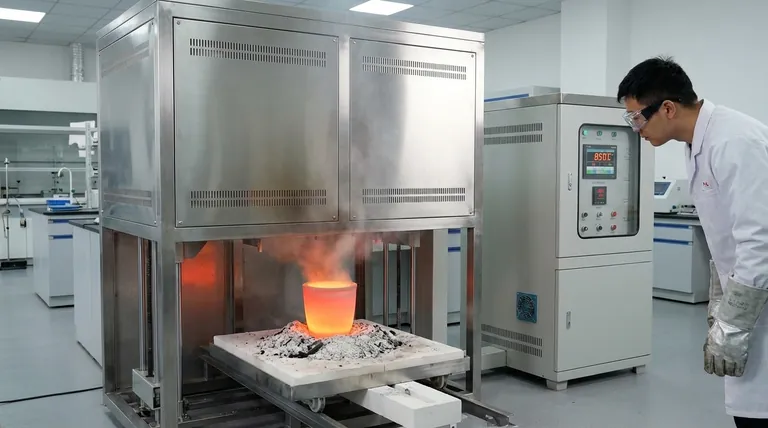
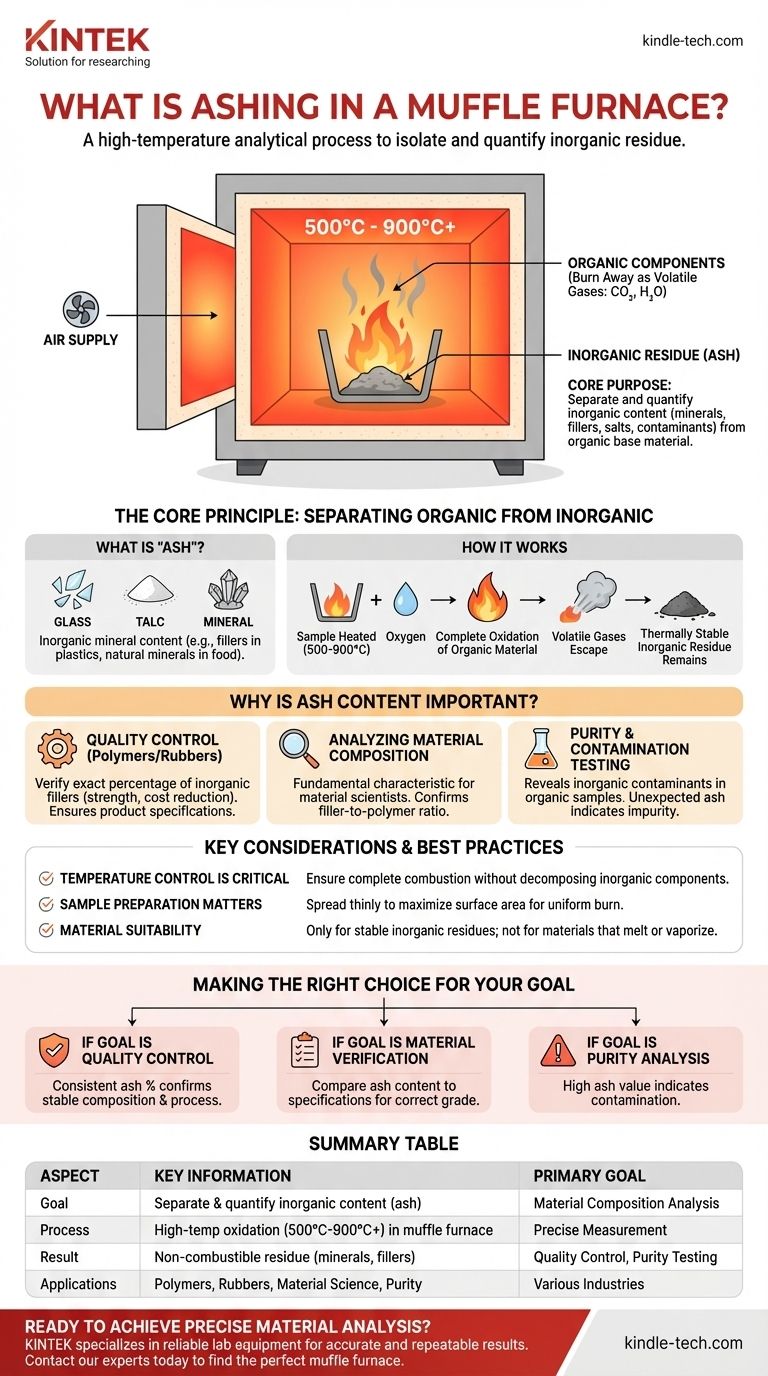
Ashing in a muffle furnace is a high-temperature analytical process used to completely burn away the organic components of a sample. This is done in order to isolate and measure the weight of the remaining non-combustible, inorganic residue, which is known as ash.
