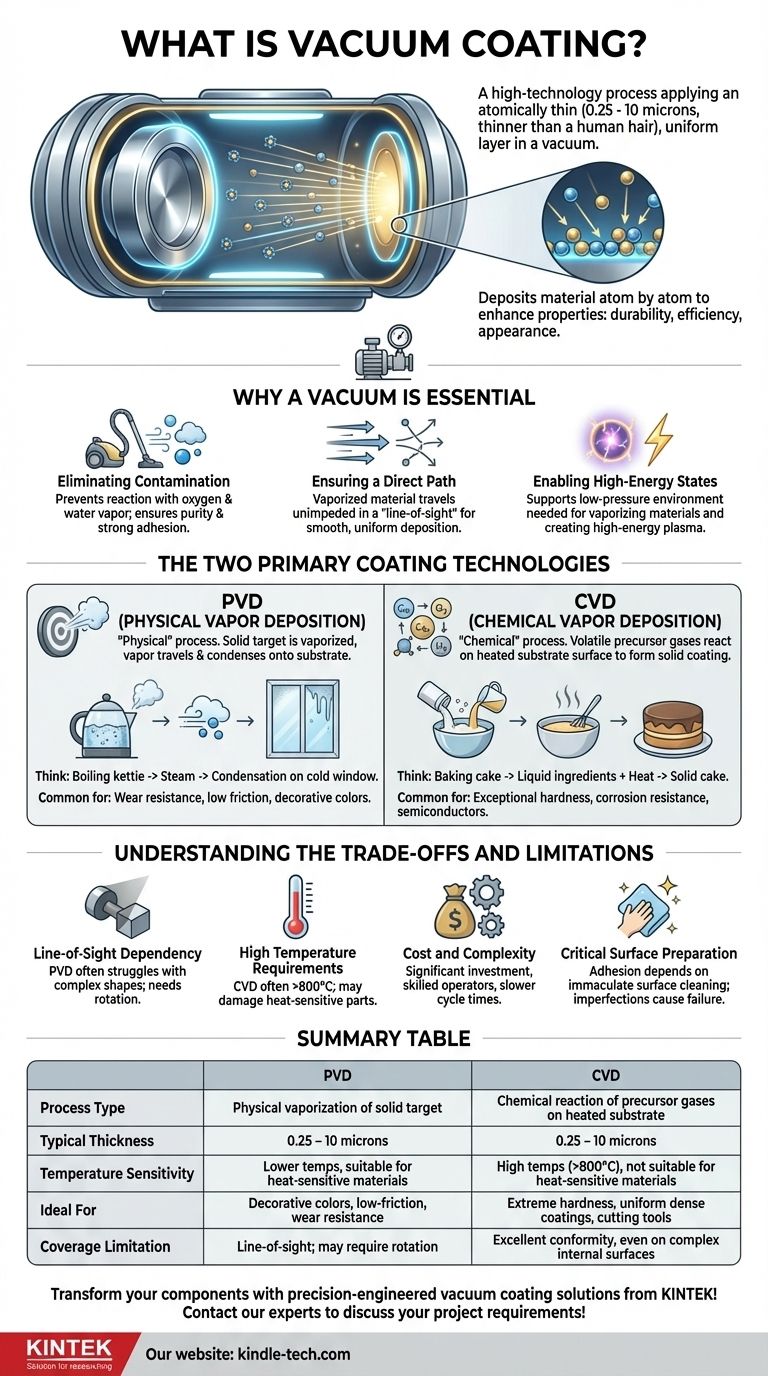
In essence, a vacuum coating is a high-technology process used to apply an exceptionally thin, uniform layer of material onto an object's surface inside a vacuum chamber. This process isn't like painting; it involves depositing material atom by atom to fundamentally enhance the object's properties, such as its durability, efficiency, or appearance. These coatings are incredibly fine, often ranging from just 0.25 to 10 microns thick—many times thinner than a human hair.
The core purpose of using a vacuum is to eliminate all air and water vapor. This pristine environment prevents contamination and allows coating materials to travel from their source to the object's surface without interference, ensuring a pure, dense, and highly adherent final layer.

Why a Vacuum is Essential
The vacuum itself is not just a setting; it is the critical tool that enables the entire process. Without it, high-performance thin-film coatings would be impossible to create for three key reasons.
