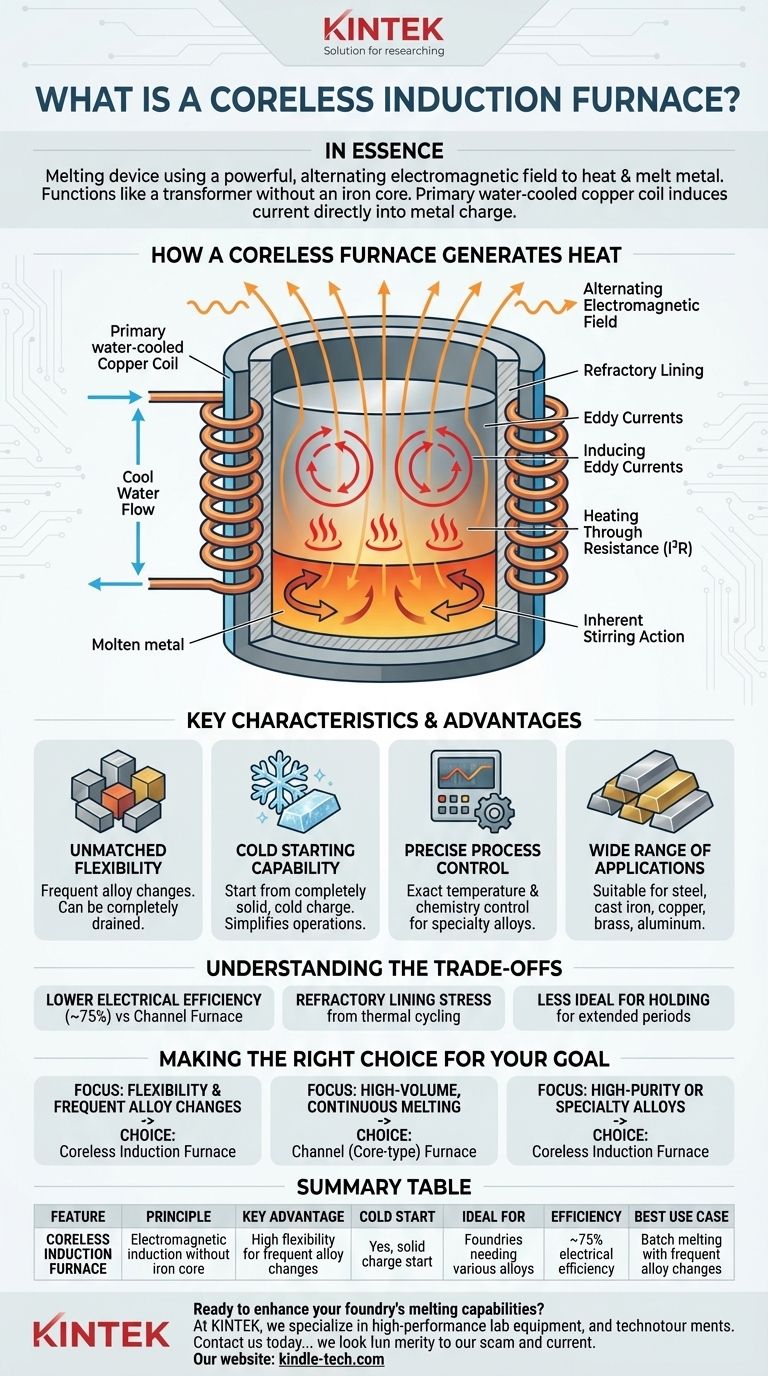
In essence, a coreless induction furnace is a melting device that uses a powerful, alternating electromagnetic field to heat and melt metal. It functions like a transformer where there is no central iron core. Instead, a primary water-cooled copper coil induces an electrical current directly into the metal charge itself, which acts as the secondary coil and heat source.
The defining characteristic of a coreless furnace is its operational flexibility. The absence of an iron core allows it to be started from cold and completely emptied, making it ideal for foundries that need to produce a variety of different metal alloys.

