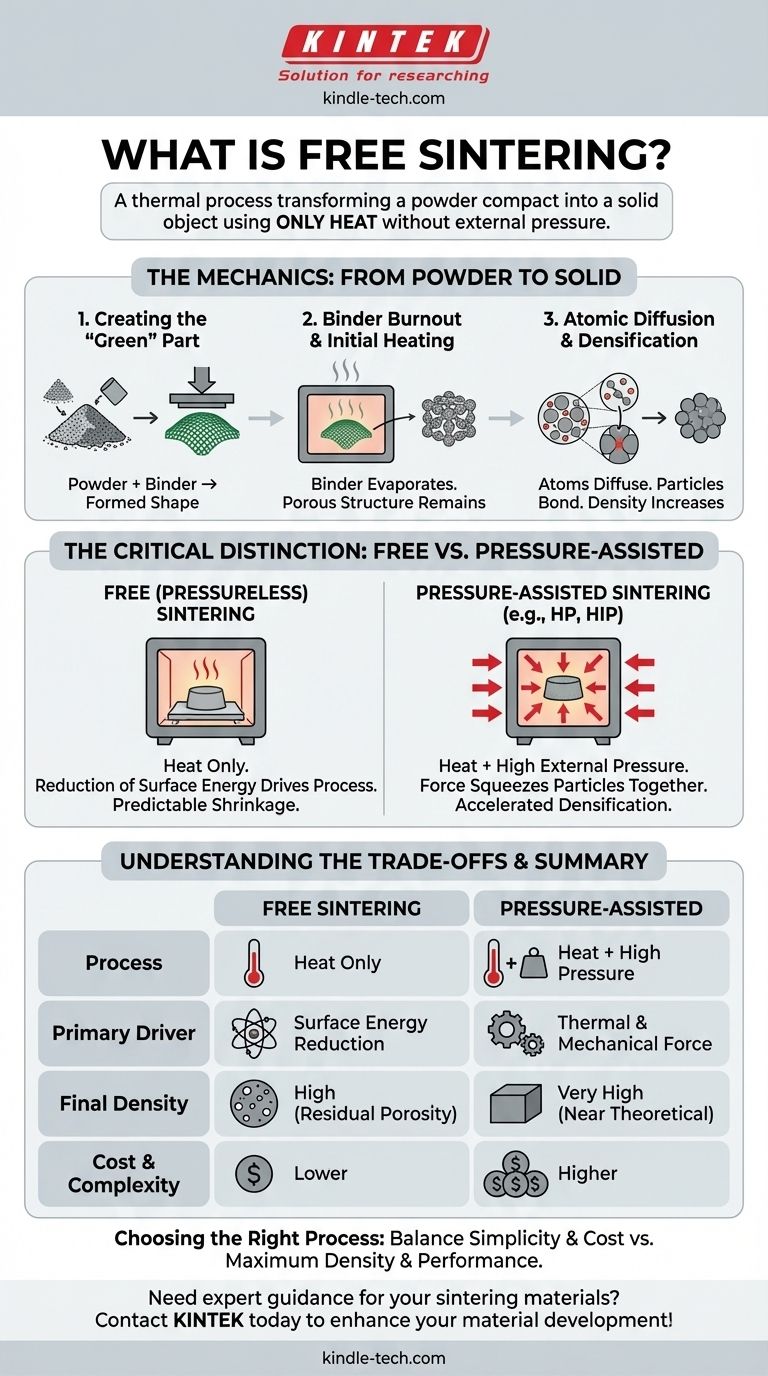
At its core, free sintering is a thermal process used to transform a powder compact into a solid object without applying any external pressure during heating. Also known as pressureless sintering, the part is "free" to shrink and densify on its own in a furnace, driven purely by the reduction of surface energy. This contrasts with methods like hot pressing, where heat and high pressure are applied simultaneously to force the material together.
The term "free" is the critical distinction. It separates this common and cost-effective method from pressure-assisted techniques, highlighting that consolidation is achieved through temperature and time alone, not external force.

