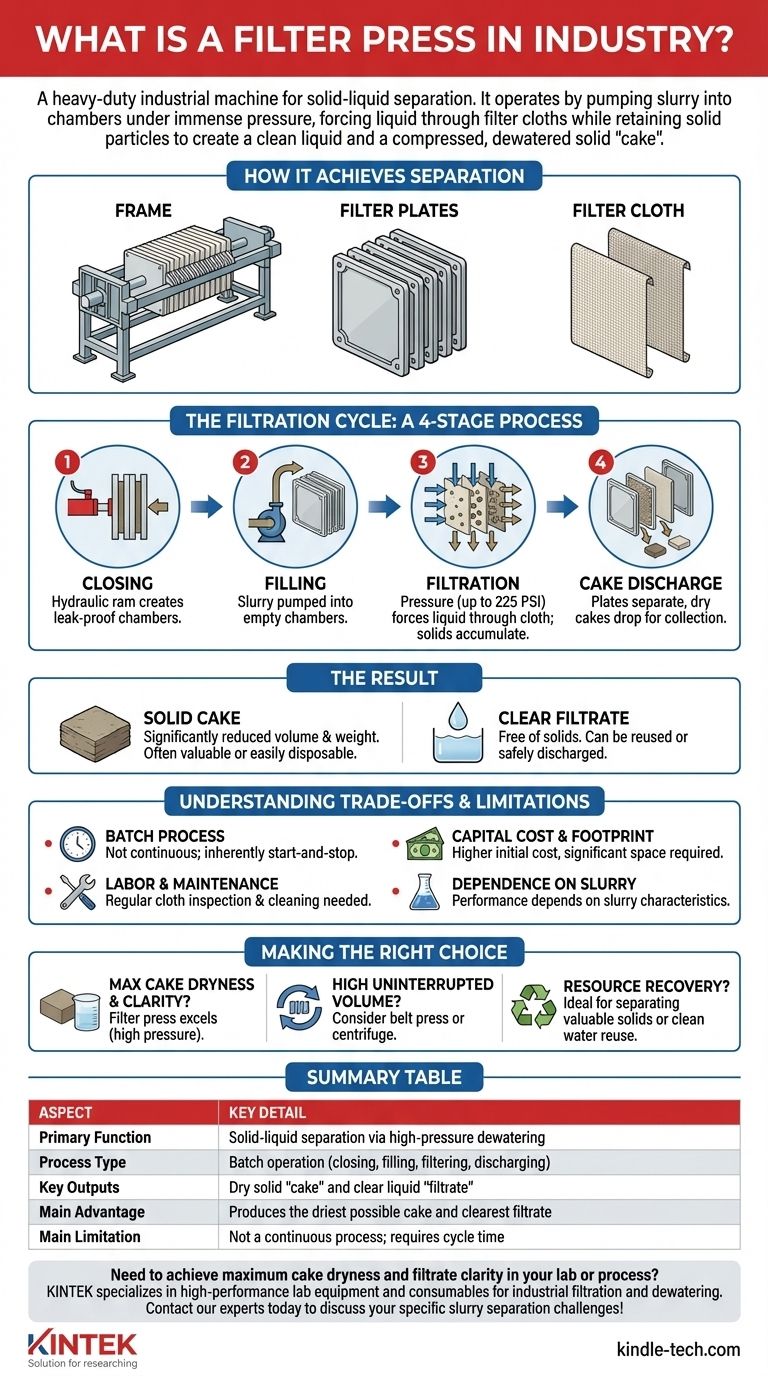
At its core, a filter press is a heavy-duty piece of industrial machinery designed for solid-liquid separation. It operates by pumping a slurry (a semi-liquid mixture) into a series of chambers and applying immense pressure, which forces the liquid out through filter cloths while retaining the solid particles. The result is a clean liquid stream and a compressed, dewatered solid "cake."
A filter press is not simply a filter; it is a high-pressure dewatering system. Its primary purpose is to transform a large volume of liquid waste or process slurry into two manageable components: a compact, dry solid and a clear liquid, drastically reducing disposal costs and enabling resource recovery.

How a Filter Press Achieves Separation
Understanding a filter press is best done by looking at its core components and the distinct phases of its operational cycle. It is a deceptively simple yet powerful mechanical process.
The Core Components: Frame, Plates, and Cloth
A filter press is built around three key elements. The frame is the steel skeleton that holds everything together and houses the powerful hydraulic system used for closing.
