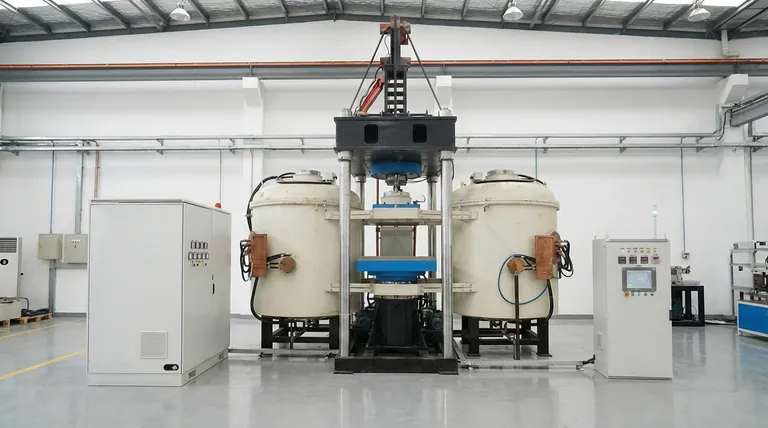
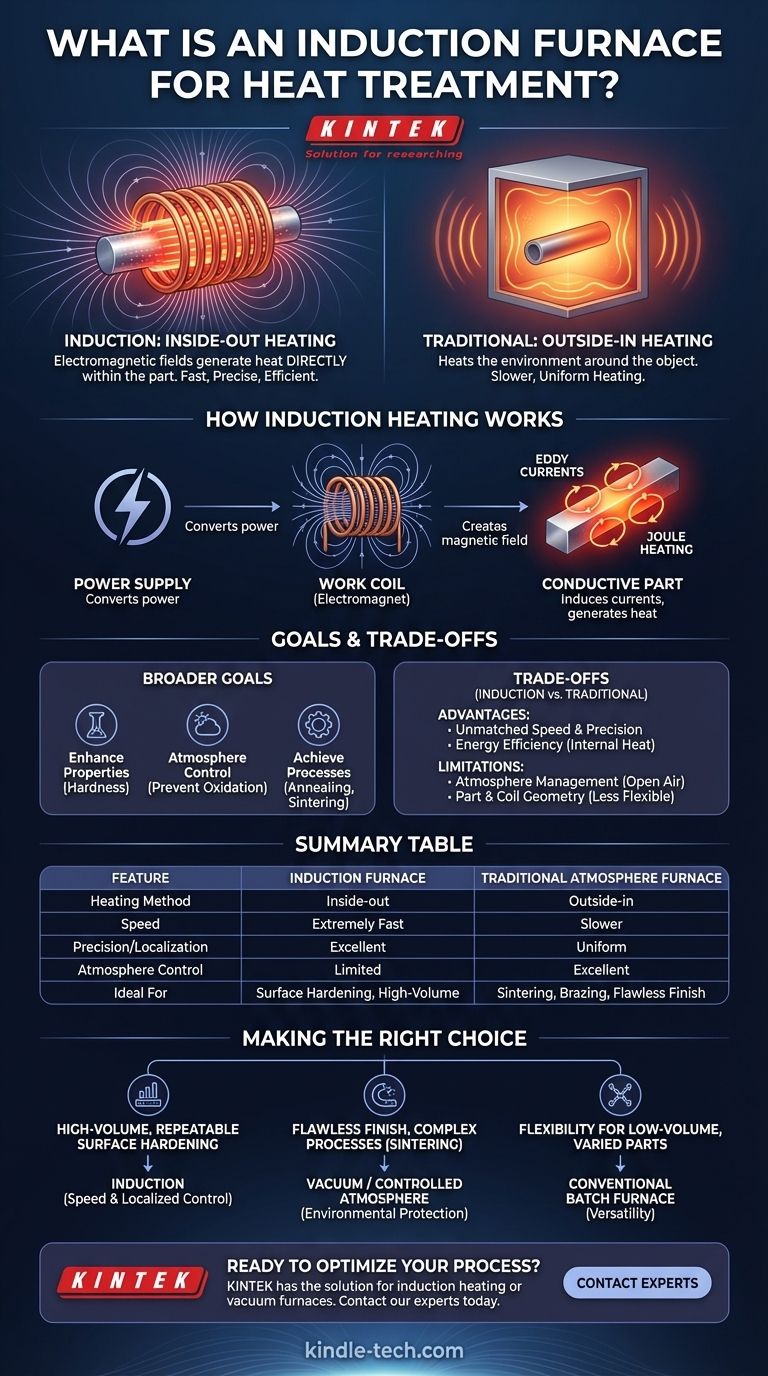
At its core, an induction furnace for heat treatment uses electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the part itself. Unlike traditional furnaces that heat the air or chamber around an object, induction heating turns the conductive workpiece into its own heat source. This process is incredibly fast, precise, and efficient, as it relies on inducing an electrical current inside the material, which generates heat due to the material's natural resistance.
