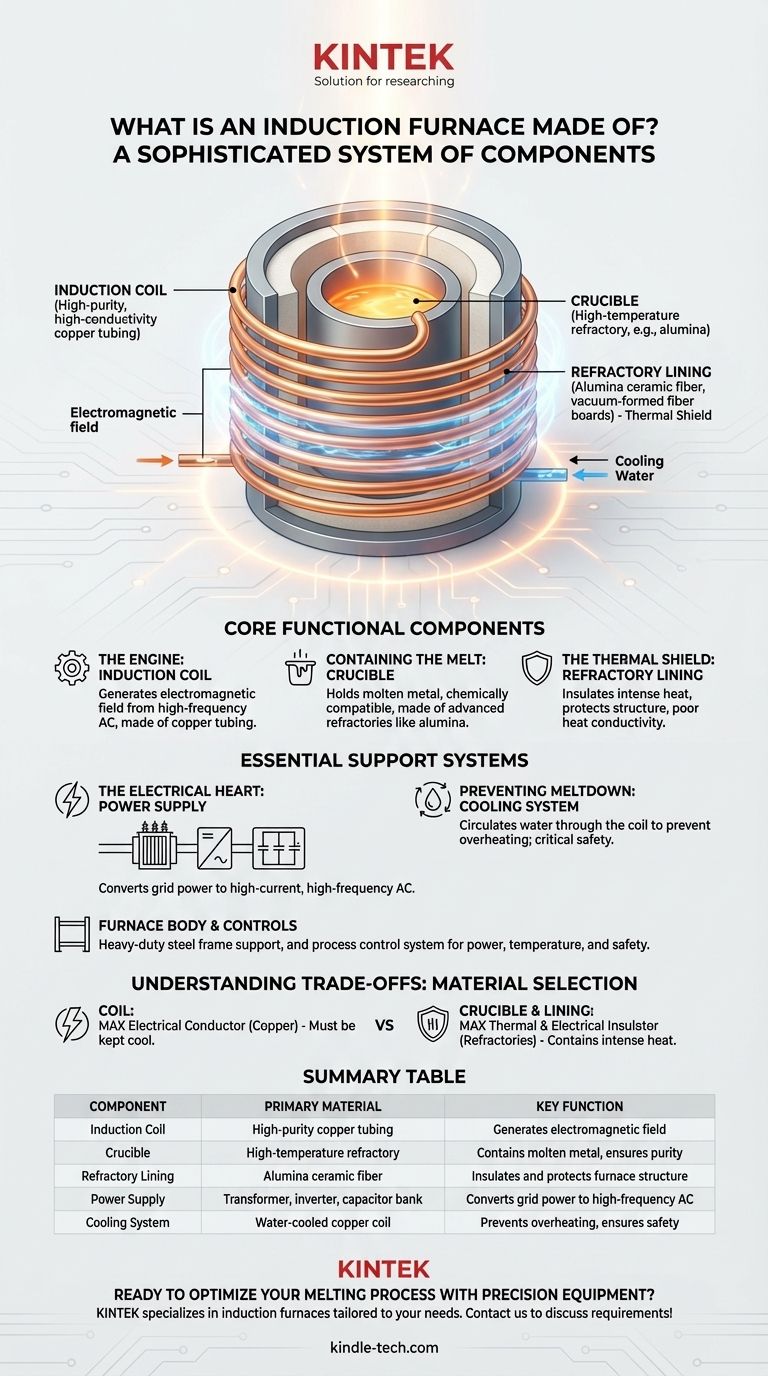
At its core, an induction furnace is not made of a single material but is a sophisticated system of components working in concert. The primary elements are a water-cooled copper induction coil, a crucible made of high-temperature refractory materials, a robust power supply, and a structural furnace body, all managed by a precise control system.
The design of an induction furnace is a deliberate exercise in material science. It pairs a highly conductive material (the copper coil) to generate an electromagnetic field with a highly resistant, insulating material (the refractory crucible) to contain the intense heat this field produces in the metal.