The filter plates are the heart of the machine. These square or rectangular plates are lined up along the frame, and when pressed together, they form a series of sealed chambers.
On each plate is a filter cloth, which is the actual filtering medium. This woven fabric is chosen specifically for the particle size and chemistry of the slurry being processed.
The Filtration Cycle: A Step-by-Step Process
The operation follows a clear, four-stage cycle.
- Closing: A hydraulic ram presses the stack of filter plates together with immense force, creating a leak-proof series of chambers.
- Filling: The slurry is pumped into the press, filling all the empty chambers between the plates.
- Filtration: As pumping continues, pressure builds inside the chambers (often to 225 PSI or higher). This pressure forces the liquid component of the slurry through the filter cloth, leaving the solid particles behind. The solids accumulate and compress, forming a dense cake.
- Cake Discharge: Once the chambers are full of solids and liquid flow stops, the press is opened. The plates separate, allowing the dry, solid cakes to drop out for collection.
The Result: Solid Cake and Clear Filtrate
The process yields two distinct outputs. The solid filter cake is significantly reduced in volume and weight compared to the original slurry, making disposal far cheaper and easier. In many cases, the cake itself is a valuable product or can be further processed.
The liquid that passes through the cloths, known as the filtrate, is now free of solids. This clear liquid can often be reused in the plant, saving water, or safely discharged in compliance with environmental regulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, the filter press is not a universal solution. Its strengths are balanced by specific operational characteristics that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
It's a Batch Process, Not Continuous
This is the most significant trade-off. The cycle of closing, filling, filtering, and discharging takes time. This means the process is inherently start-and-stop, which can be a bottleneck compared to continuous systems like a belt press or centrifuge.
Labor and Maintenance Requirements
While modern presses are highly automated, they are not "set-it-and-forget-it" machines. The filter cloths are the most critical component and require regular inspection and cleaning to prevent "blinding" (clogging), which reduces efficiency. Eventually, they wear out and must be replaced.
Capital Cost and Footprint
Filter presses are heavy, robust, and precisely engineered pieces of equipment. Their initial capital cost can be higher than some alternative dewatering technologies. They also require a significant physical footprint, including the area below the press for cake discharge and collection.
Dependence on Slurry Consistency
The performance of a filter press is highly dependent on the characteristics of the slurry being processed. Factors like particle size distribution, concentration, and compressibility directly impact the cycle time, cake dryness, and filtrate clarity. Pilot testing is almost always required to size and configure a press correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a dewatering technology requires a clear understanding of your primary objective. A filter press excels in specific scenarios where its unique advantages outweigh its limitations.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible cake dryness and filtrate clarity: The high-pressure operation of a filter press makes it the superior choice, often producing a stackable, non-drip cake that no other technology can match.
- If your primary focus is processing a very high, uninterrupted volume of slurry: A continuous system like a belt press or centrifuge may be a better fit, even if it results in a wetter solid output.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery: A filter press is ideal for separating a valuable solid from a liquid or for producing clean process water for immediate reuse in your facility.
By understanding the filter press as a powerful tool for high-pressure, batch-based dewatering, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific operational and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Solid-liquid separation via high-pressure dewatering |
| Process Type | Batch operation (closing, filling, filtering, discharging) |
| Key Outputs | Dry solid "cake" and clear liquid "filtrate" |
| Main Advantage | Produces the driest possible cake and clearest filtrate |
| Main Limitation | Not a continuous process; requires cycle time |
Need to achieve maximum cake dryness and filtrate clarity in your lab or process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for industrial filtration and dewatering. Our expertise can help you select the right system to reduce disposal costs, recover valuable materials, and meet environmental standards. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific slurry separation challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the KBr method? A Guide to FTIR Sample Prep for Solid Materials
- Is lab-grown diamond business profitable? Navigate Falling Prices & Build a Profitable Brand
- What is bio-oil composed of? The Complex Chemistry of a Sustainable Fuel
- What is evaporation in thin film technology? A Guide to Core PVD Fabrication Methods
- What function does a precision heating device serve for Li-Si-N composite melts? Master Thermal Synthesis at 250°C
- Why is deposition technology an amazing scientific advancement? Unlock Atomic-Level Material Engineering
- What is the process of sputtering silicon? A Step-by-Step Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is a sputter coater? A Guide to High-Precision Thin Film Deposition



















