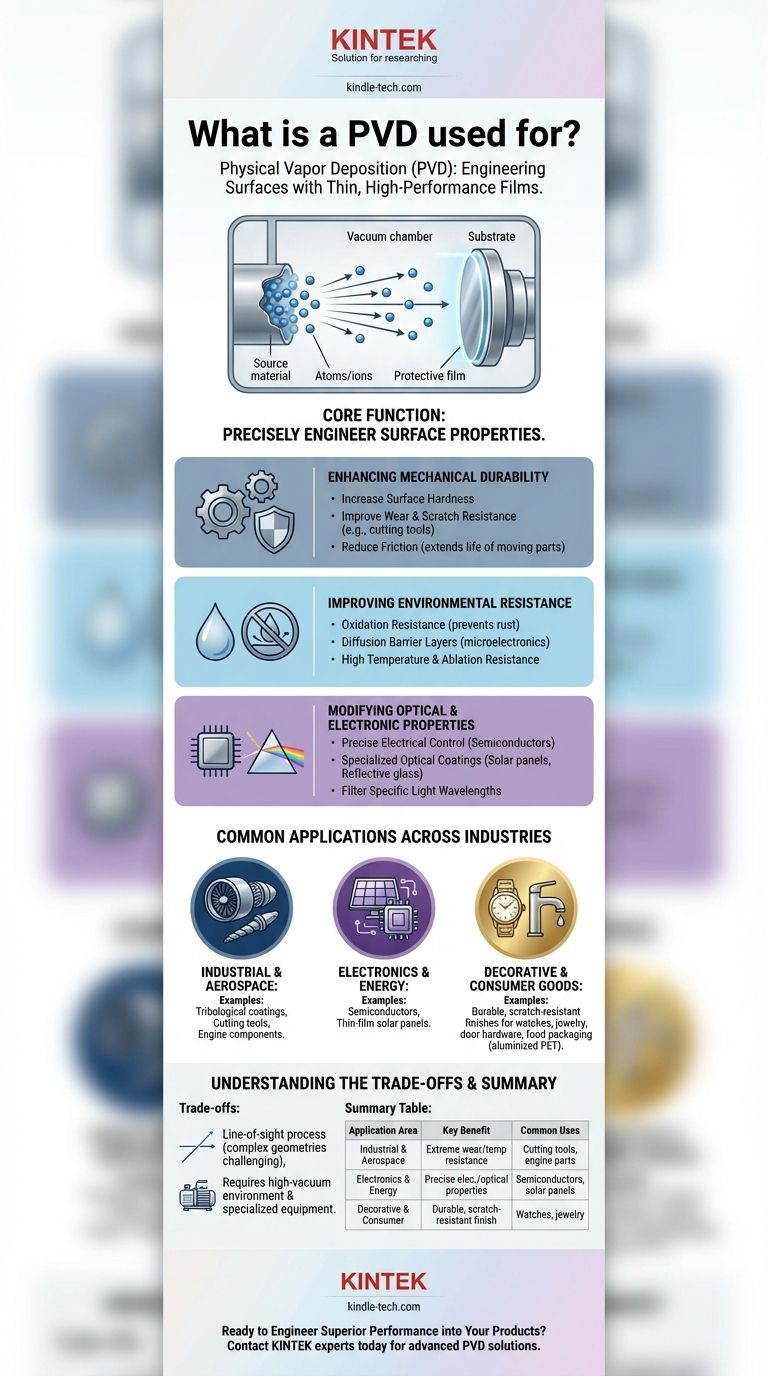
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is used to apply exceptionally thin, high-performance films onto a surface. These coatings fundamentally alter the object's properties to enhance its durability, function, or appearance. PVD is the technology behind the super-hard coatings on industrial drill bits, the reflective layers in solar panels, and the durable, metallic finishes on high-end watches and fixtures.
The true purpose of PVD is not merely to coat an object, but to precisely engineer its surface. It grants a material new properties—like extreme hardness, chemical resistance, or specific optical qualities—that it does not naturally possess.

