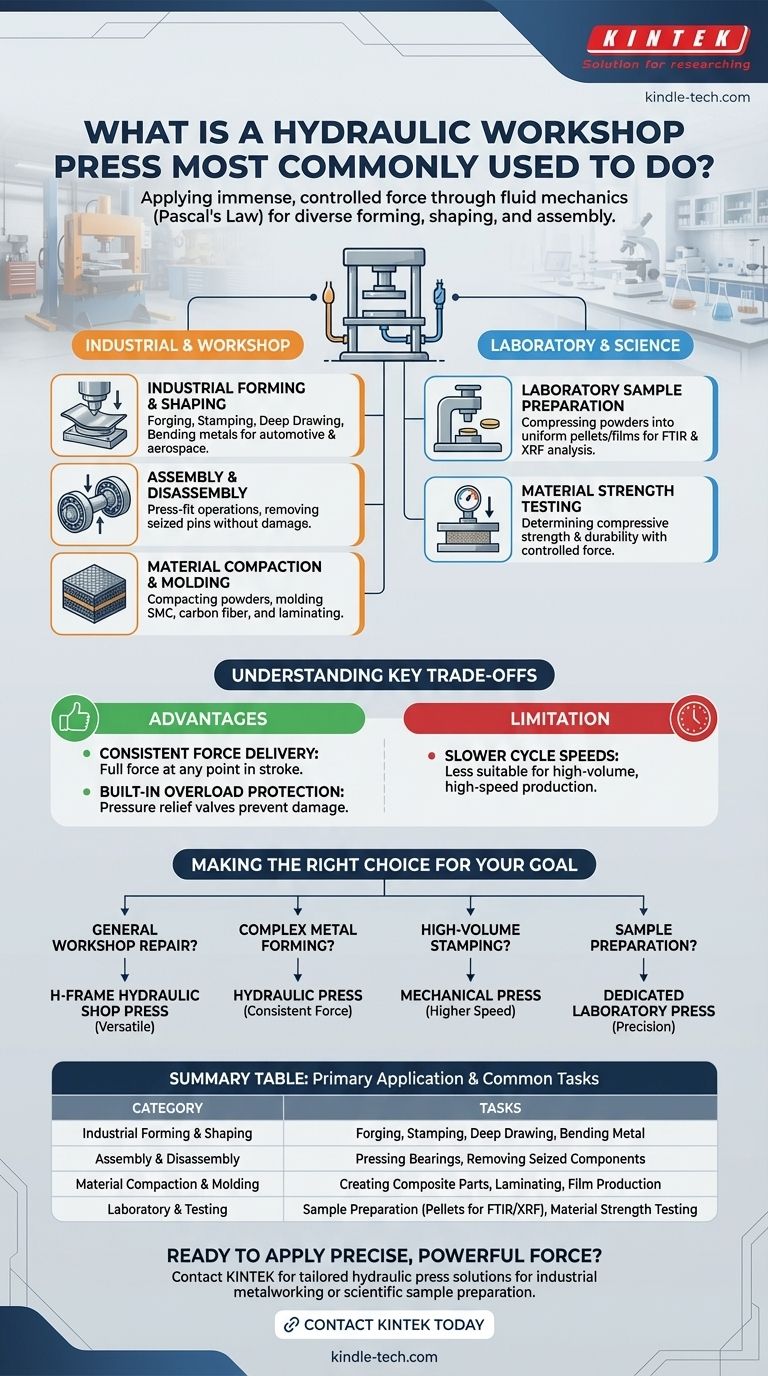
At its core, a hydraulic workshop press is a tool designed to apply immense, controlled force. It is most commonly used for a wide range of forming, shaping, and assembly operations, such as bending and stamping metal, pressing bearings into place, or compacting materials for industrial and scientific purposes.
The true value of a hydraulic press isn't tied to a single function, but to its underlying principle: using fluid mechanics (Pascal's Law) to generate enormous, precise, and evenly distributed pressure. This single capability is what allows it to perform such diverse tasks, from shaping steel beams to preparing delicate laboratory samples.

The Two Primary Arenas of Use
While versatile, the applications of hydraulic presses generally fall into two main categories: heavy industrial/workshop operations and precise laboratory work.
Industrial Forming and Shaping
This is the most common image of a hydraulic press at work. It involves permanently changing the shape of raw materials, primarily metals, through immense force.
Key operations include forging (shaping metal using compressive forces), stamping (creating a specific shape with a die), deep drawing (stretching sheet metal into a form), and bending. These processes are fundamental in the automotive, aerospace, and appliance manufacturing industries.
