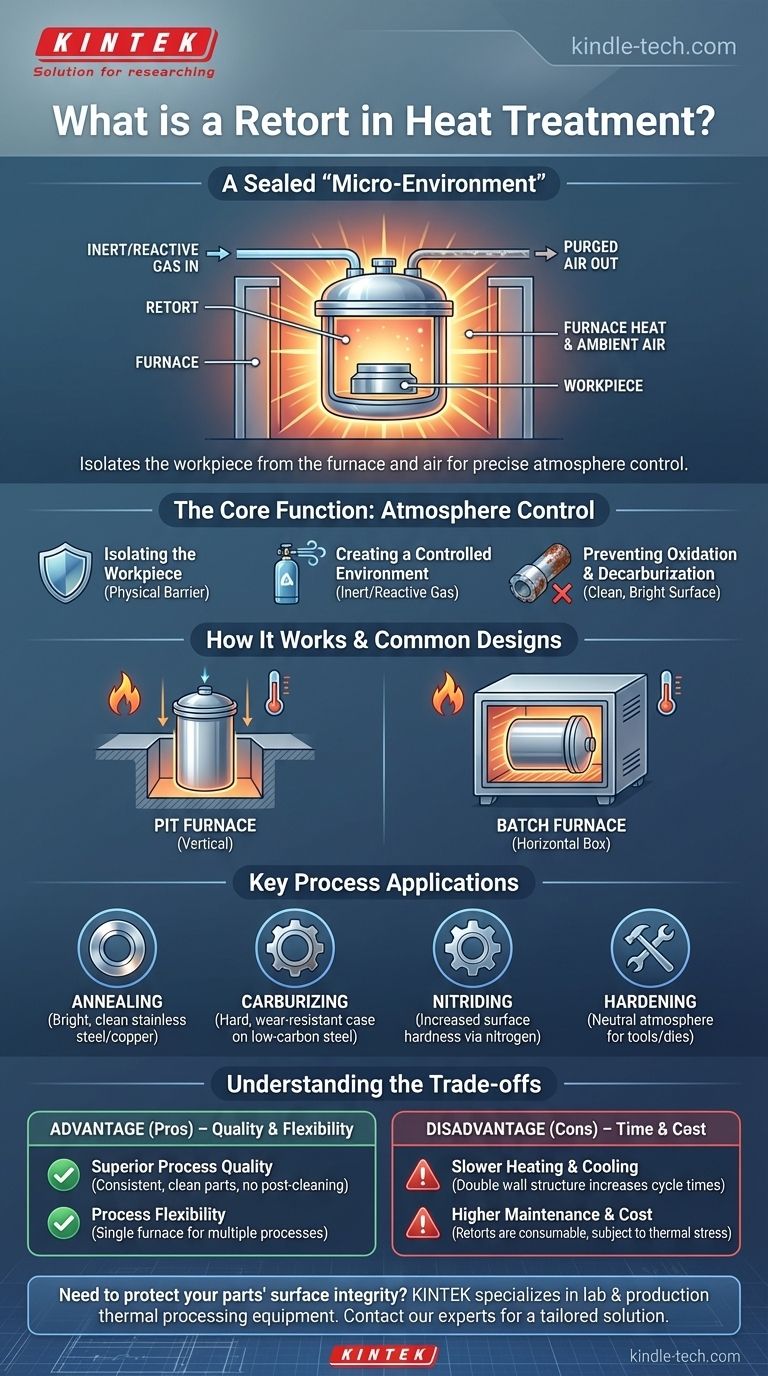
In the simplest terms, a retort is a sealed, often metallic, container used inside a furnace during heat treatment. Its purpose is to isolate the workpiece from the furnace's direct heating environment and the outside air. This separation allows for precise control over the gaseous atmosphere surrounding the part, which is critical for achieving specific metallurgical outcomes.
The core takeaway is this: a retort is not the furnace itself, but a specialized chamber placed within it. Think of it as creating a "micro-environment" to protect the material's surface and control chemical reactions during the heating process.