The Functional Benefits of PVD Coatings
PVD is chosen when a surface needs a specific functional improvement. The process allows for the deposition of a wide range of materials, each engineered to solve a distinct problem.
Enhancing Mechanical Durability
One of the most common uses for PVD is to make products stronger and last longer. The deposited thin films create a new, functional surface on the base material.
This includes improving wear and scratch resistance, making it ideal for cutting tools, industrial molds, and automotive parts that experience constant friction.
PVD coatings also significantly increase surface hardness and can be engineered to reduce friction, which improves efficiency and extends the life of moving components.
Improving Environmental Resistance
PVD films act as a shield, protecting the underlying material (substrate) from its environment.
This is critical for improving oxidation resistance, preventing rust and corrosion on parts exposed to moisture or chemicals.
The technology is also used to create diffusion barrier layers that prevent materials from migrating into one another, a key function in microelectronics. For more extreme environments, PVD enhances a substrate's resistance to high temperatures and ablation.
Modifying Optical and Electronic Properties
Beyond protection, PVD is a critical process for creating materials with specific optical or electrical characteristics.
It is used extensively in manufacturing semiconductor devices and thin-film solar panels, where precise layers of material are required to control the flow of electrons.
PVD also creates specialized glass coatings that can reflect heat, reduce glare, or allow certain wavelengths of light to pass through, which is essential for architectural and optical applications.
Common Applications Across Industries
Because PVD offers such a diverse range of functional benefits, it is employed across many different high-performance and consumer-facing sectors.
Industrial and Aerospace
In demanding environments, PVD is essential. It is used to create tribological coatings for cutting and forming tools, dramatically increasing their lifespan and performance.
In the aerospace industry, these coatings protect components from extreme temperatures and wear, ensuring reliability and safety.
Electronics and Energy
The precision of PVD makes it indispensable for modern electronics. It is a foundational step in fabricating semiconductors and other microelectronic components.
Its role in depositing thin, light-sensitive films is also critical for the efficiency and production of thin-film solar panels.
Decorative and Consumer Goods
PVD provides a finish that is both beautiful and exceptionally durable, far surpassing traditional methods.
It is widely used for decorative hardware for kitchens, bathrooms, and doors, as well as for jewelry and marine supplies, where it provides a long-lasting metallic luster.
The technology is even used in food packaging, such as creating the thin layer of aluminum in aluminized PET films that keeps food fresh.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is a sophisticated process with specific considerations. It is a line-of-sight process, meaning the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This can make it challenging to achieve a uniform coating on objects with complex, intricate geometries or internal surfaces.
Furthermore, PVD requires a high-vacuum environment and specialized equipment, making the initial investment and operational complexity higher than for some conventional coating methods like electroplating. The trade-off is for a level of precision, purity, and performance that those other methods cannot achieve.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Choosing PVD depends entirely on the properties you need to engineer into your product's surface.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and performance: PVD is the superior choice for industrial tools, aerospace components, and automotive parts that require maximum hardness and wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is a premium, long-lasting aesthetic: PVD provides a durable and brilliant finish for high-end consumer hardware, watches, and decorative items that must resist scratches and tarnishing.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronic or optical function: PVD is a non-negotiable process for manufacturing semiconductors, sensors, and specialized optical coatings where material purity and layer precision are critical.
Ultimately, Physical Vapor Deposition is the definitive technology for transforming a standard material into a high-performance, purpose-built product.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial & Aerospace | Extreme wear & temperature resistance | Cutting tools, engine components |
| Electronics & Energy | Precise electrical & optical properties | Semiconductors, thin-film solar panels |
| Decorative & Consumer Goods | Durable, scratch-resistant finishes | Watches, door hardware, jewelry |
Ready to Engineer Superior Performance into Your Products?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced PVD solutions for your laboratory and manufacturing needs. Whether you're developing industrial tools, electronic components, or high-end consumer goods, our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you achieve the precise surface properties required for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's PVD technology can enhance your product's durability, functionality, and value.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















