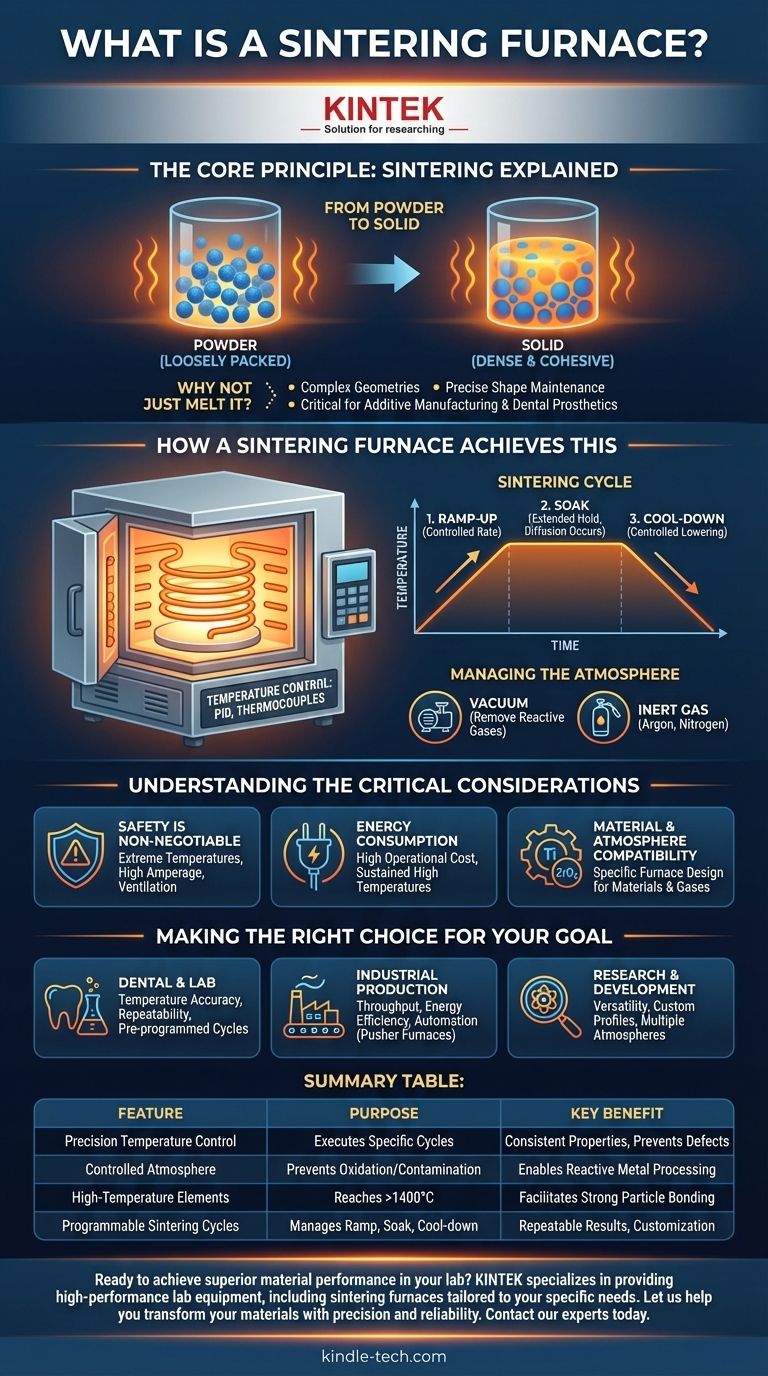
At its core, a sintering furnace is a specialized, high-temperature oven designed to transform a loosely packed powder into a solid, dense object. It achieves this remarkable feat through a process called sintering, where heat and pressure cause the particles to bond together and fuse, all without actually melting the material.
A sintering furnace is not simply a "hot box." It is a precision instrument engineered to control extreme heat and often a specific atmosphere, enabling the fundamental restructuring of a material's atomic bonds to increase its strength and density.
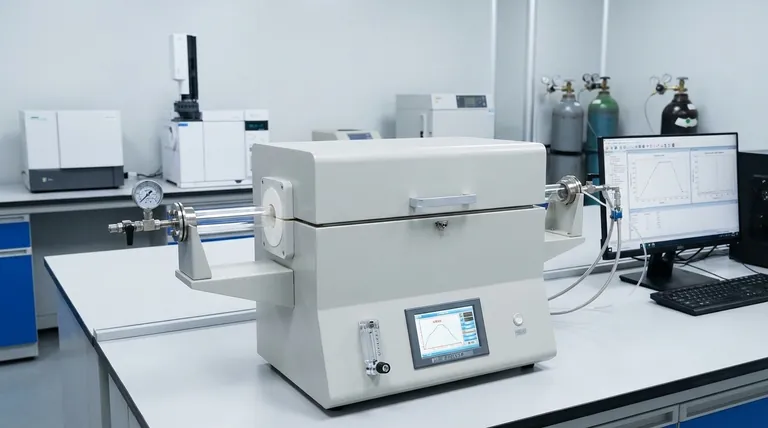

The Core Principle: Sintering Explained
To understand the furnace, you must first understand the process it facilitates. Sintering is a cornerstone of modern materials science, used in everything from dental crowns to jet engine components.
