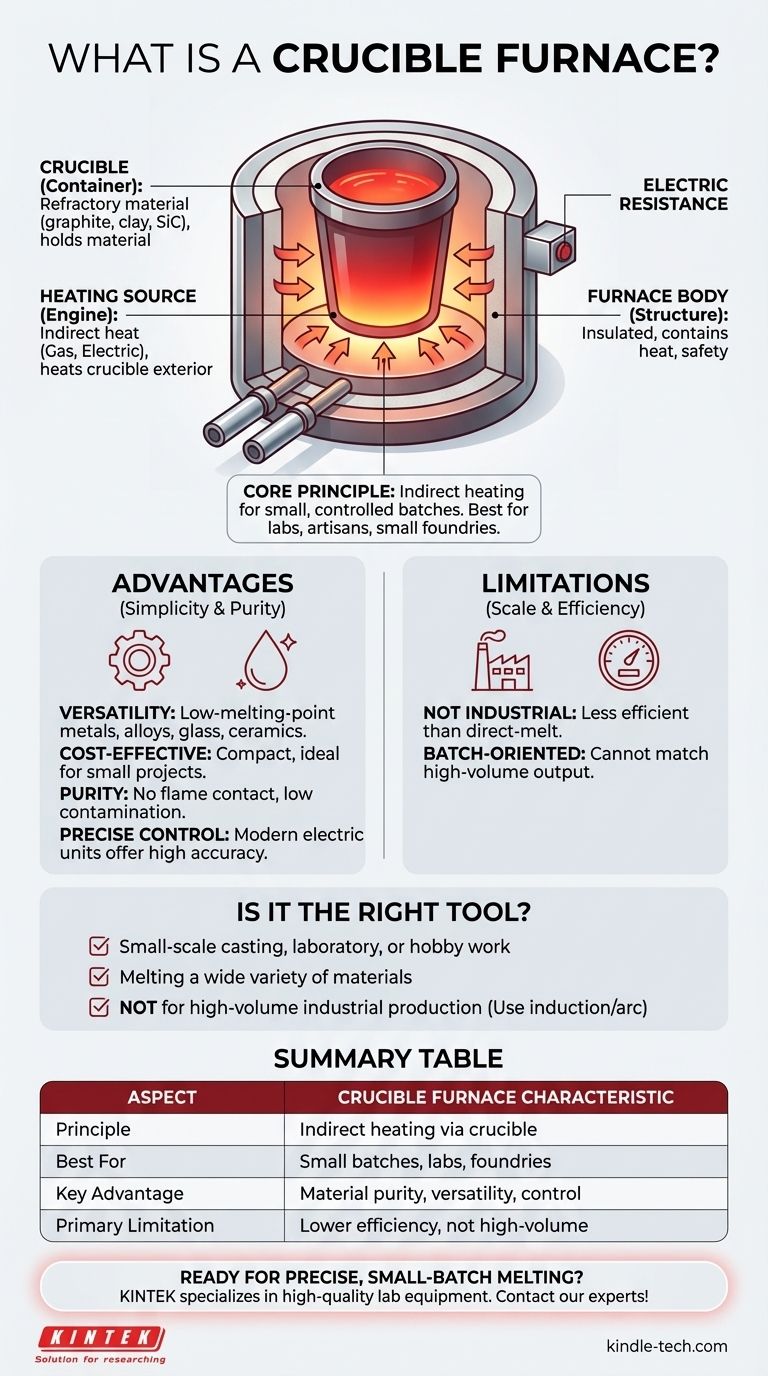
At its core, a crucible furnace is one of the simplest and oldest types of furnaces for melting materials. It operates on a straightforward principle: a durable container, called a crucible, holds the material to be melted. This crucible is then heated from the outside by a heat source, such as a gas burner or an electric element, transferring thermal energy through the crucible walls to melt the contents.
A crucible furnace is defined by its use of indirect heat. It excels at melting small, controlled batches of various materials, making it a foundational tool for laboratories, small foundries, and artisans rather than large-scale industrial production.