The Core Functional Components
An induction furnace's power comes from how its core parts interact. Each is made from a material specifically chosen for its role in the electromagnetic heating process.
The Induction Coil: The Engine of the Furnace
The heart of the furnace is the induction coil. This is a helical coil made from high-purity, high-conductivity (EC Grade) copper tubing.
When a powerful alternating current from the power supply flows through it, the coil generates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field. This field is the force that ultimately melts the metal.
The Crucible: Containing the Melt
The metal to be melted is not placed in direct contact with the coil. Instead, it is held in a crucible, which sits inside the coil.
This crucible is made from refractory materials, such as high-purity alumina, which are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures without melting, cracking, or reacting with the molten metal. This ensures the purity of the final product.
The Refractory Lining: The Thermal Shield
Surrounding the crucible and protecting the coil is the furnace lining. This is a critical insulation layer.
It is typically constructed from advanced materials like alumina ceramic fiber and vacuum-formed fiber boards. These materials have poor heat conductivity, which keeps the intense heat focused on the metal and protects the structural components of the furnace from thermal damage.
The Essential Support Systems
While the coil and crucible perform the heating, several other systems are essential for the furnace to operate safely and effectively.
The Power Supply: The Electrical Heart
The induction process requires a specific type of electricity. The power supply unit takes standard grid power and converts it into the high-current, high-frequency alternating current needed by the coil.
This unit consists of a transformer, an inverter, and a capacitor bank that work together to deliver and control the energy flow.
The Cooling System: Preventing Meltdown
The same electrical resistance that melts metal inside the crucible also generates significant heat in the copper coil itself.
To prevent the coil from melting, a cooling system constantly circulates water through the hollow copper tubing. This is an absolutely critical safety and operational feature.
The Furnace Body and Control Systems
The entire assembly is held within a furnace body, often a heavy-duty steel frame, which provides structural support.
Finally, a process control system acts as the furnace's brain, allowing operators to manage power levels, monitor temperature, and ensure a safe, efficient melting cycle. Some furnaces also include fume extraction and vacuum systems depending on the application.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Selection is Key
The material choices in an induction furnace are a study in opposites. The goal is to maximize one physical property in one component while maximizing the opposite property in the component next to it.
The coil must be an excellent electrical conductor (copper) to create the magnetic field efficiently, but it must be kept cool.
The crucible and lining must be excellent thermal insulators and electrical insulators (refractories) to contain the heat and prevent the induced current from short-circuiting through the lining itself.
The specific type of refractory material chosen for the crucible is also critical. It must be chemically compatible with the metal being melted. Using the wrong lining can lead to contamination of the melt or rapid degradation of the crucible, causing operational failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the furnace's construction allows you to better understand its operation and requirements.
- If your primary focus is on the physics of operation: Recognize that the furnace works by pairing a conductive copper coil with an insulating refractory crucible to harness electromagnetic induction for heating.
- If your primary focus is on material processing: The choice of refractory for the crucible is your most critical decision, as it must withstand the target temperature and be chemically inert to the specific metal you are melting.
- If your primary focus is on safety and efficiency: Acknowledge that the cooling and power supply systems are non-negotiable; their performance dictates the furnace's reliability and prevents catastrophic coil failure.
By understanding what an induction furnace is made of, you can better appreciate the interplay of physics and material science that makes it such an efficient and clean melting technology.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Coil | High-purity copper tubing | Generates the electromagnetic field for heating |
| Crucible | High-temperature refractory (e.g., alumina) | Contains the molten metal, ensuring purity |
| Refractory Lining | Alumina ceramic fiber | Insulates and protects the furnace structure |
| Power Supply | Transformer, inverter, capacitor bank | Converts grid power to high-frequency AC |
| Cooling System | Water-cooled copper coil | Prevents overheating and ensures safe operation |
Ready to optimize your melting process with precision equipment? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnaces tailored to your specific material processing needs. Our experts can help you select the right refractory materials and system configuration for maximum efficiency and safety. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















