In essence, Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (APCVD) is a highly scalable manufacturing process used to grow large-area, single-layer graphene films. The method involves flowing a carbon-containing gas over a heated catalyst substrate, such as a copper foil, at standard atmospheric pressure. The high temperature causes the gas to decompose, depositing a one-atom-thick layer of carbon that self-assembles into graphene.
APCVD stands out as the most promising route for industrial-scale graphene production because it eliminates the need for expensive and complex vacuum systems. However, this operational simplicity introduces a critical trade-off between manufacturing cost and the ultimate control over material quality.
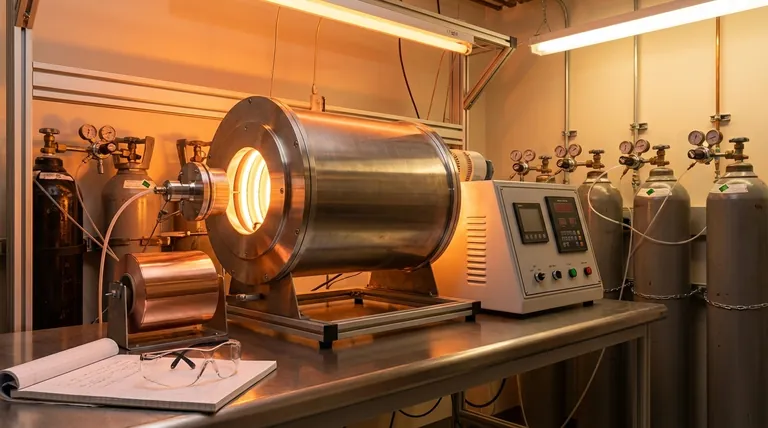

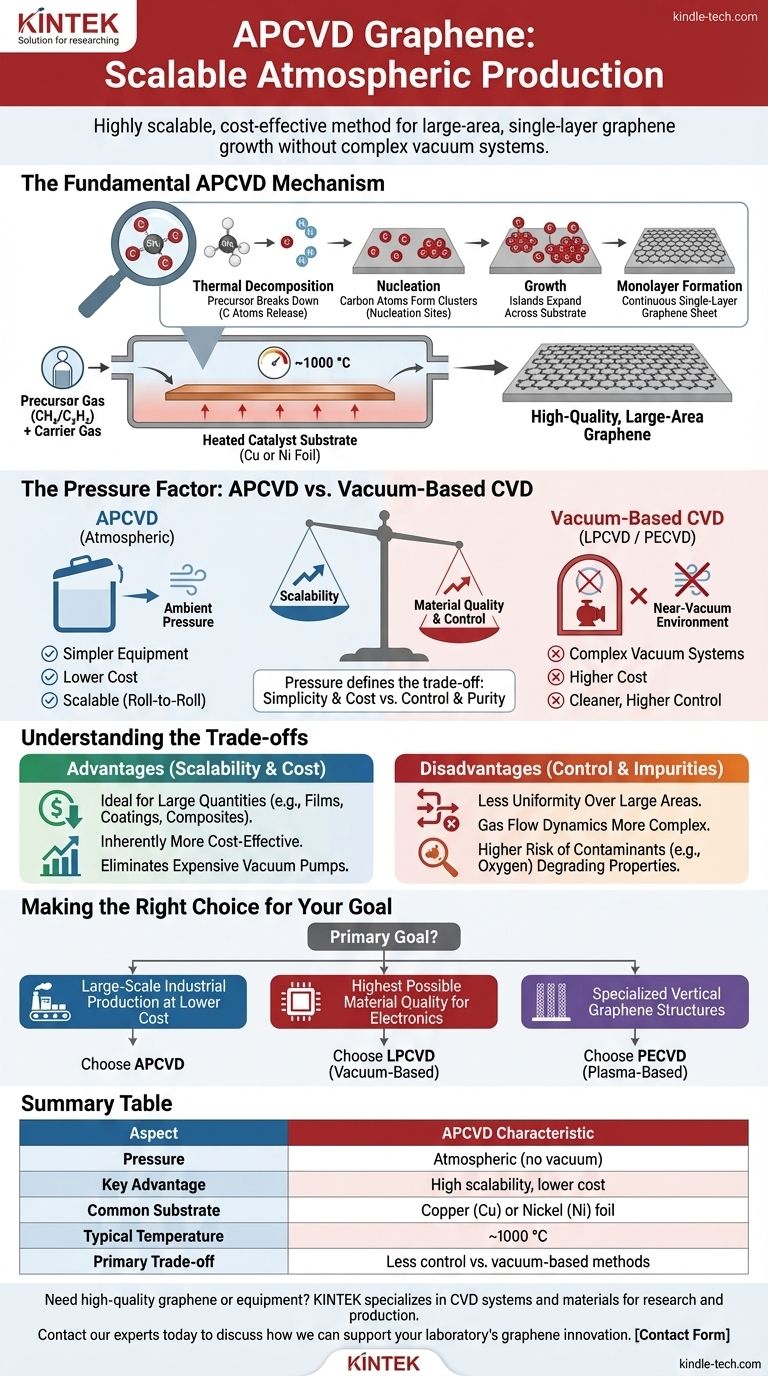
The Fundamental APCVD Mechanism
To understand APCVD, it's best to visualize it as a precise, high-temperature assembly process occurring on a metal surface. Each step is critical to forming a high-quality graphene sheet.
