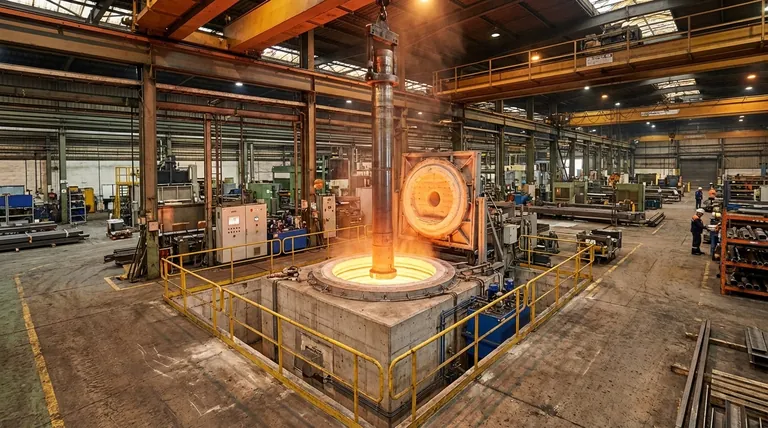
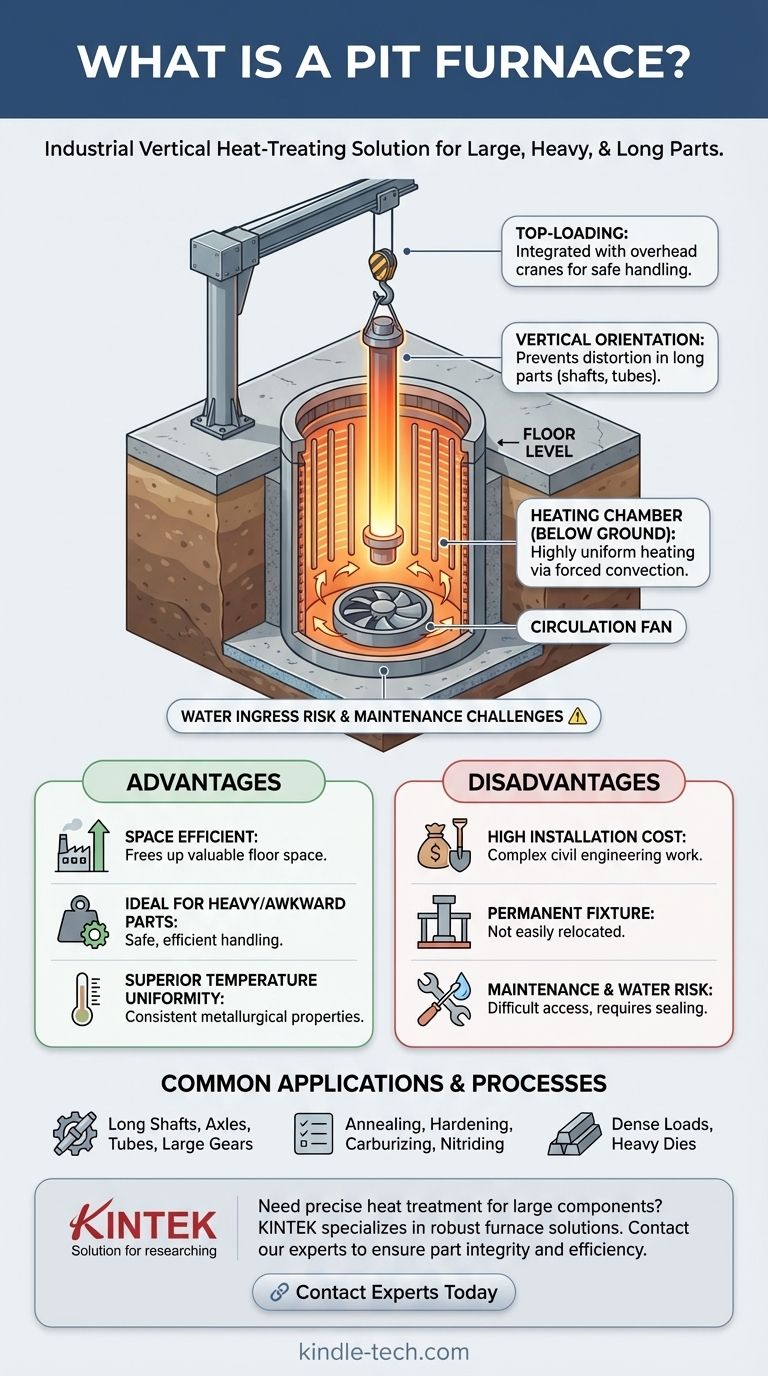
A pit furnace is an industrial heat-treating furnace that is installed vertically in a pit below the factory floor level. This design is specifically chosen for processing exceptionally long, large, or heavy parts, such as shafts, tubes, or dense loads, which are loaded and unloaded from the top using an overhead crane. Its primary function is to provide highly uniform heating in a space-efficient manner for workpieces that would be difficult to handle in a standard horizontal furnace.
