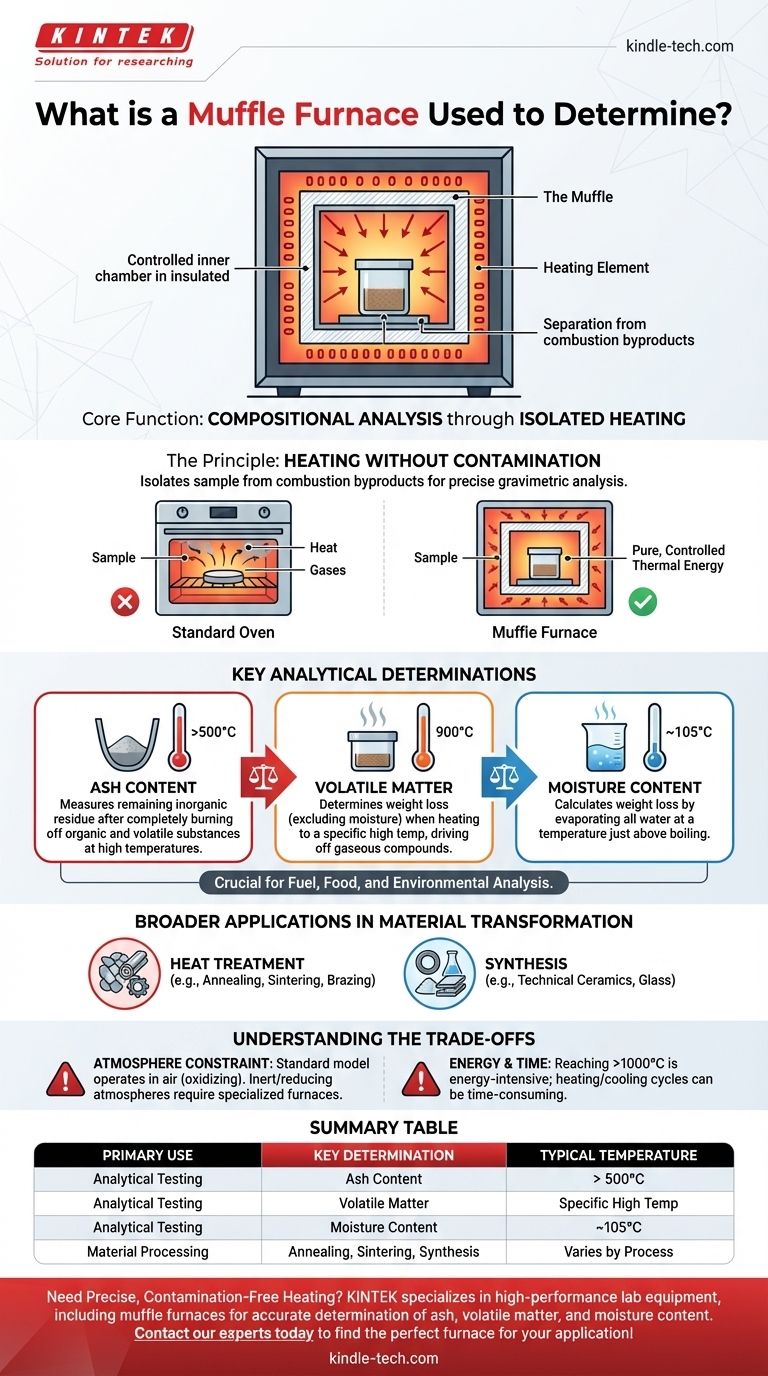
At its core, a muffle furnace is used to determine a material's composition by subjecting it to extremely high temperatures in a controlled environment. Its primary analytical uses are for measuring the ash content, volatile matter, and moisture content of a sample. This is achieved by heating the material until specific components either burn away or evaporate, allowing for precise measurement of the remaining mass.
The critical function of a muffle furnace is not just heating, but heating with isolation. It separates the sample from the combustion byproducts of the heat source, ensuring that the only variable affecting the material is pure, controlled thermal energy.