From Powder to Solid
Sintering works by heating a material to a temperature below its melting point. At this high temperature, the atoms in the individual powder particles become highly agitated and begin to migrate across the boundaries between particles, a process called atomic diffusion. This diffusion creates "necks" or bridges that grow, pulling the particles together, eliminating the voids between them, and creating a solid, cohesive mass.
Why Not Just Melt It?
Melting and casting can be a simpler process, but sintering offers critical advantages. It allows for the creation of parts with extremely complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to cast. Furthermore, because the material never becomes a liquid, the final part maintains its precise shape, a crucial factor in applications like additive manufacturing (metal 3D printing) and dental prosthetics.
How a Sintering Furnace Achieves This
A sintering furnace is far more sophisticated than a conventional oven. Its design is focused on precise control over the two most critical variables in the process: temperature and atmosphere.
Precision Temperature Control
The furnace must execute a highly specific temperature profile. This is managed by a sophisticated control system, often using thermocouples to monitor the internal temperature and a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller to precisely manage the power sent to the heating elements. These elements are often made of materials like molybdenum disilicide or silicon carbide to withstand the extreme heat.
The Sintering Cycle
The process isn't as simple as turning the heat on and off. A typical cycle involves three phases:
- Ramp-up: The temperature is increased at a controlled rate.
- Soak: The furnace holds the material at the target sintering temperature for an extended period, often for several hours. This is when the majority of the atomic diffusion and densification occurs.
- Cool-down: The temperature is lowered in a controlled manner to prevent thermal shock, which could crack the newly formed part.
Managing the Atmosphere
For many materials, especially metals, heating them to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen would cause immediate and catastrophic oxidation (rusting). Sintering furnaces prevent this by creating a controlled atmosphere, typically either a vacuum to remove all reactive gases or by flooding the chamber with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen.
Understanding the Critical Considerations
While powerful, these furnaces operate under extreme conditions, which introduces significant challenges and trade-offs.
Safety is Non-Negotiable
As noted, safety is the paramount concern. The combination of extraordinarily high temperatures, long operational times, and high amperage electrical systems creates a hazardous environment. Proper furnace design incorporates robust thermal insulation, safety interlocks to prevent opening while hot, and emergency shut-offs. If process gases are used, proper ventilation is also critical.
Energy Consumption
Maintaining temperatures often exceeding 1400°C (2550°F) for many hours requires a tremendous amount of energy. The energy consumption of a sintering furnace is a major operational cost and a key factor in industrial production calculations.
Material and Atmosphere Compatibility
A furnace designed for sintering zirconia ceramics in air cannot be used for sintering titanium powder, which requires a vacuum or argon atmosphere. The choice of heating elements, insulation, and gas handling systems dictates which materials a furnace can safely and effectively process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a sintering furnace requires a clear understanding of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is dental or laboratory work: Prioritize a furnace with exceptional temperature accuracy, repeatability, and pre-programmed cycles for specific materials like zirconia.
- If your primary focus is industrial mass production: Emphasize throughput, energy efficiency, and automation, potentially considering continuous "pusher" furnaces over smaller batch models.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Seek a versatile furnace that allows for full customization of temperature profiles and can handle different atmospheres (air, vacuum, inert gas) to test a wide range of materials.
Ultimately, understanding that the furnace is a tool for precise material transformation is the key to mastering your final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Control | Executes specific heating/cooling cycles | Ensures consistent material properties and prevents defects |
| Controlled Atmosphere (Vacuum/Inert Gas) | Prevents oxidation and contamination | Enables processing of reactive metals like titanium |
| High-Temperature Heating Elements | Reaches temperatures above 1400°C (2550°F) | Facilitates atomic diffusion for strong particle bonding |
| Programmable Sintering Cycles | Manages ramp-up, soak, and cool-down phases | Allows for repeatable results and customization for different materials |
Ready to achieve superior material performance in your lab?
Whether you are developing new materials in an R&D setting or producing high-quality dental prosthetics and industrial components, the right sintering furnace is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment, including sintering furnaces tailored to your specific needs—from versatile R&D models to efficient production systems.
Let us help you transform your materials with precision and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect sintering solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















