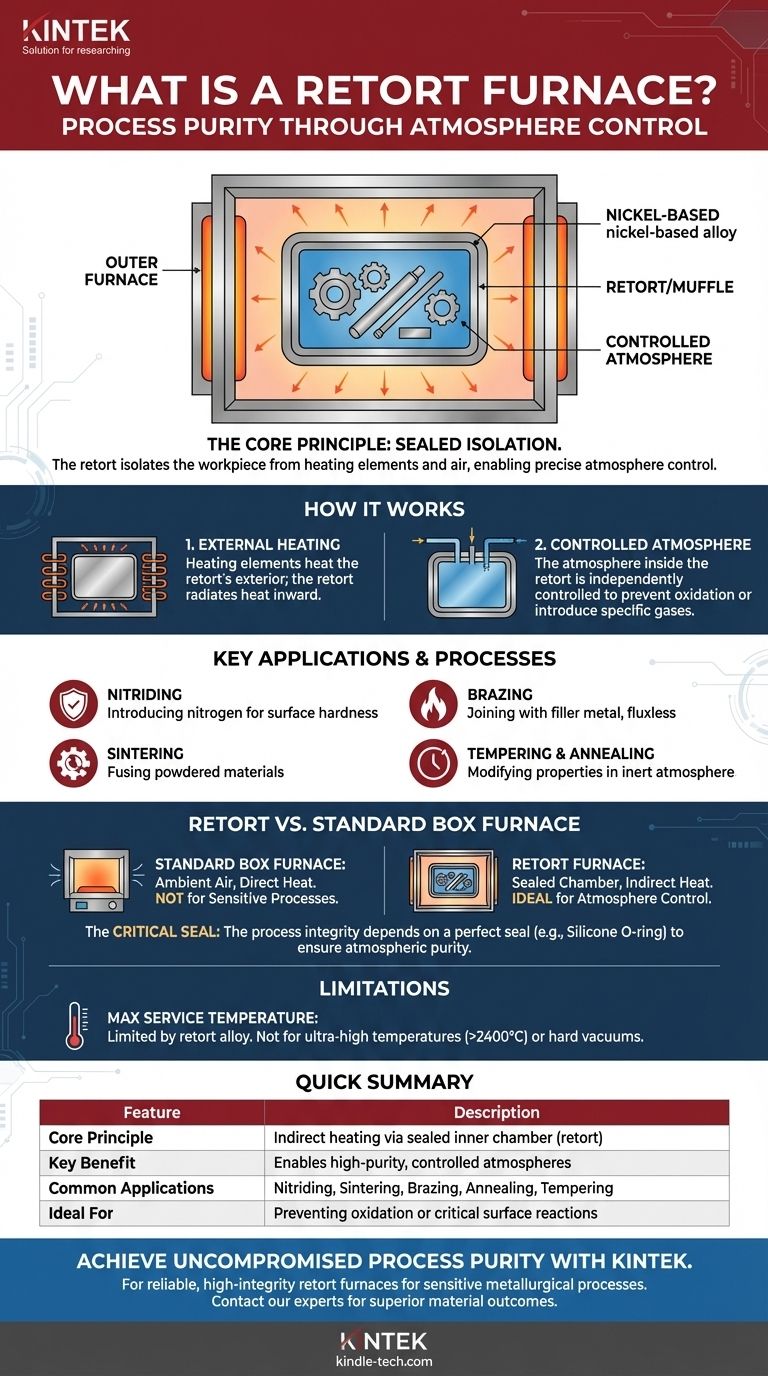
At its core, a retort furnace is a specialized type of furnace for heat-treating materials within a precisely controlled atmosphere. It achieves this by using a sealed inner container, known as a "retort" or "muffle," to completely isolate the workpiece from the furnace's heating elements and the outside air. This design is critical for thermal processes that would otherwise fail due to oxidation or contamination.
The defining feature of a retort furnace is not its heat source, but its use of a sealed internal chamber. This simple design principle is the key to creating the high-purity, controlled gas environments required for sensitive metallurgical processes.
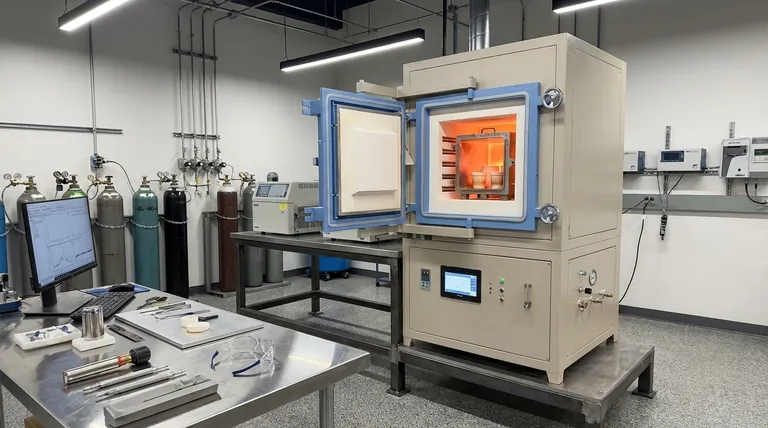

The Core Principle: Isolating the Workpiece
The function of a retort furnace revolves around the physical separation between the heat source and the material being treated. This fundamental design has significant implications for material processing.