The central distinction is this: traditional furnaces heat parts from the outside-in within a controlled environment, while induction heats parts from the inside-out. This fundamental difference makes induction unparalleled for speed and localized heating, but it requires different considerations for protecting the part's surface.

How Induction Heating Works
The principle behind induction is a direct application of electromagnetism, making it a unique and powerful tool for material processing.
The Principle of Electromagnetism
An induction heater uses a powerful electromagnet, typically a copper coil, through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed. This creates a rapidly changing and intense magnetic field within the coil's center.
Generating Internal Heat (Joule Heating)
When a conductive part (like steel or another metal) is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circular electric currents within the metal, known as eddy currents. The material's natural resistance to the flow of these currents generates precise and rapid heat—a phenomenon called Joule heating.
Key Components
The system consists of two main parts: the power supply, which converts utility power into the required frequency and amperage, and the work coil, which is engineered to create the specific magnetic field shape needed to heat the part correctly.
The Broader Goal: Why Use Heat Treatment?
Induction is one of several methods to achieve the goals of heat treatment. The ultimate purpose is always to deliberately alter a material's physical and sometimes chemical properties.
Enhancing Material Properties
As with any heat treatment process, the primary goal is to improve the material. This includes increasing its density, hardness, and high-temperature resistance, which enhances its overall performance and durability in its final application.
The Critical Need for Atmosphere Control
Many heat treatment processes require a controlled atmosphere to succeed. The environment prevents undesirable reactions like oxidation (rust), decarburization (carbon loss), and contamination from air, ensuring a high-quality component with superior mechanical properties.
Achieving Specific Process Goals
Heat treatment is not a single process. It enables critical manufacturing steps such as annealing (softening), brazing (joining), and sintering (fusing powdered material), each requiring precise temperature cycles and environmental conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Induction vs. Atmosphere Furnaces
Choosing between induction and a traditional furnace (like a vacuum or box furnace) involves a clear set of trade-offs centered on speed versus environmental control.
Advantage: Unmatched Speed and Precision
Induction's greatest strength is its ability to deliver a massive amount of energy to a very specific area in seconds. This makes it ideal for surface hardening, where only the outer layer of a part needs to be heated and quenched, leaving the core ductile.
Advantage: Energy Efficiency
Because heat is generated only within the part, very little energy is wasted heating a large furnace chamber, surrounding air, or insulation. This makes induction a highly efficient process for high-volume, repetitive tasks.
Limitation: Atmosphere Management
A standard induction setup operates in open air. For materials sensitive to oxidation at high temperatures, this is a significant drawback. While induction systems can be placed inside a vacuum or flooded with inert gas, this adds complexity and cost, negating some of its simplicity.
Limitation: Part and Coil Geometry
The effectiveness of induction heating is highly dependent on the shape of the work coil and its proximity to the part. Each part geometry may require a custom-designed coil, making induction less flexible than a large batch furnace for treating a wide variety of parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct heating method depends entirely on your production goals, material properties, and required surface finish.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable surface hardening: Induction is almost always the superior choice due to its unmatched speed and precise, localized control.
- If your primary focus is a flawless, bright finish or complex processes like sintering: A vacuum or controlled atmosphere furnace provides the essential environmental protection that induction alone cannot.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for low-volume, varied parts: A conventional batch furnace offers the versatility to handle different shapes and sizes without the need for custom-engineered coils.
By understanding the fundamental trade-off between targeted speed and environmental control, you can confidently select the technology that aligns with your specific engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Traditional Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Inside-out (via eddy currents) | Outside-in (chamber heating) |
| Speed | Extremely fast (seconds) | Slower (hours) |
| Precision/Localization | Excellent for targeted areas | Heats the entire part uniformly |
| Atmosphere Control | Limited (requires add-ons) | Excellent (integrated) |
| Ideal For | Surface hardening, high-volume production | Sintering, brazing, processes requiring a flawless finish |
Ready to Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process?
Whether your priority is the unmatched speed of induction heating for high-volume surface hardening or the flawless environmental control of a vacuum furnace for sintering, KINTEK has the solution. As your specialist in lab equipment and consumables, we provide the precise technology your laboratory needs to enhance material properties and boost efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can empower your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum system essential for Ti-22Al-25Nb hot pressing? Protect Your Alloys from Oxidation
- What role does hydraulic mechanical pressure play in W-50%Cu vacuum hot press sintering? Achieve 99.6% Density.
- Why use vacuum in hot-press sintering for boron carbide? Achieve Superior Density and Material Purity
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity



