The Mechanics of Sintering: From Powder to Solid
To understand what makes free sintering unique, we must first understand the fundamental stages of any sintering process. The goal is to bond particles together to reduce porosity and create a dense, solid component.
Stage 1: Creating the "Green" Part
The process begins with a powder, which can be metal, ceramic, or plastic. This powder is often mixed with a temporary binder (like a wax or polymer) to give it handling strength.
This mixture is then formed into the desired net shape, known as a "green" part. This can be done through various methods, including pressing, injection molding, slip casting, or additive manufacturing (3D printing).
Stage 2: Binder Burnout and Initial Heating
The green part is placed in a furnace. In the initial heating phase, the binder material is carefully burned or evaporated away, leaving behind a fragile, porous structure of the primary powder.
Stage 3: Atomic Diffusion and Densification
As the temperature rises further—approaching, but not reaching, the material's melting point—atoms on the surfaces of the particles become highly mobile.
Driven by a thermodynamic need to lower the object's total surface energy, atoms diffuse across the points of contact between particles. This process forms and grows "necks" between adjacent particles, gradually eliminating the pore spaces between them and causing the entire component to shrink and become more dense.
The Critical Distinction: Free vs. Pressure-Assisted
The term "free sintering" exists to differentiate the process from its high-performance alternative. The key difference is the role of external pressure.
Defining Free (Pressureless) Sintering
In free sintering, the green part is simply set on a tray inside a furnace with a controlled atmosphere. The densification process, as described above, occurs solely due to thermal energy and the material's natural tendency to minimize its surface area.
The component is dimensionally unconstrained and shrinks in a predictable (though not always perfectly uniform) way.
The Alternative: Pressure-Assisted Sintering
In contrast, methods like Hot Pressing (HP) or Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) apply immense external pressure to the component during the heating cycle.
This external force actively squeezes particles together, helping to collapse pores that might otherwise remain. This mechanical assistance accelerates densification and allows the part to reach a higher final density.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between free and pressure-assisted sintering is a classic engineering trade-off between cost, complexity, and final performance.
The Advantages of Free Sintering
The primary advantage of free sintering is its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. The furnace equipment does not need to contain and apply high pressures, making it less expensive and more scalable for high-volume production.
It is also ideal for producing components with highly complex geometries, such as those made by 3D printing, which would be difficult or impossible to press in a die.
The Limitations of Free Sintering
The main drawback is that it can be difficult to achieve full (100%) density. Some residual porosity often remains, which can compromise the material's ultimate mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and fatigue life.
For certain advanced ceramics or high-performance alloys, free sintering may not provide sufficient driving force to achieve the required density in a reasonable amount of time.
When Pressure-Assisted Sintering is Necessary
Pressure-assisted methods are reserved for critical applications where maximum density and superior material properties are non-negotiable. This includes aerospace components, medical implants, and high-performance cutting tools where any residual porosity could lead to failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use free sintering depends entirely on the requirements of the final part.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and shape complexity: Free sintering is almost always the correct and most economical choice for a wide range of industrial and commercial parts.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density for peak mechanical performance: Pressure-assisted sintering is the necessary, albeit more expensive, path for mission-critical applications.
- If you are developing a new material or alloy: Free sintering is an excellent starting point, but pressure may be required if the material proves difficult to densify through heat alone.
Ultimately, understanding free sintering is to understand the fundamental balance between process simplicity and the pursuit of material perfection.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Free Sintering | Pressure-Assisted Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heat only, no external pressure | Heat + high external pressure |
| Primary Driver | Reduction of surface energy | Combined thermal and mechanical force |
| Final Density | High, but may have residual porosity | Very high, near theoretical density |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler equipment | Higher cost, more complex equipment |
| Ideal For | Cost-effective, complex geometries | Mission-critical, high-performance parts |
Need to choose the right sintering process for your lab's materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing the expertise and solutions to help you achieve optimal results. Whether you're developing a new alloy or producing complex components, our team can guide you to the most efficient and effective sintering method.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs and enhance your material development process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution



