Eliminating Contamination
Normal atmosphere is filled with particles like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. If present during the coating process, these particles would react with the deposition material and embed themselves in the coating, creating impurities that compromise its strength, adhesion, and desired properties.
Ensuring a Direct Path
In a vacuum, vaporized coating material can travel in a straight, uninterrupted line from the source to the substrate (the object being coated). This "line-of-sight" deposition is crucial for creating a smooth and uniform layer. In normal air, the coating particles would collide with air molecules, scattering randomly and resulting in a weak, uneven, and porous film.
Enabling High-Energy States
Many advanced coating processes require generating a high-energy plasma, which is an ionized gas. These high-energy conditions, necessary to vaporize the source material and ensure a strong bond with the substrate, can only be created and sustained in the low-pressure environment of a vacuum.
The Two Primary Coating Technologies
While there are many variations, nearly all vacuum coating falls into two main categories: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a "physical" process. A solid source material, known as a target, is vaporized into a cloud of atoms or molecules. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto the cooler substrate, forming a solid thin film.
Think of it like boiling a kettle: steam (vapor) rises and condenses as water (a solid film) on a cold kitchen window. PVD is a highly controlled, atomic-scale version of this principle and is commonly used for wear resistance, reducing friction, and applying brilliant decorative colors.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a "chemical" process. Instead of starting with a solid, one or more volatile precursor gases are introduced into the vacuum chamber. These gases decompose and react on the surface of a heated substrate, forming the desired solid coating.
This is more like baking a cake, where liquid ingredients (the gases) react with heat to form a solid cake (the coating). CVD is renowned for creating exceptionally hard, durable, and corrosion-resistant coatings, making it vital in the manufacturing of cutting tools and semiconductors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Vacuum coating is a powerful but not universally perfect solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Line-of-Sight Dependency
Most PVD processes struggle to coat complex internal shapes or the backsides of objects, as the coating can only deposit on surfaces it can "see" from the source. Parts often must be rotated on complex fixtures to achieve full coverage.
High Temperature Requirements
CVD processes, in particular, often require the substrate to be heated to very high temperatures (often >800°C). This can damage or negatively alter the properties of the underlying material, making it unsuitable for heat-treated steels, plastics, or other temperature-sensitive components.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum deposition systems are significant capital investments. They rely on a series of pumps working in tandem to achieve the necessary high vacuum, require skilled operators, and can have slower cycle times than traditional coating methods like electroplating, making the process more expensive.
Critical Surface Preparation
The performance of a vacuum coating is entirely dependent on its adhesion to the substrate. The part's surface must be immaculately cleaned of all oils, oxides, and micro-contaminants before entering the chamber. Any imperfection will become a point of failure for the coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct process depends entirely on the material of your part and your performance goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance on a temperature-tolerant part: CVD is often the superior choice for its uniform, dense, and well-adhered coatings.
- If your primary focus is adding a durable decorative color, a low-friction surface, or a wear-resistant layer to a temperature-sensitive material: PVD provides greater flexibility with a wide range of materials at lower process temperatures.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance for a simple part: Both PVD and CVD can offer excellent solutions, with the choice often depending on the specific corrosive environment and cost constraints.
By understanding these core principles, you can leverage vacuum coating to transform a standard material into a high-performance, purpose-built component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical vaporization of a solid target | Chemical reaction of precursor gases on a heated substrate |
| Typical Coating Thickness | 0.25 - 10 microns | 0.25 - 10 microns |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Lower temperatures, suitable for heat-sensitive materials | High temperatures (>800°C), not suitable for heat-sensitive materials |
| Ideal For | Decorative colors, low-friction surfaces, wear resistance on various materials | Extreme hardness, uniform dense coatings, cutting tools, semiconductors |
| Coverage Limitation | Line-of-sight; may require rotation for complex shapes | Excellent conformity, even on complex internal surfaces |
Transform your components with precision-engineered vacuum coating solutions from KINTEK!
Whether you need to enhance wear resistance, improve corrosion protection, or achieve brilliant decorative finishes, our expertise in PVD and CVD technologies ensures your materials meet the highest performance standards.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory and industrial needs with reliable, high-quality solutions. Let us help you select the ideal coating process for your specific application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our vacuum coating solutions can add value to your products!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and sputter? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















