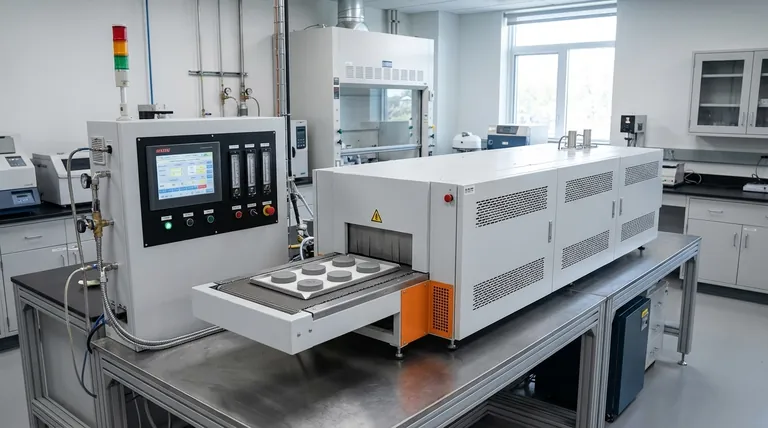
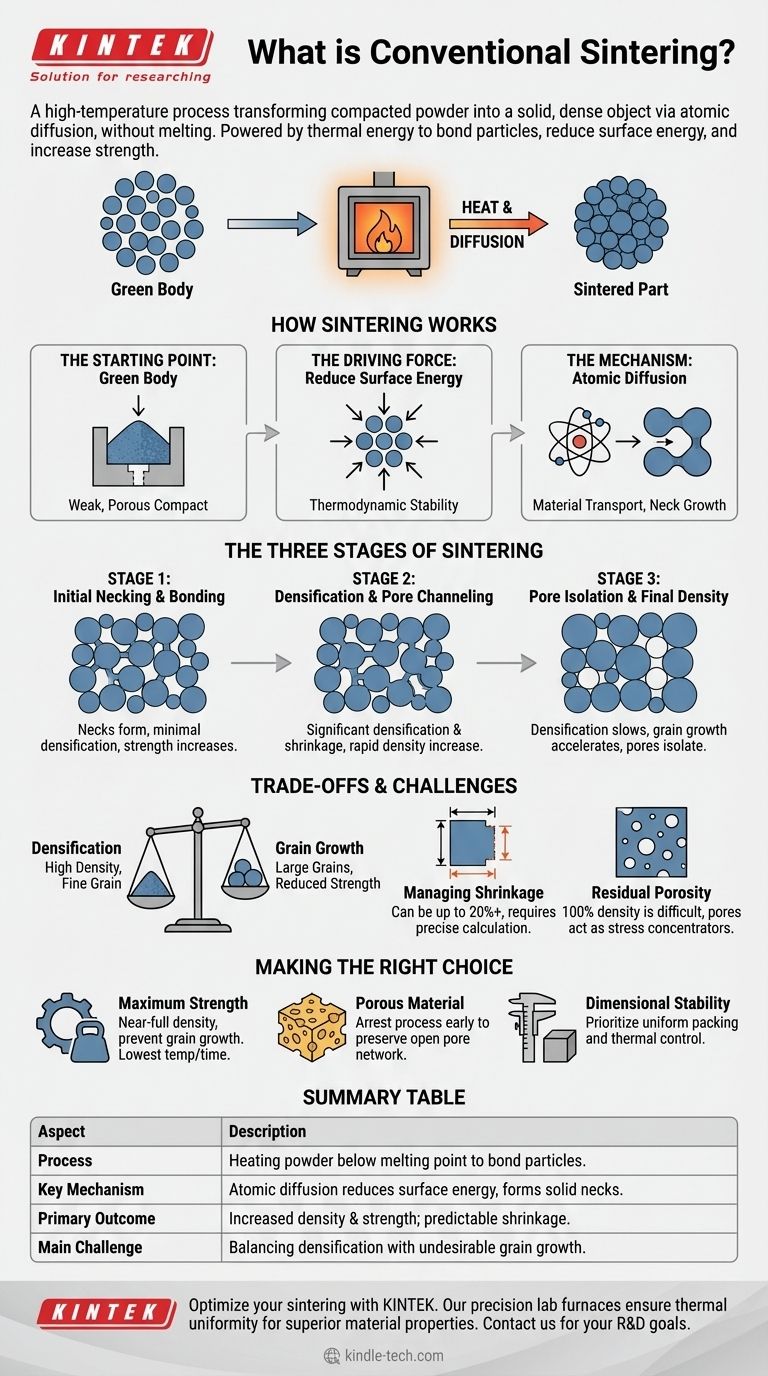
In essence, conventional sintering is a high-temperature process used to transform a compacted powder into a solid, dense object without melting it. By heating a "green body" (a weakly bound powder compact) to a specific temperature, the individual particles fuse together, reducing porosity and dramatically increasing the material's strength and density.
