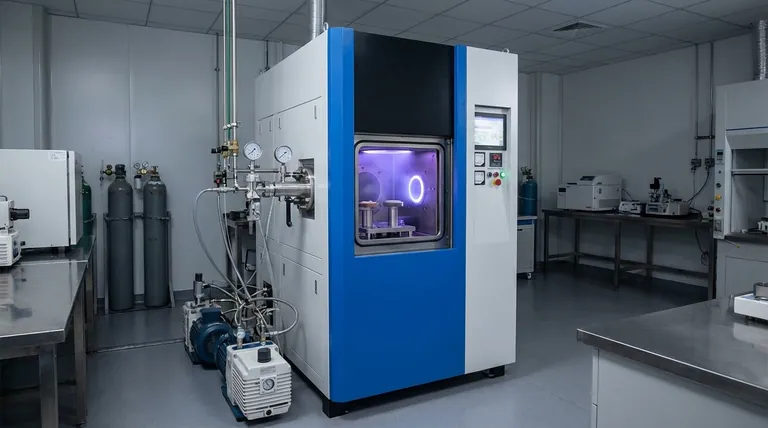
In essence, a sputtering machine is a highly specialized piece of equipment used to deposit extremely thin films of a material onto a surface. It operates under a vacuum and uses a process called physical vapor deposition (PVD), where atoms are physically ejected from a source material (the "target") and land on the object to be coated (the "substrate"), forming a precise and uniform layer.
A sputtering machine is best understood as an atomic-scale spray painter. It provides unparalleled control for creating high-quality, uniform thin films, which are foundational to modern electronics, optics, and advanced materials.

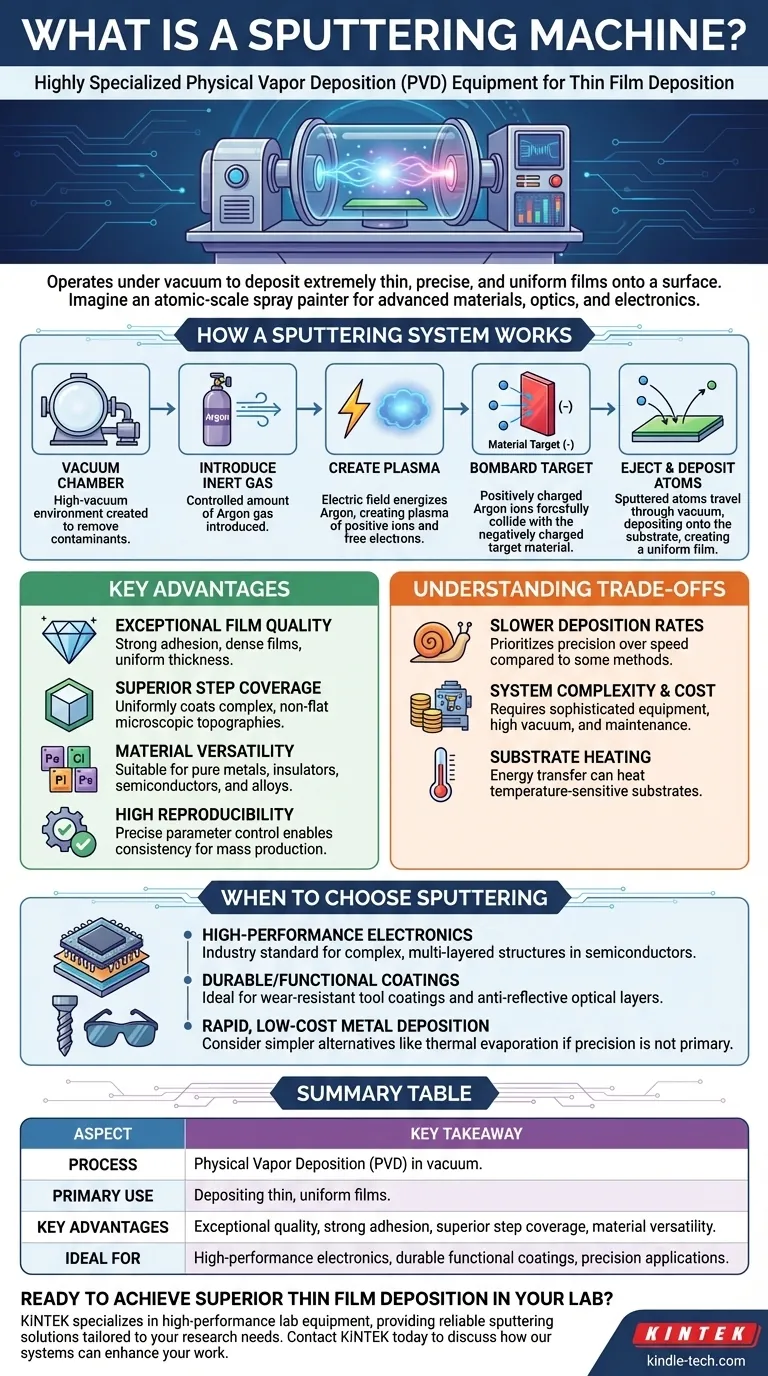
How a Sputtering System Works
Sputtering is a physical process, not a chemical one. It relies on momentum transfer in a controlled vacuum environment, almost like a game of atomic billiards.