The core decision to use a pit furnace is driven by the geometry and weight of the parts being treated. It is a strategic choice for leveraging vertical space to prevent part distortion, improve temperature uniformity, and safely integrate with heavy-duty material handling systems.

The Core Design and Operation
A pit furnace's unique construction directly serves its function. By understanding its key components, you can see why it excels at specific tasks.
Vertical Loading and Orientation
The most defining feature is its top-loading, vertical orientation. Parts are lowered into the heating chamber from above, typically with a crane.
This vertical positioning is critical for long, slender components like shafts, axles, or gun barrels. Heating these parts horizontally can cause them to sag or distort under their own weight at high temperatures.
Heating Chamber and Atmosphere Control
The main body of the furnace, the cylindrical heating chamber, is located in the pit. It is typically heated by electric resistance elements arranged along the interior walls or through gas-fired burners.
Many pit furnaces are designed to manage a controlled atmosphere. This allows for processes like carburizing, nitriding, hardening, and annealing by introducing specific gases (e.g., nitrogen, endothermic gas) to prevent oxidation or to chemically alter the surface of the parts.
Forced Convection for Uniformity
A powerful fan, usually located in the furnace lid or at the base, is essential for its operation. This fan vigorously circulates the internal atmosphere, ensuring heat is transferred evenly throughout the chamber.
This forced convection is what guarantees excellent temperature uniformity, a non-negotiable requirement for achieving consistent metallurgical properties across a large or densely packed load.
Understanding the Advantages and Limitations
A pit furnace is a specialized piece of equipment, not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its benefits are significant, but they come with specific trade-offs.
Advantage: Superior Space Efficiency
By locating the bulk of the furnace below ground, pit furnaces free up valuable factory floor space. Only the lid and loading area are at the working level, creating a less cluttered and potentially safer environment.
Advantage: Ideal for Large, Awkward Parts
The top-loading design is perfectly suited for integration with overhead cranes, which are standard in facilities that handle heavy materials. This makes loading and unloading massive, multi-ton components much safer and more efficient than with a horizontal furnace.
Disadvantage: High Installation Cost and Inflexibility
The primary drawback is the significant upfront cost and complexity of installation. This involves major civil engineering work to excavate a pit, pour a concrete foundation, and ensure proper drainage and safety measures.
Once installed, a pit furnace is a permanent fixture. It cannot be easily moved or relocated if factory layouts change, representing a long-term capital commitment.
Disadvantage: Maintenance and Water Ingress
Maintenance can be more challenging. Accessing heating elements or other components at the bottom of the pit requires specialized procedures and safety precautions.
Furthermore, the pit must be properly sealed and protected from groundwater. Water ingress can cause catastrophic damage to the furnace and presents a significant operational risk in areas with a high water table.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace type depends entirely on your operational needs and the characteristics of the parts you are processing.
- If your primary focus is processing long shafts or parts susceptible to distortion: A pit furnace is often the only viable choice to maintain geometric integrity during heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is handling extremely heavy dies, gears, or dense baskets of parts: The top-loading pit furnace design provides a safe and efficient material handling workflow.
- If your primary focus is flexibility, lower initial cost, or processing varied, smaller loads: A conventional horizontal box furnace or a batch-style integral quench furnace would likely be a more practical and economical solution.
Ultimately, a pit furnace is a purpose-built solution that provides unparalleled performance when the workpiece demands a vertical, high-uniformity approach.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Orientation | Vertical, top-loading |
| Primary Use | Long, heavy, or dense parts (e.g., shafts, dies) |
| Key Advantage | Prevents part sagging/distortion; excellent temperature uniformity |
| Common Processes | Annealing, hardening, carburizing, nitriding |
| Installation | Permanent, below floor level (pit) |
| Material Handling | Integrated with overhead cranes |
Need to heat-treat large or heavy components with precision?
KINTEK specializes in industrial lab equipment, including robust furnace solutions for demanding applications. Our expertise can help you determine if a pit furnace is the right choice for your large-scale heat treatment needs, ensuring part integrity and process efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and explore how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















