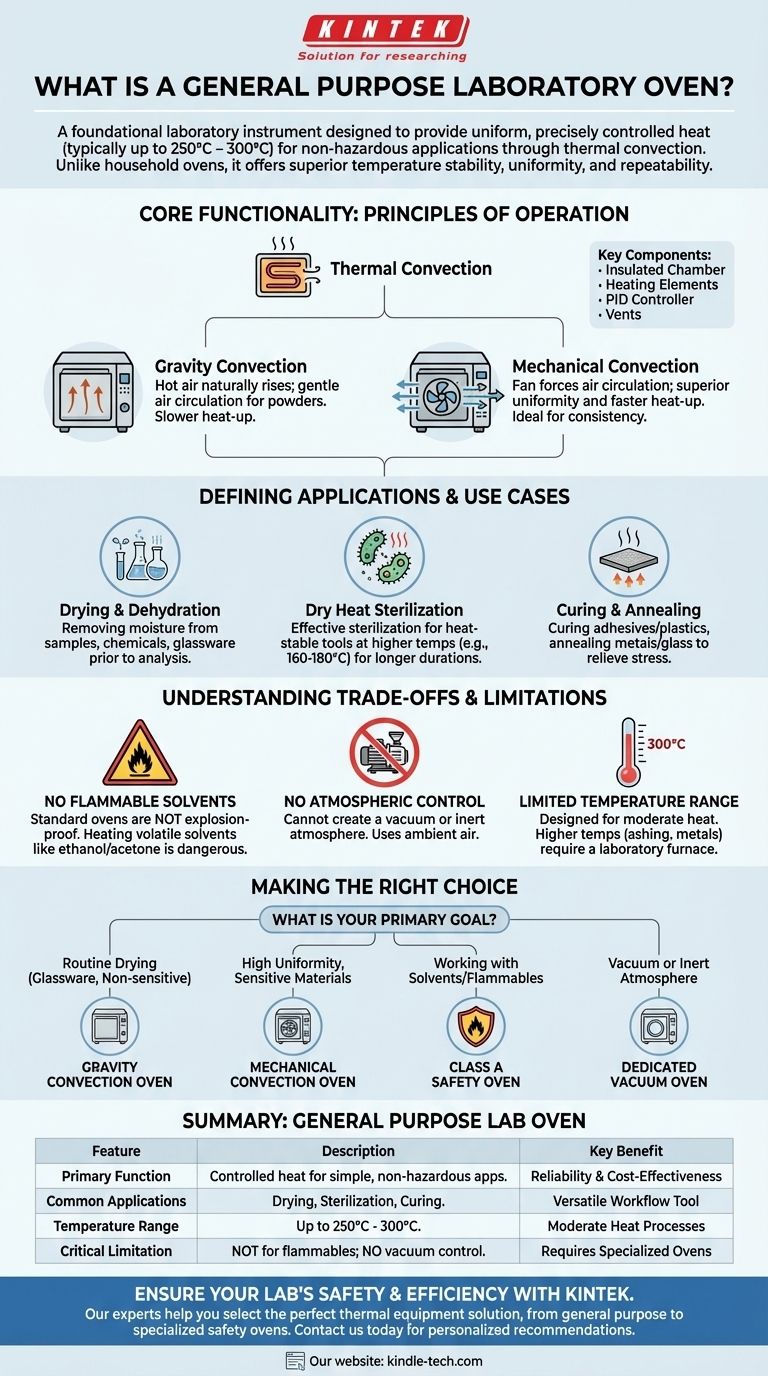
A general purpose laboratory oven is a foundational piece of equipment designed to provide uniform, precisely controlled heat in an insulated chamber. It utilizes thermal convection to heat its contents for applications like drying, curing, sterilizing, and sample preparation, typically operating at temperatures up to 250°C or 300°C. Unlike household ovens, it is engineered for temperature stability, uniformity, and repeatability.
The core purpose of a general purpose lab oven is to provide reliable, consistent heat for simple, non-hazardous applications. Its value lies in its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, but it is critical to understand its limitations, especially regarding flammable materials and atmospheric control.

Core Functionality: The Principles of Operation
A laboratory oven is more than just a heated box; it's a precision instrument. Its effectiveness hinges on a few key principles and components working in concert.
