In the simplest terms, biomass conversion efficiency is a measure of how effectively a system converts the chemical energy stored in raw organic material—like wood, crops, or waste—into a usable form of energy, such as electricity, heat, or fuel. It is the single most important metric for assessing the technical performance and economic viability of any biomass energy project, representing the ratio of energy output to the initial energy input.
The core challenge of biomass is not simply achieving the highest possible efficiency number. The 'best' conversion pathway is determined by a trade-off between the type of biomass feedstock you have and the specific form of energy you need to produce.
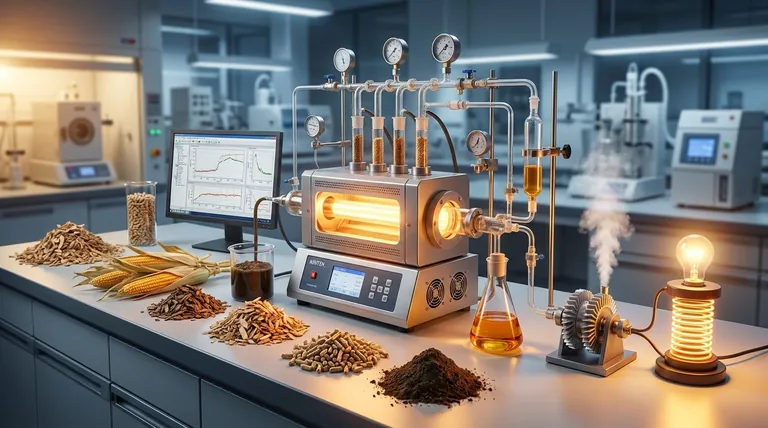

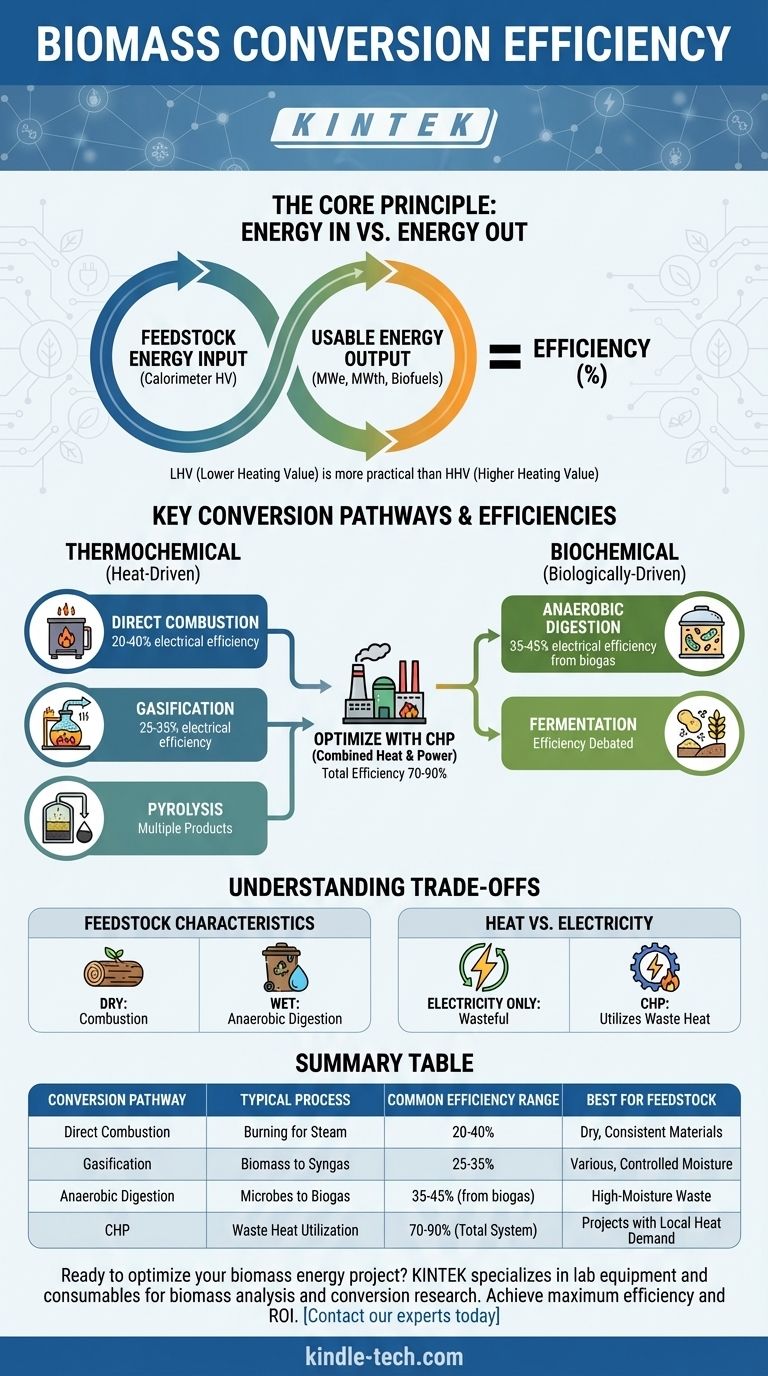
The Core Principle: Energy In vs. Energy Out
To properly evaluate any biomass system, you must have a clear and consistent understanding of how its efficiency is calculated. The calculation hinges on defining two key values: the usable energy produced and the potential energy of the initial feedstock.
The Numerator: Usable Energy Output
The "output" is the specific type of useful energy the system is designed to create. This is never a single, universal unit and must be clearly defined.