The Vacuum Chamber
The entire process takes place within a high-vacuum chamber. This is critical to remove air and other particles that could contaminate the film or interfere with the process.
Introducing an Inert Gas
A small, precisely controlled amount of an inert gas, typically Argon, is introduced into the chamber. This gas is not meant to react with anything; it will serve as the "bullets" for the process.
Creating a Plasma
A strong electric field is applied within the chamber. This field energizes the Argon gas, stripping electrons from the Argon atoms and creating a plasma—a glowing, high-energy cloud of positively charged Argon ions and free electrons.
Bombarding the Target
The material you want to deposit (e.g., gold, titanium, silicon dioxide) is set up as a "target," which is given a negative electrical charge. The positive Argon ions from the plasma are forcefully accelerated toward and collide with this negatively charged target.
Ejecting and Depositing Atoms
When the high-energy Argon ions strike the target, they physically knock out, or "sputter," atoms from the target material. These ejected atoms travel through the vacuum and deposit onto the substrate, gradually building up a thin, uniform film.
Key Advantages of the Sputtering Process
The physical nature of sputtering provides several distinct advantages that make it a cornerstone of high-tech manufacturing.
Exceptional Film Quality
Sputtered films exhibit strong adhesion because the depositing atoms have high kinetic energy, allowing them to embed slightly into the substrate surface. This also results in films that are very dense and uniform in thickness.
Superior Step Coverage
Sputtering provides excellent step coverage, meaning it can uniformly coat substrates with complex, non-flat microscopic topographies. The sputtered atoms arrive at the substrate from many angles, preventing thin spots or gaps in corners and on vertical walls.
Material Versatility
The process can be used with a vast range of materials, including pure metals, insulators, and semiconductors. Critically, it allows for alloy film deposition, where the composition of the sputtered film remains identical to the alloy target.
High Reproducibility
Because the key parameters—power, time, and gas pressure—can be precisely controlled, sputtering is a highly reproducible process. This makes it ideal for mass production where consistency from one batch to the next is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sputtering is not the right solution for every application. Its primary trade-offs are related to speed and complexity.
Slower Deposition Rates
Compared to other methods like thermal evaporation, sputtering can be a slower process. It prioritizes precision, control, and film quality over raw deposition speed.
System Complexity and Cost
Sputtering systems are sophisticated and expensive. They require high-vacuum pumps, advanced power supplies, and careful maintenance, representing a significant capital investment.
Substrate Heating
The energy transferred during ion bombardment and film condensation can heat the substrate. While often manageable, this can be a concern for temperature-sensitive substrates like certain plastics or biological materials.
When to Choose Sputtering
Selecting a deposition technique depends entirely on your project's technical requirements and desired outcomes.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: Sputtering is the industry standard for its unparalleled uniformity and ability to create the complex, multi-layered structures found in semiconductor chips.
- If your primary focus is durable or functional coatings: The strong adhesion and density of sputtered films make it ideal for creating wear-resistant tool coatings, anti-reflective optical layers, and low-friction surfaces.
- If your primary focus is rapid, low-cost metal deposition on simple shapes: You might consider a simpler alternative like thermal evaporation, as the precision of sputtering may be unnecessary for your goal.
By understanding its core mechanism and trade-offs, you can leverage sputtering to achieve atomic-level control and superior film quality in your application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) in a vacuum chamber. |
| Primary Use | Depositing thin, uniform films of materials onto a substrate. |
| Key Advantages | Exceptional film quality, strong adhesion, superior step coverage, material versatility. |
| Ideal For | High-performance electronics, durable functional coatings, applications requiring precision. |
Ready to achieve superior thin film deposition in your lab?
Sputtering is a complex process, but having the right equipment makes all the difference. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable sputtering solutions tailored to your research and production needs.
Our expertise ensures you get the precision, uniformity, and material versatility required for cutting-edge applications in semiconductors, optics, and advanced materials.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our sputtering systems can enhance your work and deliver the exceptional film quality you demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application










