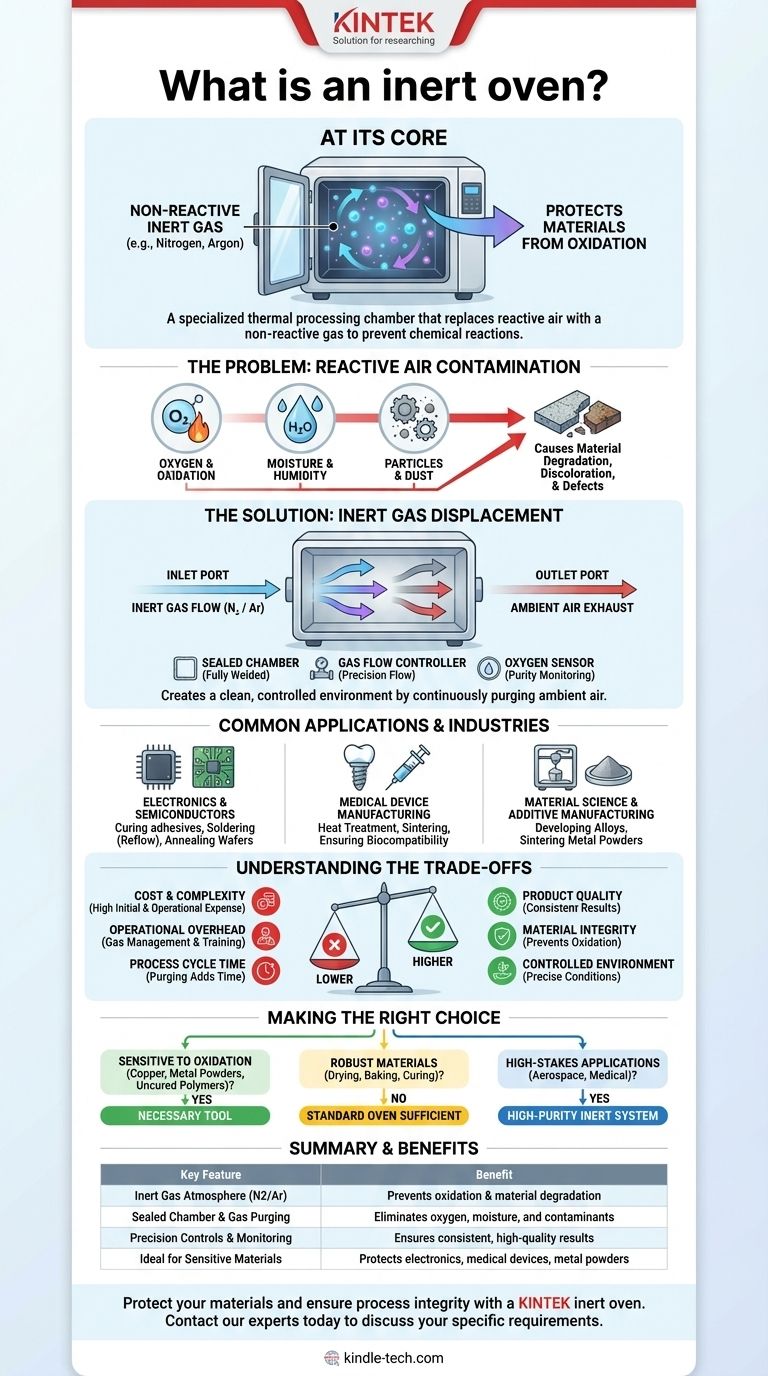
At its core, an inert oven is a specialized thermal processing chamber that replaces the reactive, oxygen-rich air inside with a non-reactive (inert) gas. This controlled atmosphere, typically nitrogen or argon, is essential for heating materials without causing undesirable chemical reactions like oxidation.
The fundamental purpose of an inert oven is not just to heat a product, but to protect it. By eliminating oxygen and moisture, it creates a stable environment that prevents material degradation, ensuring the integrity and quality of the final result.

The Problem: Why Air Is Often a Contaminant in Heating
To understand the value of an inert oven, you must first recognize that the air we use in standard ovens is a reactive mixture. Heat acts as a catalyst, accelerating these unwanted reactions.
The Role of Oxygen in Oxidation
Oxygen is highly reactive, especially at elevated temperatures. When you heat many materials in the presence of oxygen, you trigger oxidation.
This can manifest as visible changes, like the discoloration of metals or the charring of polymers, or as invisible but critical changes to the material's structural, chemical, or electrical properties.
