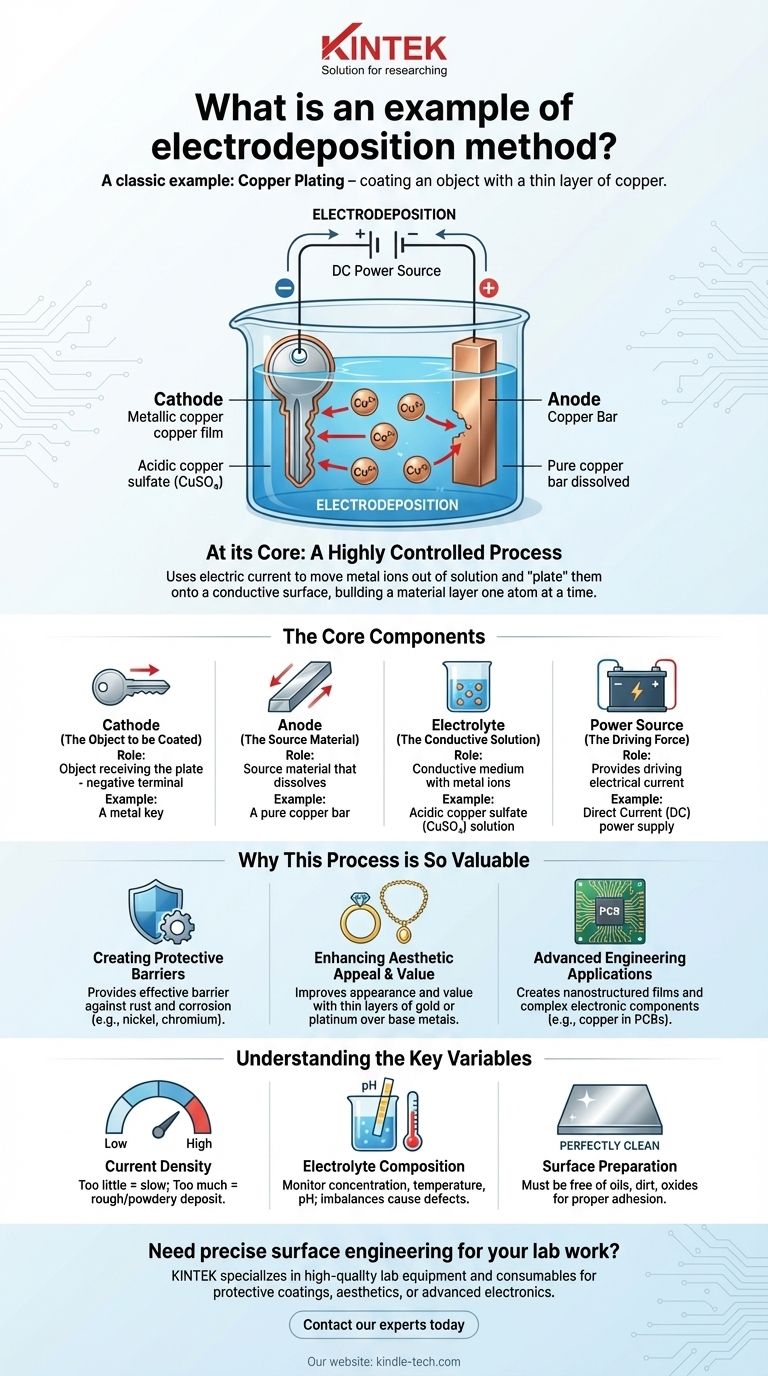
A classic example of electrodeposition is copper plating, where an object is coated with a thin layer of copper. In this process, the object to be plated (like a key) and a piece of pure copper are submerged in an acidic copper sulfate solution. When an electrical current is applied, the copper from the solution is precisely deposited onto the key, forming a uniform metallic film.
At its core, electrodeposition is a highly controlled process that uses an electric current to move metal ions out of a solution and "plate" them onto the surface of a conductive object. It's a method for building a material layer one atom at a time.

How Electrodeposition Works: The Core Components
To understand any electrodeposition process, you must first understand its four essential components, which work together in a simple circuit.
The Cathode (The Object to be Coated)
The cathode is the object you want to plate. It is connected to the negative terminal of the power source. This negative charge attracts the positively charged metal ions that are floating in the solution.
