At its core, a sinter furnace is a high-temperature industrial oven that bonds particles of a material together into a solid object. It accomplishes this through a process called sintering, which uses intense heat, and sometimes pressure, to fuse the material without melting it to the point of becoming a liquid.
A sinter furnace is not merely an oven; it is a precision-engineered environment. Its primary function is to transform powdered or compacted materials into dense, high-performance parts by controlling heat, atmosphere, and sometimes pressure with extreme accuracy.
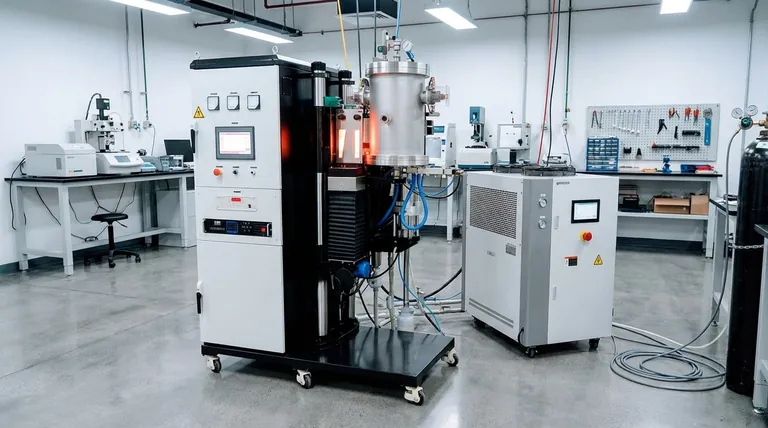

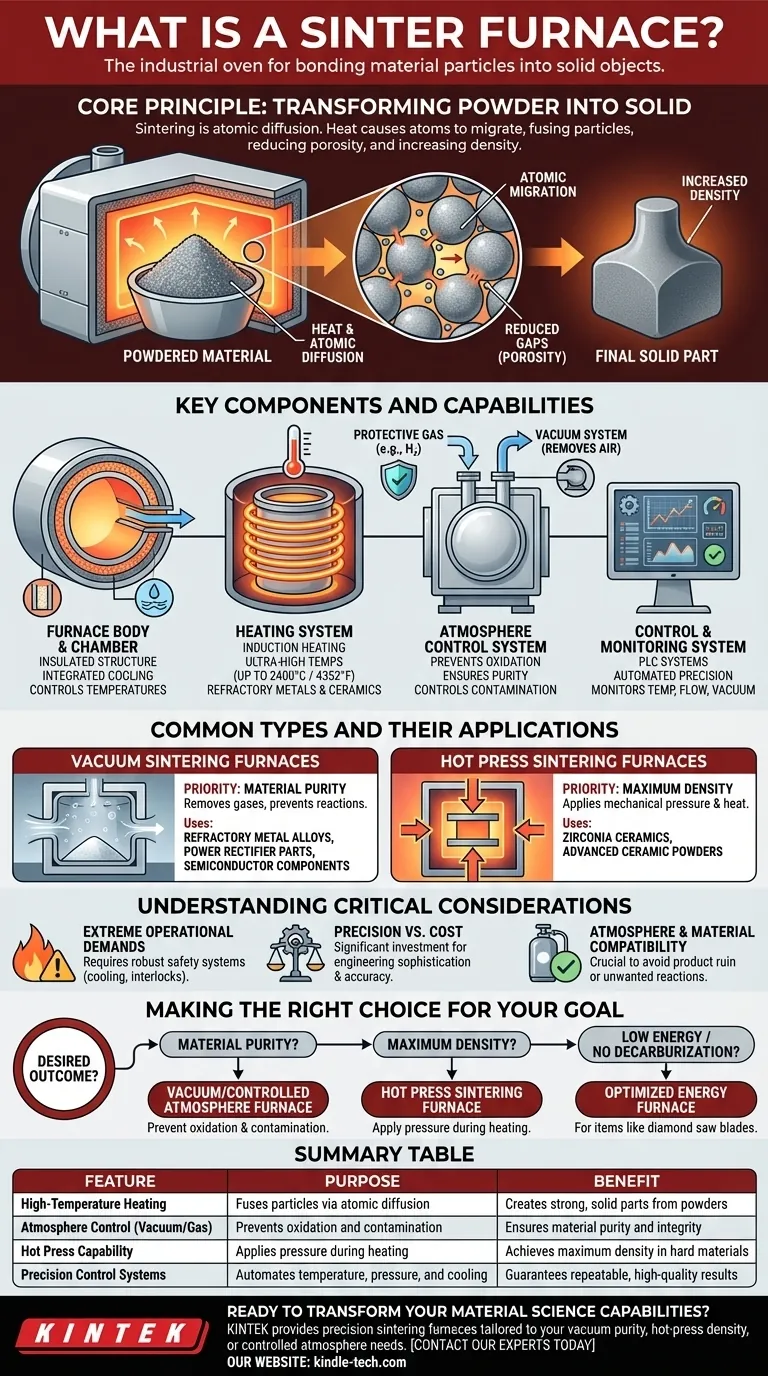
The Core Principle: Transforming Powder into Solid
Sintering is a process of atomic diffusion. When a powdered or compacted material is heated to a high temperature below its melting point, atoms at the contact points between particles migrate across the boundaries.
