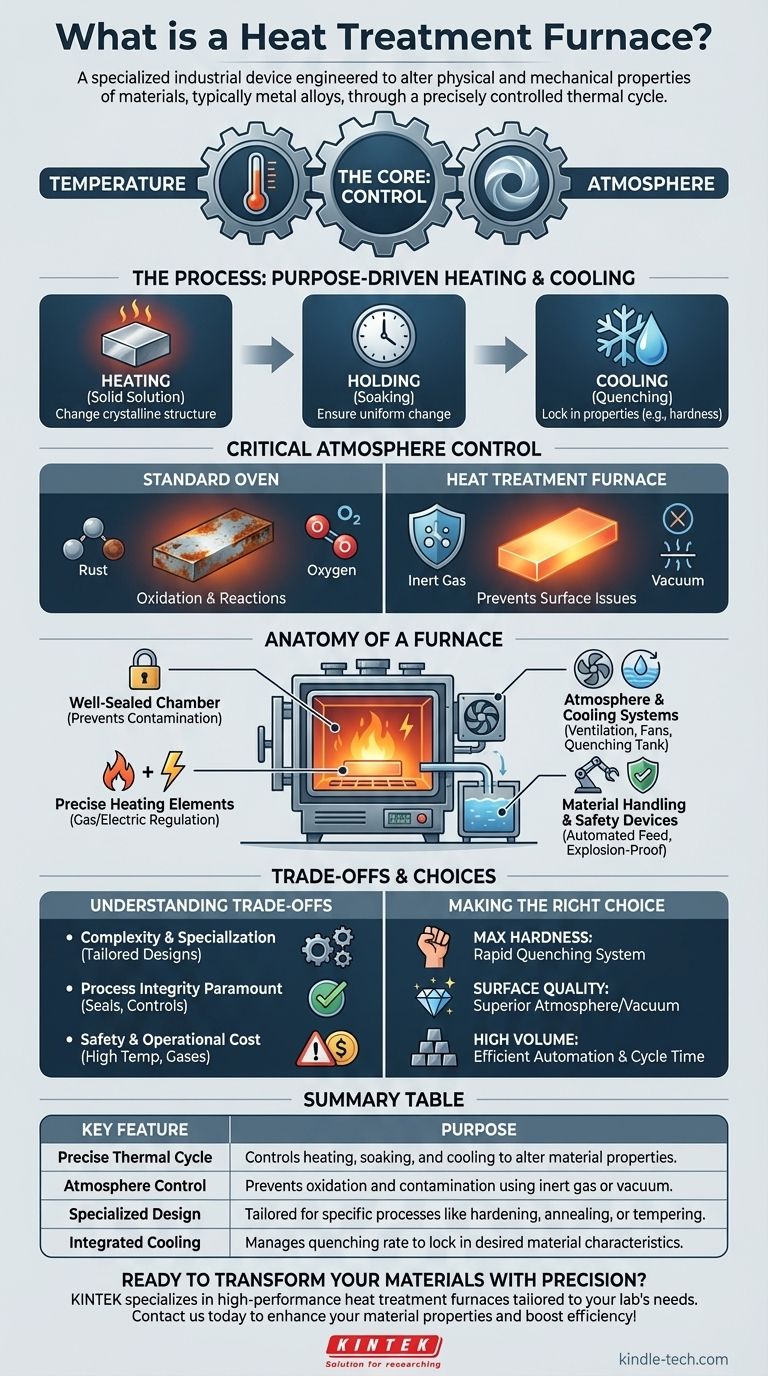
At its core, a heat treatment furnace is a specialized industrial device engineered to alter the physical and mechanical properties of materials, typically metal alloys. It achieves this not just through heating, but by subjecting the material to a precisely controlled thermal cycle of heating, holding at a specific temperature, and then cooling in a managed way.
The crucial difference between a simple furnace and a heat treatment furnace is control. It's a high-precision instrument designed to manipulate a material's internal structure by managing three critical variables: temperature, time, and atmosphere.

