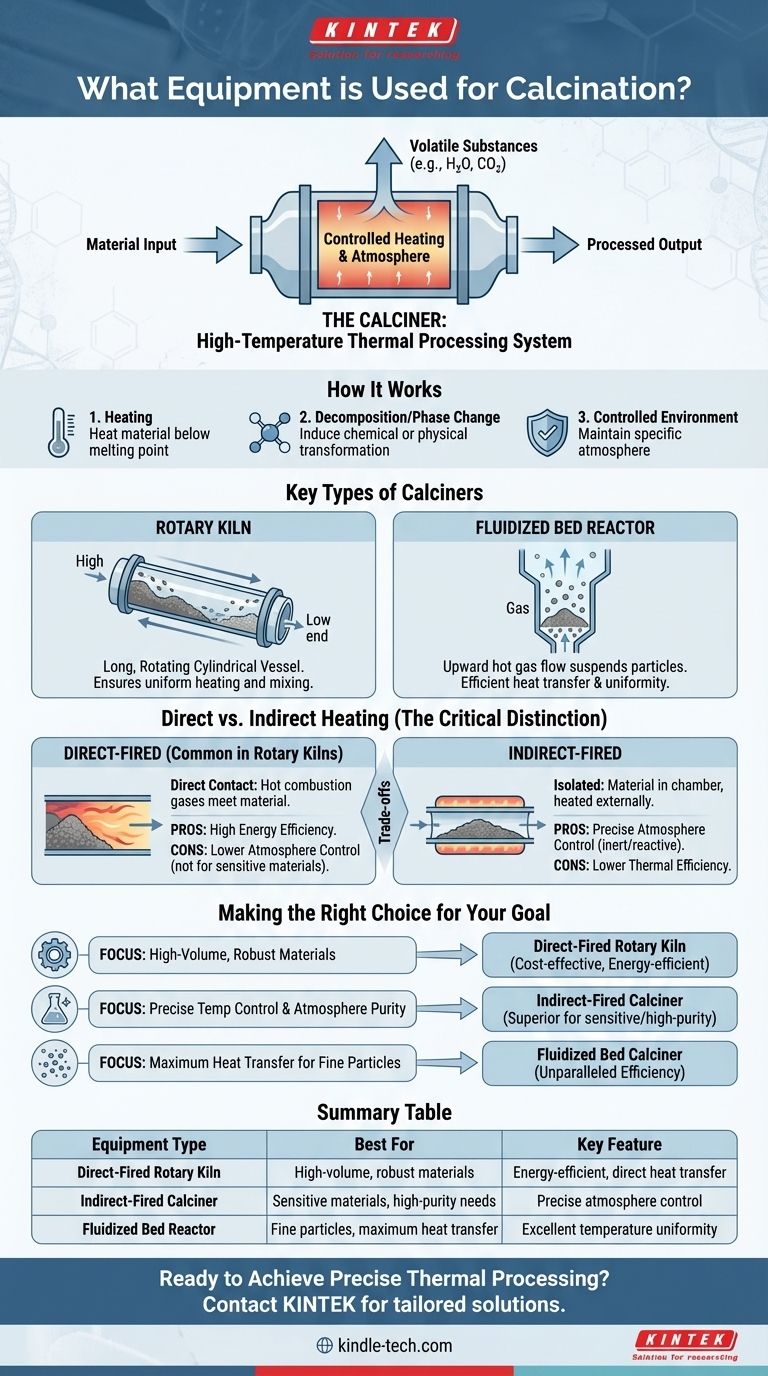
How Calcination Equipment Works
Calcination equipment is fundamentally a high-temperature thermal processing system. Its goal is to heat a material to a point below its melting point to drive off volatile substances (like water or carbon dioxide) and induce a chemical or physical change.
The Central Role of the Calciner
A calciner is purpose-built for this process. It is designed to handle continuous or batch processing of materials ranging from fine powders to larger granules and pellets.
The operation revolves around heating the material in a controlled environment. The specific design of the calciner determines exactly how this is achieved.
Key Types of Calciners
The two dominant designs for industrial calciners are rotary kilns and fluidized bed reactors. Each offers a different mechanism for material handling and heat transfer.
A rotary kiln is a long, rotating cylindrical vessel, often slightly inclined. Material is fed into the upper end and slowly moves to the lower end as the kiln rotates, ensuring uniform heating and mixing.
A fluidized bed calciner uses an upward flow of hot gas to suspend the material particles, creating a fluid-like behavior. This "fluidization" results in extremely efficient heat transfer and excellent temperature uniformity throughout the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The most critical distinction in calciner technology is the method of heating, as it directly impacts process control and final product quality.
Direct-Fired Calciners
In a direct-fired system, the hot combustion gases come into direct contact with the material being processed. This is common in many rotary kilns.
This method is highly energy-efficient because heat is transferred directly to the material. However, the contact with combustion gases means the process atmosphere cannot be tightly controlled, which can be a significant drawback for sensitive materials.
Indirect-Fired Calciners
In an indirect-fired system, the material is contained within a chamber (like a tube or vessel) that is heated from the outside. The combustion gases never touch the process material.
This approach allows for precise control over the atmosphere inside the chamber, making it ideal for processes that require an inert or reactive gas environment. The trade-off is typically lower thermal efficiency compared to direct-fired systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct equipment depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired characteristics of the final product.
- If your primary focus is high-volume processing of robust materials: A direct-fired rotary kiln is often the most cost-effective and energy-efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control and atmosphere purity: An indirect-fired calciner, whether rotary or fluidized bed, is the superior choice for sensitive or high-purity applications.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat transfer for fine particles: A fluidized bed calciner offers unparalleled efficiency and temperature uniformity for suitable materials.
Ultimately, the right calcination equipment is the one that provides the necessary control to achieve your specific material transformation reliably and efficiently.
Summary Table:
| Equipment Type | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-Fired Rotary Kiln | High-volume, robust materials | Energy-efficient, direct heat transfer |
| Indirect-Fired Calciner | Sensitive materials, high-purity needs | Precise atmosphere control |
| Fluidized Bed Reactor | Fine particles, maximum heat transfer | Excellent temperature uniformity |
Ready to Achieve Precise Thermal Processing?
Choosing the right calcination equipment is critical for achieving your desired material properties, whether you need high-volume processing or precise atmosphere control. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including thermal processing systems tailored to your specific laboratory needs.
Our experts can help you select the ideal system to ensure reliable and efficient material transformation. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Contact our experts now for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development



