The core principle of conventional sintering is using thermal energy to drive atomic diffusion. This process bonds particles together, minimizes surface energy, and shrinks the component, effectively turning a fragile powder shape into a robust, engineered material.

How Sintering Transforms Powder into a Solid
Conventional sintering is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy and ceramic processing. It works by fundamentally changing the structure of a material on a microscopic level, driven by thermodynamics.
The Starting Point: The "Green Body"
The process begins with a powder compact, often called a green body. This is the desired shape formed by pressing powders into a mold.
While it has shape, the green body is mechanically weak and full of empty space, or porosity, between the particles.
The Driving Force: Reducing Surface Energy
Fine powders possess a vast amount of surface area, which is an energetically unstable state. Nature always seeks the lowest energy state.
Sintering provides the thermal energy needed for the system to reduce its total surface area by bonding the particles together and eliminating the pores between them. This reduction in energy is the fundamental driving force of the process.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
Sintering occurs at temperatures below the material's melting point. Instead of melting and flowing, atoms migrate and move across the surfaces and through the bulk of the particles.
This atomic diffusion allows material to move to the contact points between particles, forming and growing "necks." These necks are the solid bridges that bond the particles, creating a strong, coherent mass.
The Three Stages of Sintering
The transformation from a powder compact to a dense solid typically follows three distinct, overlapping stages.
Stage 1: Initial Necking and Bonding
At the beginning of the process, necks form and grow at the contact points between adjacent particles.
During this stage, the overall densification is minimal, but the component gains significant strength as the particles become chemically bonded. The porosity remains largely interconnected.
Stage 2: Densification and Pore Channeling
As the necks between particles grow larger, they begin to merge. The pores form a network of interconnected, cylindrical channels.
This is the stage where most of the densification and shrinkage occurs. The object visibly shrinks as the pores are eliminated and the density rapidly increases.
Stage 3: Pore Isolation and Final Density
In the final stage, the pore channels pinch off and become isolated, spherical voids within the material.
Densification slows down dramatically, as it is now much more difficult for the remaining porosity to be removed. At the same time, grain growth (the coarsening of the material's crystal structure) can accelerate, which is often undesirable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, conventional sintering is a balancing act. Achieving the desired outcome requires managing several competing factors.
The Core Conflict: Densification vs. Grain Growth
This is the primary challenge in sintering. The same conditions that promote densification (high temperature, long time) also promote grain growth.
For most structural applications, the ideal material has maximum density and a very fine grain structure. Over-sintering can lead to large grains, which often reduces the material's strength and toughness, even if its density is high.
Managing Shrinkage
Because sintering removes porosity, the component will shrink. This shrinkage can be substantial (up to 20% or more in linear dimensions) and must be precisely calculated and compensated for when designing the initial mold and green body.
Non-uniform shrinkage can lead to warping or cracking, making process control essential for producing dimensionally accurate parts.
The Problem of Residual Porosity
Achieving 100% theoretical density is extremely difficult with conventional sintering. Small amounts of residual porosity are almost always present.
These pores can act as stress concentration sites, limiting the ultimate mechanical performance of the final component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles of sintering allows you to manipulate the process to achieve specific material properties.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength: Your goal is to achieve near-full density while rigorously preventing grain growth, often by using the lowest possible temperature and time that still achieves densification.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous material (e.g., a filter): You should arrest the sintering process in the initial or intermediate stage to preserve an open, interconnected network of pores while still providing sufficient strength.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability: You must prioritize uniform powder packing and precise thermal control to ensure predictable and consistent shrinkage throughout the part.
Mastering these variables is the key to transforming simple powders into highly engineered materials with tailored properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating powder compact below melting point to bond particles. |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion reduces surface energy, forming solid necks. |
| Primary Outcome | Increased density and strength; significant, predictable shrinkage. |
| Main Challenge | Balancing densification with undesirable grain growth. |
Ready to optimize your sintering process for superior material properties? KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and consumables essential for controlled sintering. Whether you're developing advanced ceramics or metal parts, our equipment ensures the thermal uniformity and control needed to achieve your target density and microstructure. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering and materials development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an atmosphere furnace ensure quality in BN nanotube synthesis? Precision Control for Cup-Stacked Structures
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere furnace essential for high-nickel cathode sintering? Unlock Battery Performance
- Why Use Ultra-High Vacuum Furnaces for LLZO? Ensure Chemical Stability & Interface Integrity in Solid Electrolytes
- Why is a horizontal tube furnace with a H2-N2 atmosphere used for NiO pre-treatment? Key to Catalyst Activation
- What are the main components of an industrial furnace? Explore Essential Elements for Precision Heating



