How a Coreless Furnace Generates Heat
The operating principle of a coreless furnace is based on direct induction. The heat is not applied from an external source; it is generated within the metal itself through a clean and contained process.
The Role of the Primary Coil
A coil made of high-conductivity, hollow copper tubing is the heart of the furnace. An alternating electrical current from a power supply flows through this coil, and cool water is circulated through the tubing to prevent the coil itself from overheating.
Inducing Eddy Currents
The alternating current in the coil generates a powerful and fluctuating magnetic field that penetrates the refractory lining and the metal charge held within it. This magnetic field, in turn, induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow directly within the conductive metal.
Heating Through Resistance
The metal has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance creates intense heat (I²R heating), rapidly raising the metal's temperature to its melting point and beyond. Because the heat is generated inside the material, melting is extremely fast and efficient.
The Inherent Stirring Action
The same electromagnetic forces that induce the current also create a vigorous, natural stirring motion within the molten metal bath. This stirring ensures excellent temperature uniformity and helps to thoroughly mix in alloying elements, resulting in a homogenous final product.
Key Characteristics and Advantages
The design of a coreless furnace gives it a unique set of capabilities that make it indispensable for modern metallurgy.
Unmatched Flexibility
The most significant advantage is the ability to change alloys frequently. Since the furnace can be completely drained, a foundry can melt a batch of stainless steel, empty the furnace, and then melt a batch of a different iron or non-ferrous alloy with minimal contamination.
Cold Starting Capability
Unlike some other furnace types that require a permanent molten "heel" to operate, a coreless furnace can be started with a completely solid, cold charge. This simplifies operations, reduces energy consumption during idle periods, and makes intermittent production schedules feasible.
Precise Process Control
Modern coreless furnaces are equipped with sophisticated power supplies and integrated control systems. These systems allow for precise control over power input, which translates to exact temperature management and control over metal chemistry, which is critical for producing specialty alloys.
Wide Range of Applications
This flexibility makes the coreless furnace suitable for melting nearly all types of metals, including various grades of steel, cast iron, and non-ferrous alloys like copper, brass, and aluminum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. The coreless furnace's primary strength—flexibility—comes with specific trade-offs.
Lower Electrical Efficiency
Compared to a channel induction furnace (which does have an iron core), the coreless design is less electrically efficient, typically operating around 75%. For large-scale, continuous melting of a single alloy, a channel furnace is often more energy-efficient.
Refractory Lining Stress
The thermal cycling from frequent heating and cooling can put significant stress on the refractory lining (the ceramic crucible holding the metal). This can lead to faster wear and require more frequent maintenance compared to a furnace held at a constant temperature.
Less Ideal for Holding
While a coreless furnace can hold metal at a specific temperature, it is not the most efficient design for this purpose. A channel furnace is specifically optimized to hold large volumes of molten metal efficiently for extended periods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a coreless furnace hinges on your specific production requirements.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and frequent alloy changes: The coreless induction furnace is the definitive choice due to its ability to be completely emptied and started from cold.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous melting of a single alloy: A channel (core-type) furnace will likely offer superior energy efficiency and lower operational costs.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity or specialty alloys: The coreless furnace's precise control and vigorous stirring action make it the ideal tool for achieving exact chemical compositions.
Understanding this fundamental trade-off between operational flexibility and peak efficiency empowers you to select the technology that best aligns with your production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace |
|---|---|
| Principle | Electromagnetic induction without an iron core |
| Key Advantage | High flexibility for frequent alloy changes |
| Cold Start | Yes, can start from a completely solid charge |
| Ideal For | Foundries needing to melt various alloys |
| Efficiency | ~75% electrical efficiency |
| Best Use Case | Batch melting with frequent alloy changes |
Ready to enhance your foundry's melting capabilities?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory and production needs. Whether you're melting steel, cast iron, or non-ferrous alloys, our coreless induction furnaces offer the flexibility, precise control, and reliability you require.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your metal melting processes and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the different melting methods? A Guide to Choosing the Right Industrial Furnace
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials



