The Impact of Ambient Moisture
Standard ambient air contains water vapor. For many processes, particularly in electronics or with hygroscopic (water-absorbing) materials, this moisture can interfere with curing, bonding, or lead to product defects and long-term reliability issues.
Contamination from Other Particles
Beyond oxygen and water, ambient air also contains dust and other microscopic airborne contaminants. In high-precision applications like semiconductor or medical device manufacturing, these particles can ruin a product.
How an Inert Oven Solves the Problem
An inert oven directly addresses these atmospheric issues by creating a precisely controlled, clean, and non-reactive environment.
The Principle of Gas Displacement
The core mechanism is simple: the oven chamber is sealed, and an inert gas is introduced through an inlet port. This incoming gas purges the chamber, pushing the ambient air out through an outlet port.
A continuous, low-pressure flow of the inert gas is often maintained throughout the heating cycle to ensure any residual oxygen or outgassed contaminants are immediately removed.
Common Inert Gases: Nitrogen and Argon
Nitrogen (N2) is the most common choice. It is relatively inexpensive (especially if using a nitrogen generator) and inert enough for a vast range of applications.
Argon (Ar) is used for processes requiring an even higher degree of inertness. It is denser than nitrogen and completely non-reactive, making it ideal for highly sensitive metals like titanium or for critical welding and additive manufacturing applications.
Key System Components
An inert oven is more than just a heated box with a gas hookup. Key components include a fully welded, sealed inner chamber to prevent leaks, precision gas flow controllers (flowmeters), and an oxygen sensor to monitor and verify the atmospheric purity inside the chamber.
Common Applications and Industries
The need to prevent oxidation during heating is critical across numerous advanced industries.
Electronics and Semiconductors
Inert ovens are essential for curing adhesives and encapsulants, soldering processes (reflow), and annealing wafers without oxidizing delicate circuits and components.
Medical Device Manufacturing
Materials used in medical implants and devices must have pristine surfaces and predictable properties. Inert atmospheres are used during heat treatment and sintering to prevent any surface oxidation that could affect biocompatibility or performance.
Material Science and Additive Manufacturing
Researchers use inert ovens to develop new alloys and polymers in a controlled environment. In metal 3D printing, an inert atmosphere is non-negotiable for sintering metal powders into a solid part without creating oxides that would compromise its structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an inert atmosphere is not always the necessary choice. Understanding the downsides is key to making an objective decision.
Cost and Complexity
Inert ovens are significantly more expensive than their standard counterparts due to the required sealing, control systems, and safety features. The ongoing cost of the inert gas supply is also a major operational expense.
Operational Overhead
Managing a gas supply, whether from high-pressure cylinders or a dedicated generator, adds logistical and safety complexity. Operators require specific training to handle the gas systems safely and effectively.
Process Cycle Time
Achieving a very low oxygen level (measured in parts per million, or PPM) requires a purging cycle before heating can begin. This can add significant time to the overall process, reducing throughput compared to a standard oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use an inert oven hinges entirely on the sensitivity of your material to the ambient atmosphere during heating.
- If your primary focus is processing materials sensitive to oxidation (e.g., copper, uncured polymers, metal powders): An inert atmosphere oven is a necessary tool to prevent product degradation and ensure quality.
- If your primary focus is simply drying, baking, or curing robust materials where surface oxidation is not a concern: A standard convection or gravity oven is the more cost-effective and simpler solution.
- If your primary focus is high-stakes applications requiring absolute control (e.g., aerospace alloys, medical implants): A high-purity inert gas system, likely using argon and equipped with real-time oxygen monitoring, is the required standard.
Ultimately, selecting an inert oven is a strategic decision to control the atmosphere, ensuring your thermal process yields the intended, uncompromised result.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Inert Gas Atmosphere (N2/Ar) | Prevents oxidation & material degradation |
| Sealed Chamber & Gas Purging | Eliminates oxygen, moisture, and contaminants |
| Precision Controls & Monitoring | Ensures consistent, high-quality results |
| Ideal for Sensitive Materials | Protects electronics, medical devices, and metal powders |
Protect your materials and ensure process integrity with a KINTEK inert oven.
Does your thermal process involve heat-sensitive materials like metals, polymers, or electronic components? Oxidation and contamination can ruin a product batch and compromise quality. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including reliable inert atmosphere ovens designed to create a pure, controlled environment for your most critical applications.
We provide solutions for industries such as electronics, medical device manufacturing, and additive manufacturing. Our ovens ensure your materials are heated without the damaging effects of oxygen, safeguarding your research and production outcomes.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how a KINTEK inert oven can enhance your lab's capabilities and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality



















