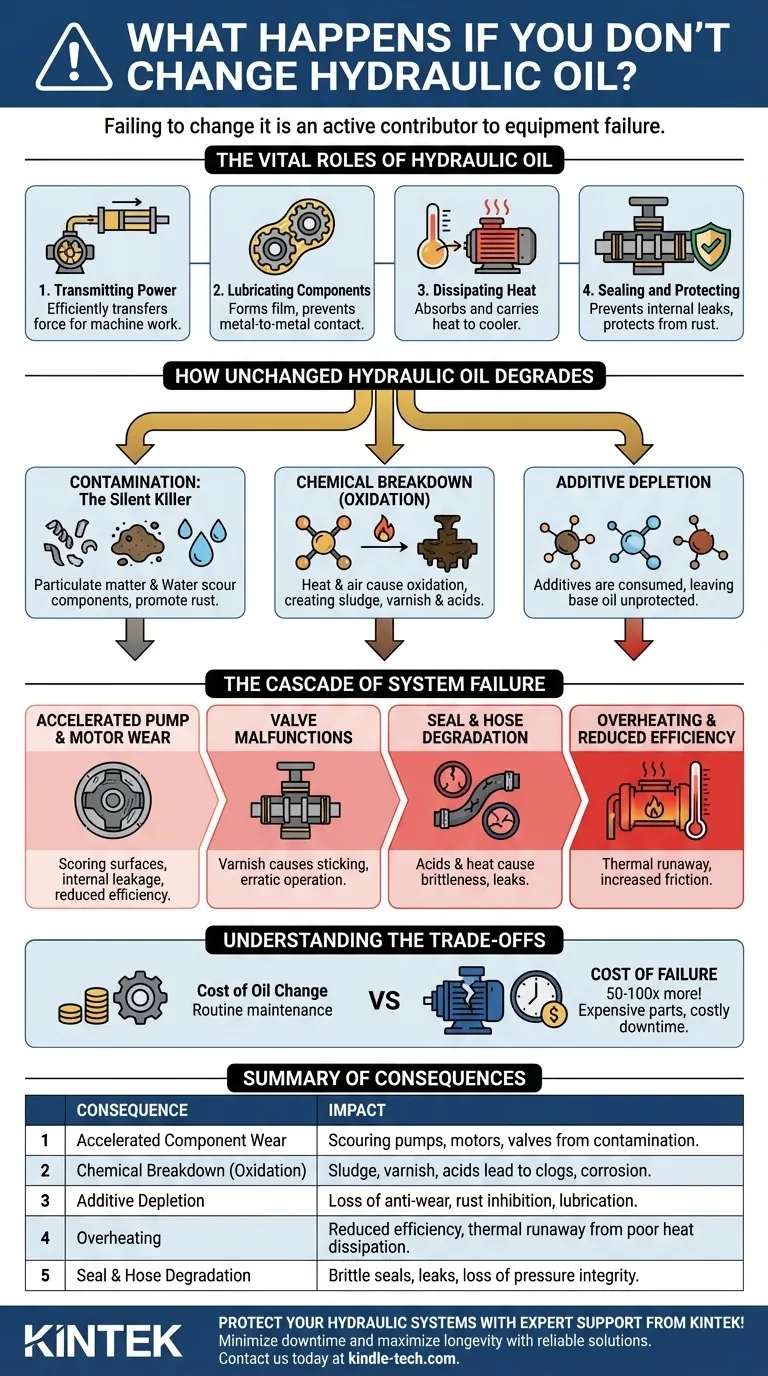
Failing to change hydraulic oil is not a passive act but an active contributor to equipment failure. Over time, the oil degrades and becomes contaminated, leading to accelerated component wear, decreased system efficiency, overheating, and ultimately, catastrophic failure of critical parts like pumps, valves, and cylinders.
Forgoing hydraulic oil changes is not a cost-saving measure; it is a high-risk gamble against the fundamental principles of machine operation. The fluid is a working component whose degradation directly leads to expensive, premature equipment failure and costly downtime.
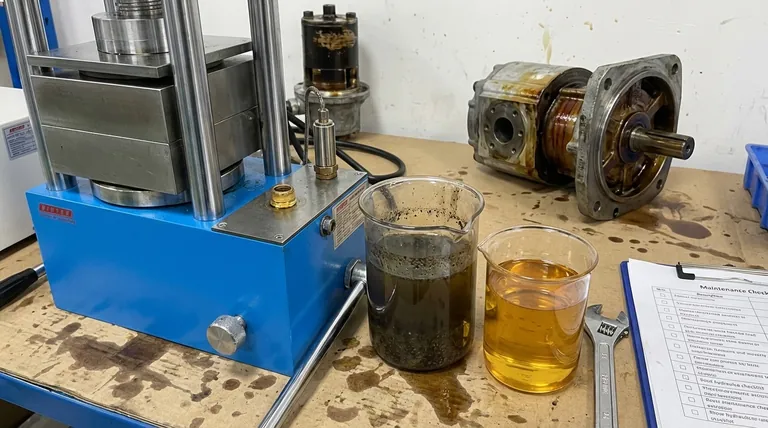

The Vital Roles of Hydraulic Oil
To understand why old oil is so destructive, you must first appreciate its four primary functions. It is far more than just a fluid.
Transmitting Power
This is the oil's most basic job. Being nearly incompressible, it efficiently transfers force from the pump to actuators like cylinders and motors, enabling the machine to do work.
Lubricating Components
Hydraulic systems are built with incredibly tight tolerances. The oil forms a critical film between moving metal parts—in pumps, motors, and valves—preventing direct metal-to-metal contact, which minimizes friction and wear.
