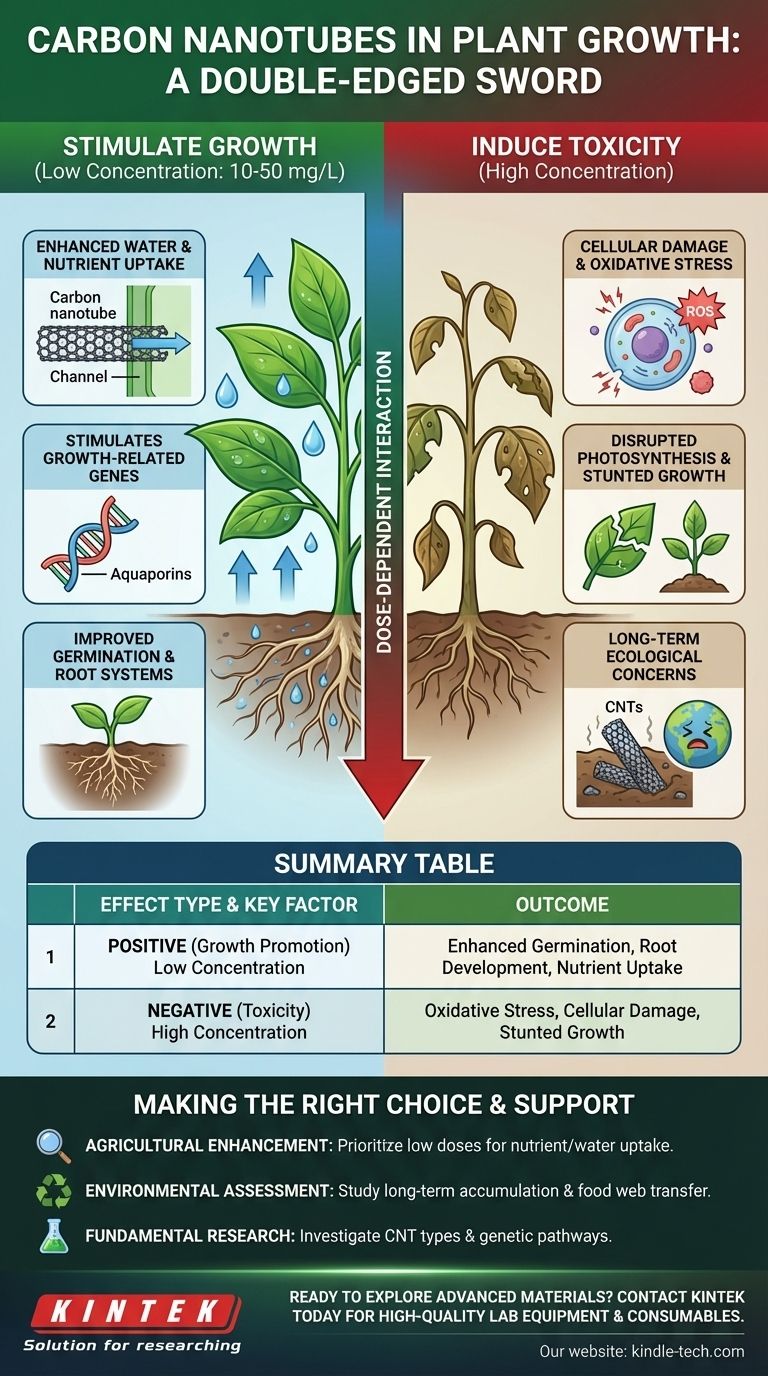
The effect of carbon nanotubes on plant growth is remarkably dual-natured. At low, controlled concentrations, certain types of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) can significantly enhance seed germination, root development, and overall plant biomass. However, these benefits quickly disappear and turn into toxic effects as the concentration increases, making the dose the single most critical factor in determining the outcome.
The interaction between carbon nanotubes and plants is a double-edged sword. While they can act as "nano-fertilizers" by improving water and nutrient uptake at the cellular level, their concentration and chemical properties ultimately determine whether they stimulate growth or induce toxicity.
