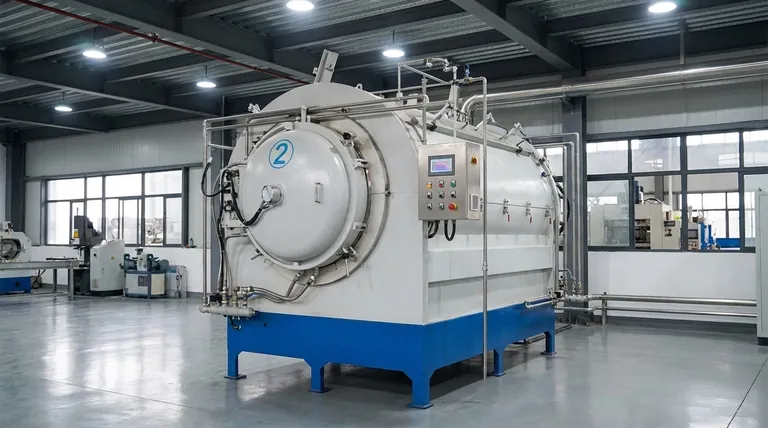
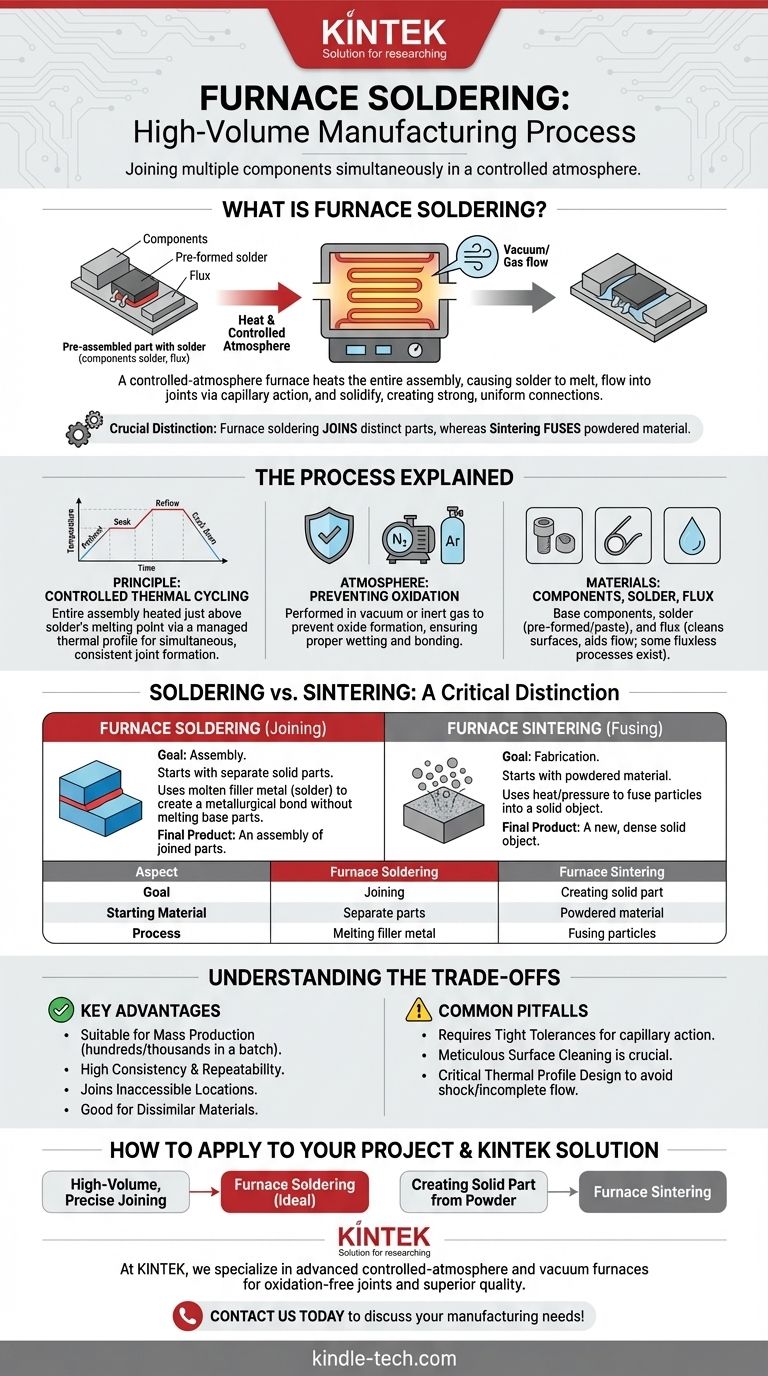
At its core, furnace soldering is a high-volume manufacturing process used to join multiple components together simultaneously. Unlike traditional soldering with an iron, this method involves placing a pre-assembled part with solder material into a controlled-atmosphere furnace. The entire assembly is heated according to a precise thermal profile, causing the solder to melt, flow into the joints via capillary action, and solidify upon cooling to create strong, uniform connections.