Assembly and Disassembly
In a typical workshop, a hydraulic press is indispensable for press-fit operations. This involves using force to assemble parts, like pressing bearings onto a shaft or into a housing.
Conversely, it's used for disassembly, such as pushing out seized pins or separating tightly fitted components without the damaging impact of a hammer.
Material Compaction and Molding
Hydraulic presses are used to compact powders into a solid form or to mold various materials. This is crucial for creating parts from sheet molded composites (SMC) and carbon fiber.
Specialized hot presses add temperature control to this process, allowing them to laminate surfaces or melt polymers into thin, uniform films.
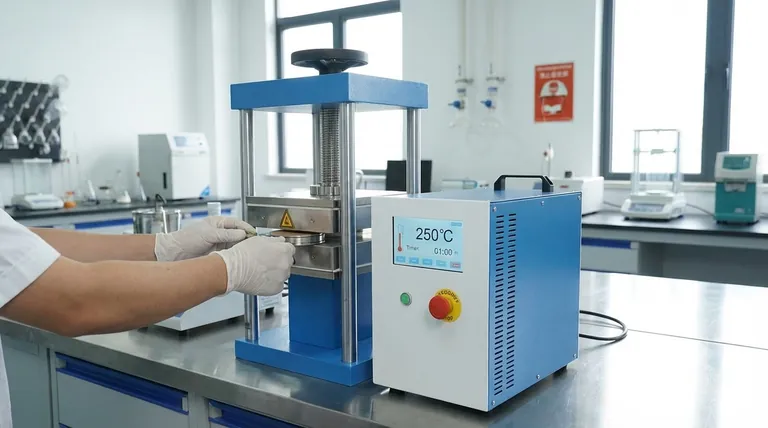
Laboratory Sample Preparation
In scientific settings, hydraulic presses are essential for preparing consistent samples for analysis. They compress powdered material into a uniform pellet or thin film.
This creates a homogenous sample that is ideal for methods like FTIR and XRF spectroscopy, ensuring accurate and repeatable measurements.
Material Strength Testing
Engineers and material scientists use hydraulic presses to test the limits of materials. By applying a controlled and measurable force, they can determine a material's compressive strength and durability.
Some configurations are also used for tension testing, where a sample is pulled apart to measure its tensile strength.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The choice of a hydraulic press over other types, like a mechanical press, is based on specific performance characteristics.
Advantage: Consistent Force Delivery
A hydraulic press can deliver its maximum rated force at any point in the ram's stroke. This is critical for deep drawing or complex forming operations that require full, sustained pressure over a long distance.
Advantage: Built-in Overload Protection
Hydraulic systems are protected by pressure relief valves. It is virtually impossible to damage the press by overloading it, as the valve will simply release excess pressure. This makes them exceptionally robust.
Limitation: Slower Cycle Speeds
Compared to mechanical presses, hydraulic systems are generally slower. The time it takes to build and release fluid pressure makes them less suitable for high-speed, high-volume operations like punching small holes in a production line.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates the type of press you need.
- If your primary focus is general workshop repair and assembly: A standard H-frame hydraulic shop press offers the best versatility for pressing bearings, bushings, and straightening parts.
- If your primary focus is complex metal forming or deep drawing: The hydraulic press's ability to apply full, consistent force throughout its stroke is a decisive advantage.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repetitive stamping: A mechanical press is often more efficient due to its significantly higher cycle speeds.
- If your primary focus is preparing samples for scientific analysis: A dedicated laboratory press, whether manual or automatic, is essential for creating consistent, high-quality pellets.
Ultimately, the hydraulic press remains a cornerstone of modern industry and science because its simple principle of force multiplication is so powerful and adaptable.
Summary Table:
| Primary Application Category | Common Tasks |
|---|---|
| Industrial Forming & Shaping | Forging, Stamping, Deep Drawing, Bending Metal |
| Assembly & Disassembly | Pressing Bearings, Removing Seized Components |
| Material Compaction & Molding | Creating Composite Parts, Laminating, Film Production |
| Laboratory & Testing | Sample Preparation (Pellets for FTIR/XRF), Material Strength Testing |
Ready to apply precise, powerful force to your projects? Whether you're in a heavy-duty workshop or a precision-focused laboratory, KINTEK's hydraulic presses deliver the controlled power you need for forming, assembly, and material testing. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a solution tailored to your specific application, from industrial metalworking to scientific sample preparation. Contact KINTEL today to find the perfect hydraulic press for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability



