What is a "Retort"?
A retort is a sealed container, typically made from a durable, high-temperature nickel-based alloy. This container holds the parts to be heat-treated and is placed inside the main furnace chamber.
The atmosphere inside the retort can be controlled independently of the atmosphere outside of it.
How External Heating Works
The heating elements, whether electric resistance coils or gas burners, are located outside the retort. They heat the retort from the exterior, and the retort, in turn, radiates that heat to the workpiece inside.
This indirect heating method protects the heating elements from potentially corrosive process gases introduced into the retort. Crucially, it also prevents byproducts from the heating elements from contaminating the workpiece.
Why This Matters for Material Processing
This isolation is essential for processes where the surface chemistry of a material is critical. By controlling the gas inside the retort, operators can prevent unwanted reactions like oxidation or introduce specific gases to create desired reactions.
Key Applications and Processes
A retort furnace is the ideal choice for any thermal process that demands a specific, non-air atmosphere. Its design can be configured as either a horizontal or vertical apparatus depending on the application.
Processes Requiring a Defined Atmosphere
Many advanced heat treatments are only possible within a controlled environment. A retort furnace is perfectly suited for processes such as:
- Nitriding: Introducing nitrogen into the surface of a steel part.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials together below their melting point.
- Brazing: Joining metals using a filler metal, often requiring a fluxless, oxygen-free environment.
- Tempering & Annealing: Modifying a metal's hardness and ductility in an inert atmosphere to prevent surface discoloration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the retort furnace design introduces specific considerations that differ from simpler, non-isolated furnaces. Understanding these trade-offs is key to its proper application.
The Critical Role of the Seal
The integrity of the process depends entirely on how well the retort is sealed. A poor seal negates the entire purpose of the furnace.
Two common methods are used: a trough filled with sand that the retort lid sits in, or a silicone O-ring gasket compressed by clamps. The silicone O-ring gasket provides a much more reliable and verifiable seal, ensuring the highest level of atmospheric purity.
Retort vs. Standard Box Furnace
A "box furnace" simply describes the general shape of the furnace chamber. A retort furnace is a functional design that can be built within a box furnace frame.
The key difference is the presence of that sealed inner chamber. A standard box furnace heats parts directly in ambient air, making it unsuitable for atmosphere-sensitive processes.
Material and Temperature Limitations
The retort itself is a consumable component with a maximum service temperature determined by its alloy. While the furnace may be capable of higher temperatures, the process is limited by what the retort can withstand without degrading.
For ultra-high temperature applications (approaching 2400°C) or processes requiring a hard vacuum, more specialized equipment like a vacuum furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision to use a retort furnace should be driven by the chemical requirements of your heat-treatment process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity atmosphere control: The retort furnace is the ideal choice, especially a model using a high-integrity gasket seal.
- If you are performing simple heat-treating in ambient air: A standard box furnace without a retort is more cost-effective and sufficient for your needs.
- If your process demands a vacuum or exceptionally high temperatures: You should investigate specialized equipment like a dedicated vacuum sintering furnace.
Ultimately, selecting a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize process purity and atmospheric precision for superior material outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Indirect heating via a sealed inner chamber (retort) to isolate the workpiece. |
| Key Benefit | Enables high-purity, controlled atmospheres (inert or reactive gases) for sensitive processes. |
| Common Applications | Nitriding, Sintering, Brazing, Annealing, and Tempering. |
| Ideal For | Processes where preventing oxidation or enabling specific surface reactions is critical. |
Achieve Uncompromised Process Purity with KINTEK
Does your laboratory process require precise control over atmosphere to prevent oxidation or enable critical surface reactions like nitriding or brazing? A retort furnace from KINTEK is the definitive solution for superior material outcomes.
As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, we provide the reliable, high-integrity retort furnaces you need for sensitive metallurgical processes. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your specific application, from material selection to temperature and sealing requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK retort furnace can enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure the success of your most demanding heat-treatment applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is the purpose of using an atmosphere-controlled heating furnace for Cu reduction? Achieve Active Catalytic States
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained



















