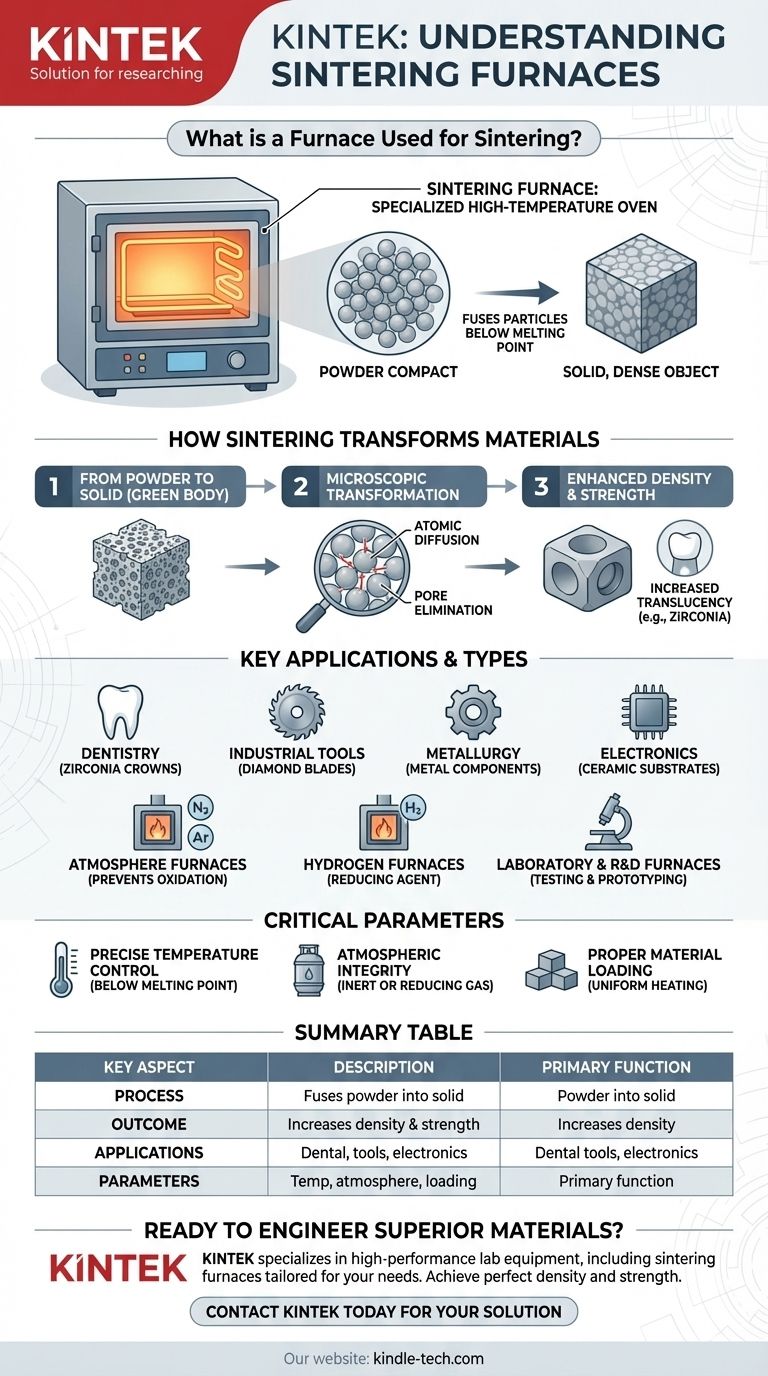
At its core, a sintering furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven used to transform a loosely packed powder into a solid, dense, and strong object. This process, known as sintering, relies on carefully controlled heat to fuse the particles together at a temperature below the material's melting point, fundamentally changing its mechanical and physical properties.
Sintering is not about melting a material; it is a sophisticated solid-state process. The furnace's true purpose is to create a precisely controlled environment of heat and atmosphere that encourages individual particles to bond and densify, turning a fragile powder compact into a robust, engineered component.
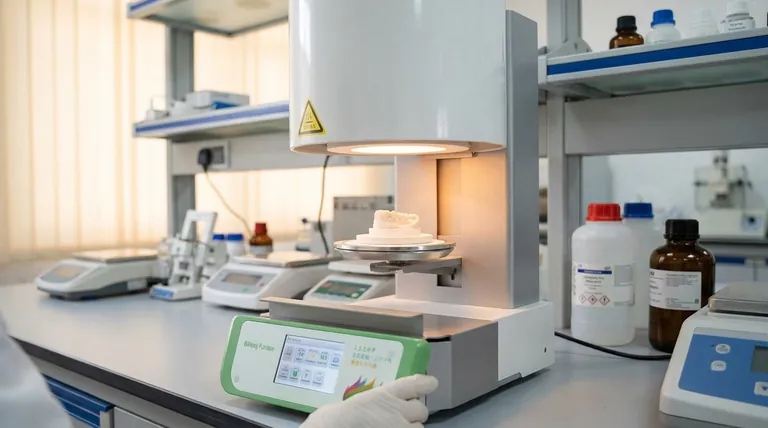

How Sintering Fundamentally Transforms Materials
The function of a sintering furnace goes far beyond simple heating. It facilitates a complex microscopic transformation that gives materials their final, high-performance characteristics.