The Anode (The Source Material)
The anode is connected to the positive terminal. Often, it is made of the same metal you want to plate (e.g., a pure copper bar for copper plating). As the current flows, the anode slowly dissolves, replenishing the metal ions in the solution that are being deposited onto the cathode.
The Electrolyte (The Conductive Solution)
The electrolyte is a liquid solution containing dissolved metal salts, which provide the ions needed for plating. For copper plating, this is typically a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO₄). This solution acts as a conductive medium, allowing ions to travel between the anode and the cathode.
The Power Source (The Driving Force)
A direct current (DC) power supply provides the energy for the entire reaction. It creates the electrical potential that pulls positive metal ions from the solution and forces them to deposit onto the negatively charged cathode, forming the metallic coating.
Why This Process is So Valuable
Electrodeposition is not just for simple coatings; it is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing and technology due to its precision and versatility.
Creating Protective Barriers
The most common use is to impart new properties to a surface. Plating an object with a layer of nickel or chromium provides an incredibly effective barrier against rust and corrosion.
Enhancing Aesthetic Appeal and Value
The jewelry industry relies heavily on electrodeposition. A thin, brilliant layer of gold or platinum can be deposited over a less expensive base metal, dramatically improving its appearance and value at a low cost.
Advanced Engineering Applications
In high-tech fields, this method is used to create nanostructured films and complex electronic components like printed circuit boards (PCBs). The ability to deposit extremely thin, uniform layers of conductive materials like copper is essential for modern electronics.
Understanding the Key Variables
Achieving a high-quality coating is not automatic. The process is highly sensitive to several factors, and controlling them is critical to success.
Current Density
The amount of electrical current relative to the surface area of the object is crucial. Too little current results in a slow and inefficient process. Too much current can cause a rough, powdery, or burnt-looking deposit that does not adhere well.
Electrolyte Composition
The concentration, temperature, and pH of the electrolyte bath must be constantly monitored. Imbalances can lead to uneven plating, poor adhesion, and defects in the final coating.
Surface Preparation
This is perhaps the most common point of failure. The surface of the cathode must be perfectly clean, free of any oils, dirt, or oxides. Any contamination will prevent the deposited layer from adhering properly, causing it to peel or flake off.
Applying This Knowledge
How you approach electrodeposition depends entirely on your final goal.
- If your primary focus is corrosion protection: Prioritize creating a thick, non-porous coating by carefully controlling the current density and plating time.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics: Emphasize surface preparation and use additives in the electrolyte to ensure a bright, mirror-like finish.
- If your primary focus is high-tech fabrication: Absolute control over all variables, especially electrolyte purity and current, is non-negotiable to achieve specific nanostructures and electrical properties.
Ultimately, electrodeposition is a powerful tool for precisely engineering surfaces to give them properties they would not otherwise possess.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Electrodeposition | Example for Copper Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Cathode | Object to be coated (negative terminal) | A metal key |
| Anode | Source material that dissolves (positive terminal) | A pure copper bar |
| Electrolyte | Conductive solution with metal ions | Acidic copper sulfate (CuSO₄) solution |
| Power Source | Provides the driving electrical current | Direct Current (DC) power supply |
Need precise surface engineering for your lab work?
Whether you're developing protective coatings, enhancing material aesthetics, or fabricating advanced electronic components, the right equipment is key to successful electrodeposition. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your research and manufacturing processes.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve uniform, high-quality deposits and optimize your electroplating results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of specialized photoelectrochemical electrolytic cells in HER? Precision Evaluation for Lab
- How does a three-electrode electrochemical cell ensure scientific accuracy? Achieve Precise Corrosion Analysis
- What is the important precaution regarding electrode polarity when setting up an electrolysis cell? Avoid Costly Mistakes and Failed Experiments
- What is the necessity of a constant-temperature electrochemical testing system? Ensure Precision in Perovskite Research
- How do electrode systems and electrolytic cell units facilitate the removal of heavy metals in electro-kinetic systems?
- What are the advantages of electrodeposition for GQDs on TiO2? Enhance Adhesion and Precision in Your Research
- Why is electrolytic deposition used? To Engineer Superior Surface Properties
- How is a three-electrode electrochemical electrolytic cell utilized to evaluate Zr-Nb alloy corrosion resistance?



