Dissipating Heat
As hydraulic oil is forced through the system, friction and inefficiencies generate significant heat. The fluid absorbs this heat from components and carries it to the reservoir or a cooler to be dissipated, preventing overheating.
Sealing and Protecting
The oil helps form seals in components like spool valves and pumps, preventing internal leakage that would reduce efficiency. It also contains additives that protect metal surfaces from rust and corrosion.
How Unchanged Hydraulic Oil Degrades
Hydraulic oil does not last forever. It is subjected to immense stress that breaks it down through three primary mechanisms.
Contamination: The Silent Killer
Contamination is the leading cause of hydraulic system failure. Particulate matter (tiny metal shavings from wear, dirt from the environment) acts like liquid sandpaper, scouring and eroding precision components.
Water contamination is equally destructive. It promotes rust, reduces the oil's lubricating properties, and can cause additive depletion, leading to corrosion and accelerated wear.
Chemical Breakdown (Oxidation)
Exposure to heat, air, and pressure causes the oil's molecules to oxidize. This chemical reaction permanently changes the fluid, creating sludge, varnish, and corrosive acids.
Sludge clogs filters and passageways, while varnish coats internal surfaces, causing valves to stick and reducing heat dissipation. Acids attack seals and metal surfaces throughout the system.
Additive Depletion
Hydraulic oil is a carefully balanced formula of base oil and a package of critical additives. These additives (anti-wear, anti-foam, rust inhibitors) are sacrificial; they are consumed over time as they do their job.
Once these additives are depleted, the base oil is left unprotected and cannot perform its functions effectively, leading to rapid wear and chemical breakdown.
The Cascade of System Failure
Using degraded and contaminated oil sets off a chain reaction of failures that grow progressively worse.
Accelerated Pump and Motor Wear
Pumps and motors are the heart of the system and are extremely sensitive to contamination. Abrasive particles score the surfaces of vanes, pistons, and gears, causing internal leakage. This reduces efficiency, leading to slower operation and an inability to generate full pressure.
Valve Malfunctions
Varnish and sludge deposits cause spool valves to stick or seize. This results in erratic, unpredictable machine operation, loss of precision control, and potential safety hazards.
Seal and Hose Degradation
The acids formed during oil oxidation, combined with excessive heat, make rubber seals and hoses brittle. This causes them to crack and fail, leading to both internal and external leaks.
Overheating and Reduced Efficiency
This creates a destructive feedback loop. As oil thickens with sludge and components wear, friction increases, generating more heat. Simultaneously, the degraded oil is less effective at carrying that heat away. The system runs hotter, which accelerates oil oxidation even faster, leading to a thermal runaway condition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neglecting oil changes is often framed as saving money, but this view fundamentally misunderstands the costs involved.
The Cost of Oil vs. The Cost of Failure
A hydraulic oil change is a routine maintenance expense. The cost of replacing a failed variable displacement piston pump, plus the lost revenue from unplanned downtime, can easily be 50 to 100 times the cost of the fluid change that would have prevented the failure.
Relying on Filters Alone
Filters are essential for removing solid particles, but they have limitations. They cannot remove dissolved water, acids, or sludge. Critically, filters do not replenish depleted additives. A system with clean but chemically-depleted oil is still on a path to failure.
"Topping Off" Is Not a Solution
Adding new oil to a reservoir of old, contaminated fluid is a poor strategy. You are merely diluting the contaminants and acids temporarily. This does not address the core problem and provides a false sense of security.
Making the Right Maintenance Decision
Your approach to hydraulic maintenance should be based on your operational goals and the working environment of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability for critical equipment: Adhere to a strict maintenance schedule based on operating hours or calendar time, and consider using oil analysis to detect problems before they become failures.
- If your primary focus is managing a large fleet of equipment: Implement a scheduled maintenance program based on manufacturer recommendations and use oil analysis to safely optimize change intervals, preventing both premature changes and in-service failures.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a poorly performing system: Make inspecting the hydraulic oil's condition (color, smell, clarity) your first step. It is often the root cause of issues like slow operation, excess noise, or overheating.
Proactive oil management is the single most effective strategy for ensuring the reliability and longevity of any hydraulic system.
Summary Table:
| Consequence of Unchanged Oil | Impact on System |
|---|---|
| Accelerated Component Wear | Scouring of pumps, motors, and valves from particulate contamination |
| Chemical Breakdown (Oxidation) | Formation of sludge, varnish, and acids leading to clogs and corrosion |
| Additive Depletion | Loss of anti-wear, rust inhibition, and lubricating properties |
| Overheating | Reduced efficiency and thermal runaway from poor heat dissipation |
| Seal and Hose Degradation | Brittle seals, leaks, and loss of pressure integrity |
Protect your hydraulic systems with expert support from KINTEK!
Don't let neglected maintenance lead to expensive breakdowns. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for laboratory hydraulic system needs. Our expertise ensures your equipment runs efficiently, minimizing downtime and maximizing longevity.
Contact us today to discuss your maintenance strategy and keep your operations running smoothly!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the potential hazards in a hydraulic press? Understanding the Risks of Crushing, Injection, and Failure
- What are the failures of a hydraulic press? Prevent Downtime and Ensure Safety in Your Lab
- What is an automatic press machine? High-Precision Force for Modern Manufacturing
- What is the construction of a hydraulic press based on? Unlocking the Power of Pascal's Law
- What is the efficiency of a hydraulic press? Harness Unmatched Force Multiplication for Your Lab