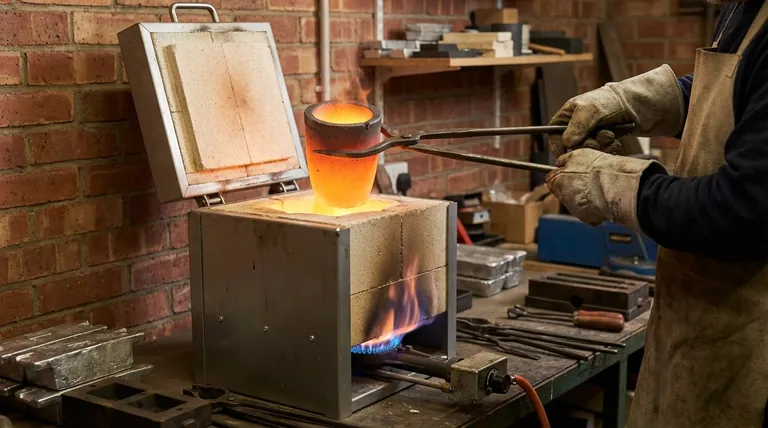

The Core Components of a Crucible Furnace
The design is fundamentally simple, revolving around two key parts that work in tandem to achieve the melt.
The Crucible (The Container)
The crucible is the heart of the furnace. It is a pot-like container specifically designed to withstand extreme temperatures without reacting with the material inside.
Crucibles are made from highly refractory (heat-resistant) materials, most commonly graphite, clay, or silicon carbide. The choice of material depends on the metal being melted and the temperatures required.
The Heating Source (The Engine)
The heating source never directly touches the material being melted. Instead, it heats the outer surface of the crucible.
The two most common heat sources are gas-fired burners, which use fuels like propane or natural gas, and electric resistance elements, which generate heat when electricity passes through them.
The Furnace Body (The Structure)
The crucible and heating elements are housed within an insulated furnace body. This structure contains the intense heat, improving efficiency and ensuring safety. Modern furnaces often include lids to retain heat and may feature advanced systems for temperature control.
Understanding the Advantages and Limitations
A crucible furnace's simplicity is both its greatest strength and its primary weakness, creating a clear set of trade-offs.
Key Advantage: Versatility and Simplicity
Because the melt is fully contained within the crucible, this type of furnace is incredibly versatile. It can be used for a wide range of materials, including low-melting-point metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze, as well as alloys, glass, and ceramics.
Their straightforward operation and often compact size make them cost-effective and ideal for small-scale projects.
Key Advantage: Purity and Control
The indirect heating method ensures the flame or heating elements do not contaminate the molten material. This is crucial for creating specific alloys or maintaining material purity.
Modern electric crucible furnaces can offer very precise temperature control, which is essential for working with sensitive metals.
Key Limitation: Scale and Efficiency
Crucible furnaces are not well-suited for large industrial applications. The process of heating a container from the outside is less energy-efficient than methods that heat the metal directly, like an induction furnace.
They are inherently batch-oriented and cannot match the high-volume output of larger, more specialized industrial furnaces.
Is a Crucible Furnace the Right Tool?
Choosing a furnace depends entirely on the scale and requirements of your work.
- If your primary focus is small-scale casting, laboratory research, or hobby work: A crucible furnace offers the perfect combination of control, versatility, and cost-effectiveness for small batches.
- If your primary focus is melting a wide variety of different materials: The crucible's self-contained nature is ideal, as it prevents cross-contamination between different melts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: This furnace is likely too inefficient, and you should investigate direct-melt technologies like induction or arc furnaces.
Ultimately, the crucible furnace remains a vital and relevant tool precisely because of its fundamental and adaptable design.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Crucible Furnace Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Principle | Indirect heating via a container (crucible) |
| Best For | Small batches, labs, foundries, artisans |
| Key Advantage | Material purity, versatility, precise control |
| Primary Limitation | Lower efficiency, not for high-volume production |
Ready to achieve precise, small-batch melting with a crucible furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including crucible furnaces, designed for the exacting needs of laboratories, research facilities, and artisans. Our solutions ensure material purity, temperature control, and reliability for your specific applications. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals



