The Role of Thermal Convection
The primary method of heat transfer is thermal convection. A heating element warms the air inside the chamber, and this heated air then transfers energy to the samples. The method of air circulation is a key differentiator.
Gravity convection ovens rely on the natural principle that hot air rises. Heating elements are located at the bottom, and as air heats, it rises and circulates, displacing cooler, denser air. This method is gentle and ideal for fine powders or materials that could be disturbed by airflow.
Mechanical convection ovens (also called forced-air ovens) use a fan to actively circulate the heated air. This provides superior temperature uniformity and faster heat-up and recovery times, making it suitable for applications where temperature consistency throughout the chamber is critical.
Key Components for Precision
Every general purpose oven contains several critical components:
- An insulated chamber to maintain thermal efficiency.
- Heating elements to generate heat.
- A temperature controller, often a microprocessor-based PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, to precisely maintain the desired setpoint.
- Vents or ports to allow moisture to escape during drying applications.
Defining Applications and Use Cases
The versatility of a general purpose oven makes it a workhorse in nearly every type of laboratory, from academic research to industrial quality control.
Sample Drying and Dehydration
This is the most common application. Ovens are used to remove moisture from biological samples, chemicals, glassware, and other materials prior to weighing, analysis, or further processing.
Dry Heat Sterilization
For heat-stable instruments, glassware, and certain powders, a lab oven can provide effective sterilization. It uses higher temperatures (e.g., 160-180°C) for a longer duration compared to an autoclave, which uses steam under pressure.
Curing and Annealing
In materials science and manufacturing, ovens are used for curing adhesives, plastics, and rubbers, or for annealing metals and glass to relieve internal stresses and improve ductility.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Trusting a general purpose oven for the wrong task can lead to failed experiments or, more critically, serious safety hazards. Understanding its limitations is non-negotiable.
Never for Flammable Solvents
Standard ovens are not explosion-proof. Heating volatile or flammable solvents like ethanol, acetone, or hexane can cause vapors to accumulate. An ignition source, such as the arcing from an electrical component, can cause a catastrophic explosion. For these applications, a specialized Class A safety oven with specific safety features is mandatory.
No Atmospheric Control
A general purpose oven operates using the ambient air in the room. It cannot create a vacuum or an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon). If you need to dry samples under vacuum to lower the boiling point or prevent oxidation, you must use a vacuum oven.
Limited Temperature Range
These ovens are designed for moderate heat applications, typically topping out around 300°C. For processes requiring significantly higher temperatures, such as ashing, heat treating metals, or certain ceramic processes, a laboratory furnace is the appropriate instrument.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal equipment depends entirely on your specific scientific or industrial goal. Use these guidelines to make a safe and effective decision.
- If your primary focus is routine drying of glassware or non-sensitive samples: A standard gravity convection oven is the most cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving highly uniform temperatures for sensitive materials or faster drying times: A mechanical (forced-air) convection oven is the superior option.
- If your primary focus is working with solvents or flammable materials: You must use a specialized Class A safety oven designed to prevent explosions.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture under vacuum or in an inert atmosphere: A dedicated vacuum oven is required, as a general purpose oven cannot provide this control.
Understanding these core distinctions ensures you select a tool that is not only effective but also fundamentally safe for your application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides uniform, controlled heat for simple, non-hazardous applications. | Reliability and cost-effectiveness for routine tasks. |
| Common Applications | Drying, dehydration, dry heat sterilization, curing, and annealing. | Versatility across various laboratory workflows. |
| Temperature Range | Typically up to 250°C - 300°C. | Suitable for moderate heat processes. |
| Critical Limitation | NOT safe for flammable solvents; cannot control atmosphere (vacuum/inert gas). | Highlights the need for specialized ovens for specific hazards. |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with the right thermal equipment.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable laboratory equipment, including a full range of ovens tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require a standard general purpose oven for drying or a specialized safety oven for flammable materials, our experts can help you select the perfect solution.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK be your trusted partner in meeting all your laboratory equipment and consumable needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- What is the function of a laboratory oven in W18Cr4V steel sample preparation? Expert Microstructural Drying Guide



