This migration fuses the individual particles together, reduces the gaps (porosity) between them, and causes the overall part to shrink and increase in density. The furnace is the tool that makes this transformation possible in a controlled and repeatable way.
Key Components and Capabilities
A modern sintering furnace is a complex system. Its design is focused on creating a perfectly stable and pure environment for this atomic-level process.
The Furnace Body & Chamber
The furnace body is the main structure critériosing the heating chamber. It is heavily insulated to contain extreme temperatures and often includes an integrated, high-performance cooling system, such as internal circulation of pure water, to protect the structure and rapidly cool the product.
The Heating System
This is the heart of the furnace. Many advanced furnaces use medium-frequency induction heating to achieve rapid and uniform temperatures. These systems can reach ultra-high temperatures, often up to 2400°C (4352°F), necessario for sintering refractory metals and advanced ceramics.
The Atmosphere Control System
Many materials will oxidize or become contaminated if heated in open air. To prevent this, sintering furnaces operate with a controlled atmosphere.
- Vacuum: A vacuum system removes air and other gases, creating a pure environment ideal for sintering sensitive metals like tungsten and molybdenum, or for producing semiconductor components.
- Protective Gas: An inert or reactive gas, such as hydrogen, can be introduced to protect the material from oxidation and, in some cases, to actively remove surface contaminants. This is crucial for preventing issues like decarburization.
The Control and Monitoring System
Precision is everything. Furnaces use sophisticated PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems to automate and monitor every variable. This includes intelligent temperature control, digital monitoring of cooling water flow, and vacuum levels, ensuring the process is both safe and perfectly repeatable.
Common Types and Their Applications
While all sinter furnaces share the same basic principle, they are often specialized for different materials and outcomes.
Vacuum Sintering Furnaces
These are used when material purity is the absolute priority. By removing atmospheric gases, they prevent unwanted chemical reactions. They are essential for producing high-performance refractory metal alloys, power rectifier parts, and semiconductor components.
Hot Press Sintering Furnaces
For materials that are difficult to densify, these furnaces add another variable: mechanical pressure. A large press acts on the material while it is being heated. This combination of heat and pressure is used to create exceptionally dense and strong parts from materials like zirconia ceramics and other advanced ceramic powders.
Understanding the Critical Considerations
Sintering furnaces are powerful tools, but jejich operation involves significant challenges and trade-offs.
Extreme Operational Demands
These furnaces operate at extraordinarily high temperatures and use very high amperage, often for long, continuous cycles. This makes safety the single most important design feature. Robust cooling systems, automated interlocks, and comprehensive monitoring are not optional luxuries; they are fundamental necessities.
Precision vs. Cost
The ability to maintain a high vacuum, uniform temperature, and controlled atmosphere requires exceptional structural design and manufacturing accuracy. This level of engineering sophistication means that sintering furnaces are a significant capital investment.
Atmosphere and Material Compatibility
The choice of operating atmosphere is not arbitrary. It is dictated entirely by the material being processed. Using the wrong atmosphere (or failing to achieve a pure one) can ruin the product, cause unwanted chemical reactions, and compromise the final component's integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of sintering process you need depends directly on the desired outcome for your material.
- If your primary focus is material purity and high-performance metals: You need a vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace to prevent oxidation and contamination.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in hard materials: A hot press sintering furnace, which adds high pressure to the heating process, is the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing items like diamond saw blades or certain ceramic inserts: A furnace optimized for low energy consumption and preventing decarburization will yield the best results.
Ultimately, a sinter furnace is a powerful tool of material transformation, enabling the creation of advanced components that would be impossible to form through traditional melting and casting.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Heating | Fuses particles via atomic diffusion | Creates strong, solid parts from powders |
| Atmosphere Control (Vacuum/Gas) | Prevents oxidation and contamination | Ensures material purity and integrity |
| Hot Press Capability | Applies pressure during heating | Achieves maximum density in hard materials |
| Precision Control Systems | Automates temperature, pressure, and cooling | Guarantees repeatable, high-quality results |
Ready to transform your material science capabilities? A precision sintering furnace from KINTEK is the key to producing high-performance, dense components from powdered metals and ceramics. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a solution tailored to your specific needs—whether it's vacuum purity, hot-press density, or controlled atmosphere processing. Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK sinter furnace can advance your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?



