The Principle: Heating Without Contamination
A muffle furnace is fundamentally different from a standard high-temperature oven. Its design is centered on providing a chemically clean heating environment.
How it Achieves Isolation
The "muffle" is the furnace's interior chamber, which is made from a heat-resistant material. This chamber insulates the sample, physically separating it from the heating elements.
This design prevents any byproducts of combustion or gases from the heating process from interacting with and contaminating the sample.
Why Purity is Essential
For analytical determinations, this isolation is non-negotiable. When you measure the weight loss of a sample after heating, you must be certain that the loss is due to a specific process (like moisture evaporation or organic matter combustion) and not an unintended chemical reaction with external contaminants.
Modern furnaces provide excellent temperature uniformity, ensuring the entire sample is treated homogenously for reliable and repeatable results.
Key Analytical Determinations
While muffle furnaces have many uses, they are the standard instrument for several specific quantitative tests, particularly in fuel, food, and environmental analysis.
Determining Ash Content
This is the most common application. A sample is heated to a high temperature (typically over 500°C) to completely burn off all organic and volatile substances.
The non-combustible, inorganic residue that remains is the ash. Its weight is a critical quality metric in industries from food science to coal analysis.
Measuring Volatile Matter
This process involves heating a sample to a specific high temperature in a controlled manner.
The weight lost during this heating (after accounting for moisture) represents the volatile matter—compounds that are driven off as gases at that temperature.
Analyzing Moisture Content
Although often done in a standard drying oven, a muffle furnace can also determine moisture content.
By heating the sample to a temperature just above the boiling point of water (e.g., 105°C), all water is evaporated. The resulting loss in mass is recorded as the moisture content.
Broader Applications in Material Transformation
Beyond quantitative analysis, the controlled high-temperature environment of a muffle furnace is essential for creating or altering materials.
Heat Treatment of Materials
Processes like annealing (softening metals), sintering (fusing powdered materials into a solid mass), and brazing rely on the precise temperature control offered by a muffle furnace.
Synthesis of Advanced Materials
The furnace is used to create technical ceramics, form specialized glass, and conduct high-temperature chemical synthesis where a clean environment is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, the standard muffle furnace has operational considerations that are important to understand.
Atmosphere is a Key Constraint
A standard muffle furnace operates in a normal air atmosphere (primarily nitrogen and oxygen). This is ideal for ashing, where combustion is the goal.
However, for processes that require an inert (e.g., argon) or reducing (e.g., hydrogen) atmosphere to prevent oxidation, a more specialized and expensive furnace is required.
Energy and Time
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1000°C or higher is an energy-intensive process. The heating and cooling cycles can also be time-consuming, depending on the furnace's insulation and the required thermal profile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select and use a muffle furnace effectively, you must first clarify your objective.
- If your primary focus is compositional analysis (food, coal, environmental samples): You are using the furnace as a tool for gravimetric analysis to accurately determine ash, moisture, or volatile content.
- If your primary focus is materials science (metals, ceramics): You are using the furnace to physically transform materials through processes like annealing, sintering, or synthesis.
- If your primary focus is general lab work (chemistry, pharmaceuticals): You are using the furnace for high-temperature sample preparation, destroying organic matrices to isolate inorganic analytes for further testing.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace provides the pristine, high-temperature environment required for precise material analysis and intentional transformation.
Summary Table:
| Primary Use | Key Determination | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Testing | Ash Content | > 500°C |
| Analytical Testing | Volatile Matter | Specific High Temperature |
| Analytical Testing | Moisture Content | ~105°C |
| Material Processing | Annealing, Sintering, Synthesis | Varies by Material & Process |
Need precise, contamination-free heating for your analytical testing or material processing? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for accurate determination of ash, volatile matter, and moisture content. Our solutions ensure reliable, repeatable results for your laboratory. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the 3 official methods in determining ash and water content? A Guide to Proximate Analysis
- What temperature should a muffle furnace be for ash content? Achieve Accurate Results with the Right Heat
- What is difference between hot air oven and muffle furnace? Key Differences in Temperature and Applications
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- How hot can metal get? From Melting Points to Plasma Temperatures



