From Powder to Solid
The starting point is a "green body," which is a component formed by compressing powdered material. This object is fragile and porous. The furnace's job is to heat this green body to a specific temperature where the atoms in the particles become mobile.
The Microscopic Transformation
At the sintering temperature, a process of atomic diffusion begins. Material migrates across the contact points between particles, causing the boundaries to grow and fuse. This process actively eliminates the pores (empty spaces) between the particles, causing the entire object to shrink and become significantly more dense.
The Result: Enhanced Density and Strength
The primary outcomes of successful sintering are dramatically increased density and mechanical strength. By eliminating internal porosity, the material becomes less prone to fracture. For some materials, like the zirconia used in dental crowns, this process also increases translucency, yielding a more natural appearance.
Key Sintering Furnace Applications and Types
Sintering is not a one-size-fits-all process. Different materials and industries require specialized furnaces to achieve the desired results, making them essential in numerous high-tech fields.
Atmosphere Furnaces
Many advanced materials, especially ceramics and metals, require an atmosphere-controlled furnace. This equipment allows operators to replace the air inside with a specific gas, such as nitrogen or argon. This controlled atmosphere prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, ensuring the material's purity and final properties.
Hydrogen Furnaces
For certain high-temperature alloys and special materials, a hydrogen furnace is used. Hydrogen acts as a "reducing" agent, which can remove surface oxides from the particles, promoting even stronger bonding during sintering and annealing.
Specialized Industry Applications
Sintering furnaces are workhorses in many sectors:
- Dentistry: To process zirconia crowns and bridges, giving them their final, tooth-like hardness and appearance.
- Industrial Tools: For manufacturing super-hard components like diamond saw blades, where diamond grit is sintered into a metal matrix.
- Metallurgy: For the heat treatment and consolidation of metal components, including parts made from steel and copper powders.
- Electronics: To produce ceramic substrates and other components used in electronic devices.
Laboratory and R&D Furnaces
For research, prototyping, and small-scale production, lab-scale furnaces are used. These smaller units, including advanced microwave sintering furnaces, allow scientists and engineers to test new material compositions and establish the precise parameters needed for larger-scale manufacturing.
Understanding the Critical Parameters
Achieving a successful outcome with sintering depends on precise control over several key factors. Mismanaging these can lead to failed parts or inconsistent quality.
Precise Temperature Control
The most critical parameter is temperature. The furnace must maintain a temperature high enough to allow atoms to diffuse but remain safely below the material's melting point. If the material melts, the process fails, and the part's shape and internal structure are ruined.
Atmospheric Integrity
The atmosphere inside the furnace is not passive. For many materials, oxygen is an enemy that causes oxidation, weakening the final product. Maintaining a pure, controlled atmosphere of inert or reducing gas is essential for high-performance applications.
Proper Material Loading
How components are placed in the furnace is crucial for ensuring uniform heating. Improper loading can create hot or cold spots, leading to uneven shrinkage, warping, or internal stresses in the final product. It is vital to follow established procedures for loading specific materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of furnace and process you need is dictated entirely by your end goal and the material you are working with.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing high-performance ceramics or metals: An atmosphere-controlled furnace is non-negotiable to prevent oxidation and ensure material purity.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A smaller, flexible lab-scale furnace is ideal for testing new material compositions and perfecting process parameters.
- If your primary focus is producing specialized industrial components: The furnace choice will be dictated by the material, such as a hydrogen furnace for specific alloys or a pressure-assisted furnace for diamond tools.
Ultimately, a sintering furnace is a tool of atomic-level engineering, enabling the creation of advanced materials with properties unattainable through conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fuses powder particles into a solid, dense object below the melting point. |
| Key Outcome | Dramatically increases density, mechanical strength, and material performance. |
| Common Applications | Dental crowns (zirconia), industrial tools (diamond blades), metal components, electronics. |
| Critical Control Parameters | Precise temperature, controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, hydrogen), proper material loading. |
Ready to engineer superior materials with precision sintering?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including sintering furnaces tailored for your specific material and industry needs—whether for R&D, dental ceramics, or industrial manufacturing. Our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect density and strength for your components.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sintering requirements and discover the right furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics



