The Core Principle: More Than Just Heat
A common misconception is that these furnaces are simply high-temperature ovens. In reality, their function is far more sophisticated, centered on transforming a material's properties to meet specific engineering requirements.
Purpose-Driven Heating and Cooling
The entire process is a carefully prescribed recipe. An alloy is heated to a specific temperature to change its crystalline structure, a phase known as a solid solution.
It is then held at that temperature for a sufficient duration—a "soaking" period—to ensure the change is uniform throughout the material.
Finally, the material is cooled at a calculated rate. This might be a rapid cooling or "quenching" to lock in the desired properties, creating a supersaturated and often harder state.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The second key component of heat treatment is the atmosphere inside the furnace's sealed chamber. Heating metals to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen causes oxidation (rust) and other undesirable surface reactions.
To prevent this, the furnace atmosphere is tightly controlled. This can involve filling the chamber with inert gases or, in advanced applications, creating a near-perfect vacuum.
A vacuum furnace represents an evolution of this principle, combining vacuum technology with heat treatment to provide an environment free of contaminants for the most sensitive processes.
Anatomy of a Heat Treatment Furnace
While designs vary based on the application, several key components are fundamental to the furnace's operation and precision.
The Well-Sealed Furnace Body
The foundation is an exceptionally well-sealed chamber that contains the heat and the controlled atmosphere, preventing leaks or contamination from the outside air.
Heating Elements and Regulation
The heat source can be gas-fueled or electrically energized. More importantly, the system is designed for precise regulation, providing high energy during the initial heating phase and then maintaining a stable, constant temperature for the soaking period.
Atmosphere and Cooling Systems
These furnaces include ventilation, exhaust, and fan systems—often water-cooled and sealed—to manage the internal atmosphere. They also integrate cooling mechanisms, such as an interconnected fast-cooling chamber or an adjacent quenching tank, to control the final stage of the treatment cycle.
Material Handling and Safety
For industrial-scale operations, mechanical feeding and discharging devices automate the process of moving materials in and out of the chamber. Given the high temperatures and controlled atmospheres, robust safety and explosion-proof devices are essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The precision of a heat treatment furnace comes with inherent complexities and considerations that are critical to understand.
Complexity and Specialization
These are not general-purpose tools. A furnace designed for hardening steel may be unsuitable for annealing aluminum. The design of the heating elements, cooling systems, and atmosphere controls are all tailored to specific materials and desired outcomes.
Process Integrity is Paramount
The success of a heat treatment cycle depends entirely on the integrity of the process. A poorly sealed chamber, an inaccurate temperature controller, or an impure atmospheric gas can ruin an entire batch of expensive components.
Safety and Operational Cost
Managing high temperatures and controlled—sometimes volatile—atmospheres requires stringent safety protocols and operator training. Furthermore, the energy required to run these furnaces and the cost of atmospheric gases or vacuum systems make them a significant operational expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting or specifying a heat treatment furnace depends entirely on the final properties you need to achieve in your material.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness: Your process requires a furnace capable of precise temperature holding followed by an integrated and extremely rapid quenching system.
- If your primary focus is preventing any surface discoloration or reaction: You must prioritize a furnace with superior atmosphere control, such as a vacuum furnace or one with high-purity inert gas systems.
- If your primary focus is processing high volumes efficiently: The key features will be the furnace's size, its cycle time, and the reliability of its automated material handling systems.
Ultimately, a heat treatment furnace is an indispensable tool that transforms raw alloys into the high-performance materials that underpin modern engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Precise Thermal Cycle | Controls heating, soaking, and cooling to alter material properties. |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidation and contamination using inert gas or vacuum. |
| Specialized Design | Tailored for specific processes like hardening, annealing, or tempering. |
| Integrated Cooling | Manages quenching rate to lock in desired material characteristics. |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable heat treatment furnaces tailored to your laboratory's specific needs—whether for hardening, annealing, or complex R&D processes.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your material properties and boost your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout



