The core purpose of ashing is to separate and quantify the inorganic content (like mineral fillers, salts, or metallic contaminants) from the organic base material. This provides a clear, quantitative measure of a material's composition.

The Core Principle: Separating Organic from Inorganic
Ashing operates on the simple principle that organic and inorganic materials behave very differently at high temperatures. The muffle furnace provides the extreme, controlled heat necessary to exploit this difference.
What is "Ash"?
In this context, ash is not simply burnt residue. It refers specifically to the inorganic mineral content within a sample. This can include fillers like glass, talc, or calcium carbonate in plastics, or naturally occurring minerals in food products.
How a Muffle Furnace Achieves This
A muffle furnace heats the sample to temperatures typically ranging from 500°C to over 900°C in the presence of air. This extreme heat and oxygen supply cause the complete oxidation (combustion) of the organic, carbon-based material, converting it into volatile gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, which then leave the sample.
The End Result
Because the inorganic components are thermally stable and non-volatile at these temperatures, they remain behind in the crucible after all organic matter has been burned away. The weight of this remaining ash can be precisely measured.
Why is Ash Content Important?
Determining the ash content is a critical step in quality control and material analysis across many industries. The percentage of ash provides vital information about the sample's composition and purity.
Quality Control for Polymers and Rubbers
In the manufacturing of polymers, plastics, and rubbers, inorganic fillers are often added to enhance properties like strength, rigidity, or to reduce cost. Ashing is performed to verify the exact percentage of this filler, ensuring the final product meets its required specifications.
Analyzing Material Composition
For material scientists, the ash percentage is a fundamental characteristic of a material. It helps identify a material or confirm that the ratio of inorganic filler to organic polymer is correct according to a specific formulation.
Purity and Contamination Testing
A sample that is supposed to be purely organic should theoretically have zero ash content. Performing an ash test can quickly reveal the presence of any inorganic contaminants or impurities.
Key Considerations and Best Practices
Achieving accurate and repeatable results requires careful attention to the process. The goal is to remove all organic material without altering the inorganic residue.
Temperature Control is Critical
The selected temperature must be high enough to ensure complete combustion of all organic matter but not so high that it causes some of the inorganic components to decompose or vaporize, which would lead to inaccurate, lower-than-expected results.
Sample Preparation Matters
As noted in best practices, the sample should be spread thinly in its crucible or porcelain boat. This maximizes the surface area exposed to heat and oxygen, ensuring a uniform and complete burn. A thick, dense sample may form a charred outer layer that prevents the interior from fully combusting.
Material Suitability
The ashing method is only suitable for materials where the inorganic components are stable at the high temperatures used. It cannot be used if the inorganic residue would melt, react, or vaporize, as this would make an accurate final weight measurement impossible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The data from an ashing test is interpreted based on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control: A consistent ash percentage from batch to batch confirms that your material composition and manufacturing process are stable.
- If your primary focus is material verification: The resulting ash content can be compared against a known specification to confirm you have the correct grade of material.
- If your primary focus is purity analysis: An unexpectedly high ash value is a clear indicator of inorganic contamination within your raw or finished material.
Ultimately, ashing provides an essential and definitive measure of a material's inorganic composition.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | To separate and quantify inorganic content (ash) from an organic base material. |
| Process | High-temperature oxidation (500°C - 900°C+) in a muffle furnace. |
| Result | Precise measurement of non-combustible residue (minerals, fillers, contaminants). |
| Common Applications | Quality control for polymers/rubbers, material composition analysis, purity testing. |
Ready to achieve precise material analysis in your lab?
Ashing is a fundamental process for quality control and material verification. KINTEK specializes in providing the reliable lab equipment and consumables you need to ensure accurate and repeatable results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace and accessories for your specific application. Let us help you enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of sintering? A Guide to High-Performance Manufacturing
- What is the hottest temperature a furnace can be? Exploring Limits from 3,000°C+ to Your Application
- How hot can metal get? From Melting Points to Plasma Temperatures
- What are the four steps to the heat treating process? Master the 3 Core Stages for Superior Results
- Does heating metal make it weaker? Mastering Heat Treatment for Optimal Metal Strength



