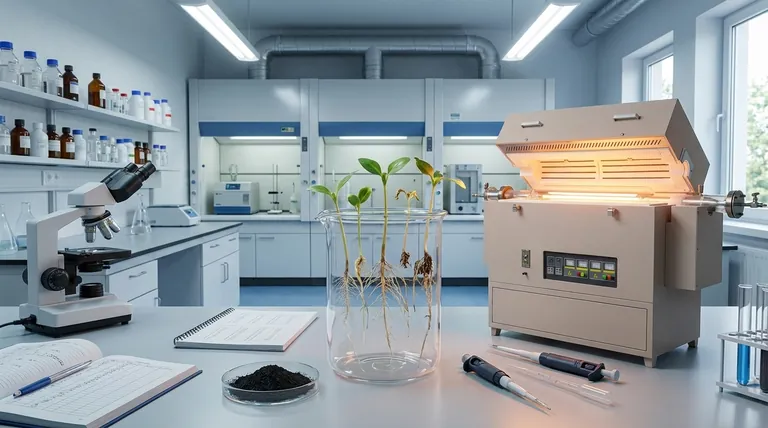

How Carbon Nanotubes Can Stimulate Growth
The positive effects of CNTs are primarily linked to their unique physical ability to interact with plants at a microscopic level. They are not a nutrient source themselves, but rather a facilitator of biological processes.
Enhancing Water and Nutrient Uptake
Carbon nanotubes possess the ability to penetrate the tough outer layer of seeds and plant cell walls.
By piercing these barriers, they can create new, nano-sized channels. These new pathways can significantly improve the transport of water and essential nutrients into the seed and root cells, accelerating growth.
Stimulating Growth-Related Genes
Research has shown that the presence of CNTs can activate or "upregulate" specific genes within the plant.
These are often genes responsible for cell division and water transport, such as aquaporins. This genetic stimulation provides a direct boost to the plant's foundational growth mechanisms.
Improving Germination and Root Systems
The combination of better water absorption and genetic stimulation leads to tangible results.
Seeds treated with low doses of CNTs often show faster germination rates and develop more robust root systems. A stronger root network is critical for the long-term health and yield of the plant.
Understanding the Risks and Trade-offs
The potential benefits of carbon nanotubes are matched by significant risks. Understanding these limitations is essential for any practical or research application.
The Critical Role of Concentration
This is the most important variable. The growth-promoting effects of CNTs are observed only at very low concentrations (typically in the range of 10 to 50 milligrams per liter).
Once the concentration exceeds a certain threshold, the effect reverses. The CNTs begin to inhibit growth and cause cellular damage, a phenomenon known as phytotoxicity.
Potential for Cellular Damage
At high concentrations, CNTs induce oxidative stress in plant cells.
This process generates harmful molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage cell membranes, disrupt photosynthesis, and ultimately lead to cell death and stunted growth.
Long-Term Ecological Concerns
The widespread application of CNTs in agriculture raises valid environmental questions.
Because they are highly stable, carbon nanotubes can accumulate in soil over time. The long-term impact of this accumulation on soil health, microorganisms, and the broader food web is still an area of active and necessary research.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Navigating the use of carbon nanotubes requires a clear understanding of your specific objective and a commitment to methodical testing.
- If your primary focus is agricultural enhancement: Prioritize using very low, carefully measured concentrations of well-characterized CNTs to explore benefits in nutrient and water uptake.
- If your primary focus is environmental risk assessment: Focus on studying the long-term accumulation of CNTs in soil and their potential transfer through the food web, especially at higher concentrations.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Investigate how different types of CNTs (e.g., single-walled vs. multi-walled) and surface modifications interact with the genetic pathways of specific plant species.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of nanotechnology for agriculture depends on a precise, dose-dependent approach that balances growth promotion with ecological responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Effect Type | Key Factor | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Positive (Growth Promotion) | Low Concentration (e.g., 10-50 mg/L) | Enhanced seed germination, root development, and nutrient uptake. |
| Negative (Toxicity) | High Concentration | Induces oxidative stress, cellular damage, and stunted growth. |
Ready to explore advanced materials for your agricultural or environmental research? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables to support your work with nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes. Whether you're studying their growth-promoting effects or assessing environmental risks, our reliable tools ensure precise, reproducible results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your lab for success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Conductive Carbon Fiber Brush for Static Removal and Cleaning
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What is a multi-position furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Flexible HVAC Installation
- What are the typical heating zone configurations and maximum temperature capabilities of tube furnaces? Find the Right Setup for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency
- What is a three zone furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Uniformity
- How does a multi-heating zone horizontal tube furnace benefit alloy testing? Maximize Thermal Uniformity and Throughput



