The Core Function: Atmosphere Control
The entire reason for using a retort comes down to one critical factor: atmosphere control. Without it, heating metals to high temperatures in the presence of air would cause undesirable reactions.
Isolating the Workpiece
A retort acts as a physical barrier. It separates the parts being treated from the furnace's heating elements (whether gas-fired or electric) and any ambient air that might leak into the main furnace chamber.
Creating a Controlled Environment
Once sealed, the air inside the retort is purged and replaced with a specific gas or gas mixture. This can be an inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) to simply prevent reactions, or a reactive gas designed to intentionally change the part's surface chemistry.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
The most common use of a retort is to prevent oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface of steel). By replacing oxygen with an inert or controlled atmosphere, the metal surface remains clean, bright, and maintains its intended hardness and properties.
How Retort Furnaces Work
While designs vary, the fundamental principle is consistent. The process involves placing the parts inside the retort, sealing it, and then placing the entire sealed container into the main furnace for heating.
The Basic Setup
The system consists of two main parts: the outer furnace, which provides the thermal energy, and the inner retort, which contains the workload and the controlled atmosphere. These retorts are typically made from high-temperature nickel-chromium alloys to withstand thermal cycling.
Common Process Applications
Retorts are essential for processes where the surface of the material cannot be compromised. This includes:
- Annealing: Especially bright annealing of stainless steel or copper.
- Carburizing: Adding carbon to the surface of low-carbon steel to create a hard, wear-resistant case.
- Nitriding: Diffusing nitrogen into the surface of steel to increase surface hardness.
- Hardening: Heating tools and dies in a neutral atmosphere to prevent decarburization.
Common Designs: Pit vs. Batch
Retort furnaces are often configured as pit furnaces, where a cylindrical retort is lowered vertically into a furnace in the floor. This is ideal for long, shaft-like parts. They also come in horizontal batch (or "box") furnace designs, which function much like a conventional oven.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using a retort provides superior quality, but it comes with clear operational trade-offs that are important to understand.
Advantage: Superior Process Quality
By perfectly controlling the atmosphere, retorts deliver clean, bright parts with highly consistent and repeatable metallurgical properties. This eliminates the need for post-treatment cleaning operations like sandblasting.
Advantage: Process Flexibility
A single retort furnace can be used for a wide variety of processes—from annealing to carburizing—simply by changing the atmosphere introduced into the retort.
Disadvantage: Slower Heating and Cooling
The retort itself is a layer of metal that heat must conduct through. This "double wall" structure means cycle times are inherently longer compared to direct-heating or vacuum furnaces, which reduces overall throughput.
Disadvantage: Higher Maintenance and Cost
Retorts are consumables. They are subjected to extreme thermal stress, which eventually leads to warping, cracking, and failure. These high-alloy containers are expensive to replace and represent a significant operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding whether a retort furnace is appropriate depends entirely on the metallurgical requirements of the part and your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is the highest surface quality and precise chemistry: A retort is essential for processes like bright annealing, carburizing, or nitriding where surface integrity is paramount.
- If your primary focus is bulk heat treatment where some surface oxidation is acceptable: A direct-fired or atmosphere furnace without a sealed retort may be a more cost-effective and higher-throughput solution.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycle times with high cleanliness: A vacuum furnace is a strong alternative, as it provides an even cleaner environment and can often heat and cool faster, though with a higher initial investment.
Ultimately, a retort is the tool you choose when the integrity and chemistry of the material's surface are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidation/decarburization; enables reactive processes | Higher operational complexity |
| Process Quality | Delivers clean, bright parts with consistent properties | Slower heating/cooling cycles |
| Process Flexibility | Single furnace can handle annealing, carburizing, nitriding | High maintenance cost (retort is a consumable) |
Need to protect your parts' surface integrity during heat treatment?
KINTEK specializes in lab and production-scale thermal processing equipment. Whether you are bright annealing stainless steel or carburizing tool steels, our expertise can help you select the right furnace technology—including retort systems—to achieve your precise metallurgical goals and improve your process reliability.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your application and get a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment



