Introducing the Precursor
The process begins by feeding a carbon source, typically a hydrocarbon gas like methane (CH₄) or acetylene (C₂H₂), into a reaction chamber. This gas is mixed with inert carrier gases.
The Role of the Catalyst Substrate
Inside the chamber is a substrate, most commonly a thin foil of copper (Cu) or nickel (Ni). This metal acts as a catalyst, dramatically lowering the energy required for the chemical reactions to occur and providing the surface upon which the graphene will form.
Thermal Decomposition
The chamber is heated to extremely high temperatures, often around 1000 °C. This intense heat breaks down the precursor gas molecules into highly reactive carbon atoms or radicals.
Nucleation and Growth
These individual carbon atoms diffuse across the hot metal surface. They eventually collide and bond, forming small, stable hexagonal clusters. This initial formation is called nucleation.
These nucleation sites act as seeds. Additional carbon atoms arriving at the surface preferentially attach to the edges of these growing islands, causing them to expand across the substrate.
Forming the Monolayer
The process is carefully timed to stop once the individual graphene islands merge, forming a continuous, single-atom-thick sheet covering the entire surface of the catalyst. For metals with low carbon solubility like copper, the growth is self-limiting, naturally stopping after one complete layer is formed.
Why Pressure Is the Defining Factor
The "Atmospheric Pressure" in APCVD is its most significant feature, creating a distinct set of advantages and challenges compared to other CVD methods.
The Simplicity of Atmospheric Pressure
Operating at ambient pressure means the process does not require a sealed vacuum chamber or expensive, high-power vacuum pumps. This drastically simplifies the reactor design, reduces equipment cost, and makes it more suitable for a continuous, roll-to-roll style of industrial production.
The Contrast with Vacuum-Based CVD
Other common methods like Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) or Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) operate in a near-vacuum. Creating a vacuum removes ambient air and other potential gas contaminants, offering a much cleaner and more controllable growth environment.
This higher degree of control allows for the synthesis of higher-purity graphene with fewer defects, but it comes at the cost of significantly more complex and expensive equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a manufacturing process always involves balancing competing priorities. APCVD is no exception.
Advantage: Scalability and Lower Cost
By eliminating the need for vacuum systems, APCVD is inherently more scalable and cost-effective. This makes it the leading candidate for applications that require large quantities of graphene, such as transparent conductive films, composites, and coatings.
Disadvantage: Growth Control and Uniformity
The less controlled environment of APCVD can make it harder to achieve a perfectly uniform, defect-free monolayer over very large areas. The gas flow dynamics are more complex at atmospheric pressure, which can lead to variations in film thickness and quality.
Disadvantage: Potential for Impurities
Operating in an environment that is not a pure vacuum means there is a higher risk of contaminants (like oxygen) being incorporated into the graphene lattice. These impurities can degrade the material's exceptional electronic and mechanical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use APCVD or another synthesis method depends entirely on the requirements of the final application.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production at a lower cost: APCVD is often the most practical choice due to its simpler and more affordable equipment.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible material quality for advanced electronics: A vacuum-based method like LPCVD may be necessary to minimize defects and achieve superior electronic performance.
- If your primary focus is fabricating specialized vertical graphene structures: Plasma-based methods like PECVD are specifically designed for these unique morphologies and operate under different principles.
Ultimately, understanding the direct relationship between process pressure, cost, and material quality is the key to selecting the optimal graphene synthesis strategy for your project.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | APCVD Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Pressure | Atmospheric (no vacuum) |
| Key Advantage | High scalability, lower cost |
| Common Substrate | Copper (Cu) or Nickel (Ni) foil |
| Typical Temperature | ~1000 °C |
| Primary Trade-off | Less control vs. vacuum-based methods |
Need high-quality graphene for your project? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material synthesis, including CVD systems. Our expertise can help you select the right process—whether it's cost-effective APCVD or high-precision LPCVD—to meet your specific research or production goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's graphene innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis

