The critical distinction to understand is that furnace soldering joins distinct, pre-formed components using a molten filler metal, whereas related furnace processes like sintering (often confused with it) create a solid object by fusing powdered materials together.

The Furnace Soldering Process Explained
Furnace soldering leverages a controlled environment to produce high-quality joints across complex assemblies in a single batch. The process relies on precise control over temperature and atmosphere to ensure the solder flows correctly without damaging the components or introducing defects.
The Principle: Controlled Thermal Cycling
The fundamental idea is to heat an entire assembly just above the melting point of the solder, but well below the melting point of the components being joined. This is done via a carefully managed heating and cooling cycle, known as a thermal profile. This ensures all joints are formed simultaneously and with consistent quality.
The Furnace Atmosphere: Preventing Oxidation
A key advantage of this method is atmospheric control. The process is typically performed in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like nitrogen). As noted in high-temperature furnace operations, this controlled environment prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces, which would otherwise inhibit the solder from properly wetting and bonding to the components.
The Materials: Components, Solder, and Flux
The assembly consists of three elements. First are the base components to be joined. Second is the solder, often applied as a pre-formed shape (like a wire or washer) or as a paste. Third is a flux, a chemical agent that cleans the surfaces and aids the flow of molten solder, though some "no-clean" or fluxless processes exist, especially in vacuum furnaces.
Soldering vs. Sintering: A Critical Distinction
The provided reference materials primarily describe furnace sintering, a fundamentally different process that is often a source of confusion. Understanding the difference is crucial for any technical application.
Furnace Soldering: Joining Separate Parts
The goal of soldering is assembly. You begin with two or more distinct, solid parts. The process uses a filler metal (solder) with a lower melting point to create a metallurgical bond between these parts without melting them. The final product is an assembly of those original components.
Furnace Sintering: Fusing Powdered Material
The goal of sintering is fabrication. You begin with a mass of powdered material (like ceramic or metal powder). By applying heat and often pressure inside a furnace, the particles are fused together to form a single, solid, and dense object. The final product is a new part created from the raw powder.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace-based process requires understanding its advantages and limitations compared to other methods.
Key Advantages of Furnace Soldering
The primary benefit is its suitability for mass production. You can process hundreds or thousands of assemblies in a single batch, ensuring high consistency. It also allows for the creation of joints in locations that are inaccessible to a traditional soldering iron and is excellent for joining dissimilar materials with different thermal expansion rates.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Success in furnace soldering depends heavily on preparation and design. The components must have tight tolerances to ensure the solder flows correctly via capillary action. All parts must be meticulously cleaned before assembly, as contaminants will ruin the joint. Finally, designing the right thermal profile is critical to avoid thermal shock or incomplete solder flow.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice between these furnace processes depends entirely on your manufacturing goal.
- If your primary focus is to join multiple pre-made components into a single, complex assembly: Furnace soldering is the correct process for creating strong, repeatable joints in high volumes.
- If your primary focus is to create a solid, dense part from a raw powder: You need furnace sintering, which is designed to fuse particles into a monolithic structure.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest-purity, oxidation-free result: A vacuum furnace is the ideal environment for both soldering and sintering, as it removes reactive gases that can cause contamination.
Ultimately, selecting the right high-temperature furnace process begins with a clear understanding of whether you are assembling existing parts or creating a new one from scratch.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Furnace Soldering | Furnace Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Joining pre-formed components | Creating a solid part from powder |
| Starting Material | Separate, solid parts | Powdered material |
| Process | Melting a filler metal (solder) | Fusing particles together |
| Final Product | An assembly of joined parts | A new, dense solid object |
Need to join complex components with precision and consistency?
Furnace soldering is ideal for high-volume manufacturing, ensuring strong, uniform bonds in complex assemblies. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and expert support you need to implement this process successfully.
Our range of controlled-atmosphere and vacuum furnaces is designed to meet the stringent demands of modern production, helping you achieve oxidation-free joints and superior product quality.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing capabilities. Let's find the perfect furnace for your project.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques



