Common outputs include:
- Electricity: Measured in megawatt-electric (MWe).
- Heat: Measured in megawatt-thermal (MWth) for steam or hot water.
- Biofuels: Measured by the chemical energy content of the liquid or gas fuel produced (e.g., ethanol, biogas).
The Denominator: Feedstock Energy Input
The "input" is the total potential energy contained within the raw biomass before conversion. This is determined by burning a sample of the fuel in a calorimeter.
This value is typically expressed as a Heating Value (HV), but it's critical to know which one is being used:
- Higher Heating Value (HHV): Assumes all water vapor produced during combustion is condensed back to liquid, releasing its latent heat. This is the absolute total energy content.
- Lower Heating Value (LHV): Assumes the water vapor remains as a gas and exits the system, meaning its latent heat is not captured. LHV is a more realistic measure of a system's practical energy potential.
The Efficiency Formula
Once the input and output are defined in consistent units (like megajoules or BTUs), the formula is straightforward:
Efficiency (%) = (Usable Energy Output / Feedstock Energy Input) x 100
Key Conversion Pathways and Their Efficiencies
The efficiency you can expect is fundamentally tied to the technology you choose. Different conversion pathways are optimized for different feedstocks and energy products.
Thermochemical Conversion (Heat-Driven)
These methods use heat to break down biomass.
- Direct Combustion: This is the most established technology, involving burning biomass in a boiler to produce steam, which then drives a turbine to generate electricity. Electrical efficiencies typically range from 20% to 40%.
- Gasification: This process uses high temperatures with limited oxygen to convert biomass into a combustible gas called "syngas." This syngas can then be burned in a high-efficiency gas turbine. Electrical efficiencies are often in the 25% to 35% range.
- Pyrolysis: This involves heating biomass in the complete absence of oxygen to produce a liquid "bio-oil," solid "biochar," and syngas. Because it yields multiple products, a single efficiency number is less meaningful; instead, you analyze the energy distribution among the outputs.
Biochemical Conversion (Biologically-Driven)
These methods use microorganisms to digest biomass.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Microbes break down wet organic materials (e.g., manure, food waste, sewage sludge) without oxygen, producing a methane-rich "biogas." This biogas can then be burned to generate electricity and heat. Electrical efficiency from the resulting biogas is typically 35% to 45%.
- Fermentation: This process uses yeast to convert the sugars and starches in crops like corn and sugarcane into ethanol. The energy efficiency is highly debated and depends heavily on the energy used to grow and process the crop.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limiting Factors
A high efficiency number on paper means nothing without understanding the real-world constraints that govern a project's success.
Feedstock Characteristics Dominate
The single greatest factor influencing your choice of technology is the biomass itself.
- Moisture Content: Burning wet biomass is extremely inefficient, as a huge amount of energy is wasted boiling off water. For this reason, high-moisture feedstocks are ideal for anaerobic digestion, not combustion.
- Composition: The amount of lignin, cellulose, and sugars determines whether a feedstock is better suited for thermochemical or biochemical conversion.
The Heat vs. Electricity Dilemma
Generating only electricity is inherently wasteful. Due to thermodynamic limits (the Rankine cycle), a typical biomass power plant converts only a third of the fuel's energy into electricity, while the remaining two-thirds are lost as low-grade waste heat.
This is why Combined Heat and Power (CHP), or cogeneration, is critical. By capturing and using this waste heat for industrial processes or district heating, a CHP plant can achieve a total system efficiency of 70% to 90%, dramatically improving project economics.
Net Energy vs. Gross Efficiency
It is crucial to look beyond the simple conversion efficiency and consider the Energy Return on Investment (EROI). A system might convert biomass to ethanol efficiently, but if it required massive energy inputs for fertilization, harvesting, transport, and refining, its net energy gain could be small or even negative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
There is no single "best" biomass technology. Your selection must be guided by your primary objective and available resources.
- If your primary focus is grid-scale electricity generation: Focus on direct combustion or gasification using dry, consistent feedstock and aim for the largest scale possible to maximize thermodynamic efficiency.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste (e.g., municipal, agricultural): Anaerobic digestion is the most efficient and logical pathway to capture energy value and reduce waste volume.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid transportation fuels: Fermentation (for sugars/starches) or advanced pyrolysis/gasification-to-liquids (for woody biomass) are the necessary pathways, but be prepared for complex processing and careful net energy analysis.
- If your primary focus is maximizing overall energy use and economic return: Prioritize Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems that utilize the waste heat from electricity generation for a local thermal demand.
Understanding the context behind the efficiency number is the key to deploying successful and sustainable biomass energy systems.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Pathway | Typical Process | Common Efficiency Range | Best For Feedstock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Combustion | Burning biomass to create steam for electricity | 20% - 40% | Dry, consistent materials (wood chips, pellets) |
| Gasification | Converting biomass to syngas for power generation | 25% - 35% | Various biomass types with controlled moisture |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Microbes breaking down wet waste to produce biogas | 35% - 45% (electrical from biogas) | High-moisture waste (manure, food waste) |
| Combined Heat & Power (CHP) | Utilizing waste heat from electricity generation | 70% - 90% (total system efficiency) | Projects with local heat demand |
Ready to optimize your biomass energy project? The team at KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for biomass analysis and conversion research. Whether you're testing feedstock energy content, optimizing conversion processes, or scaling up your bioenergy production, our precise instruments help you achieve maximum efficiency and ROI. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's biomass conversion goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating

















