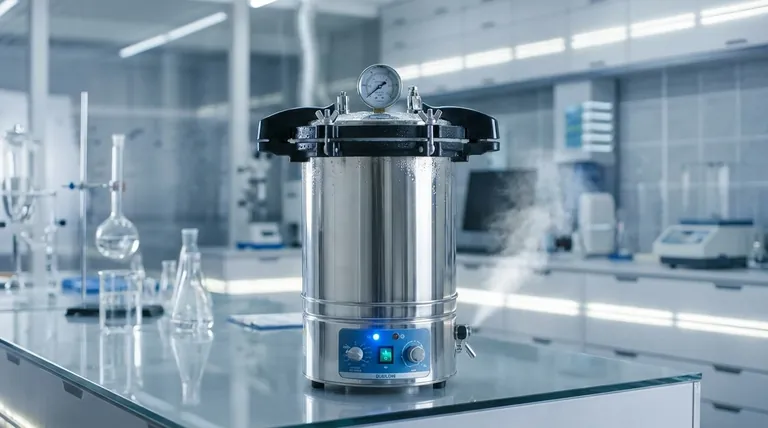
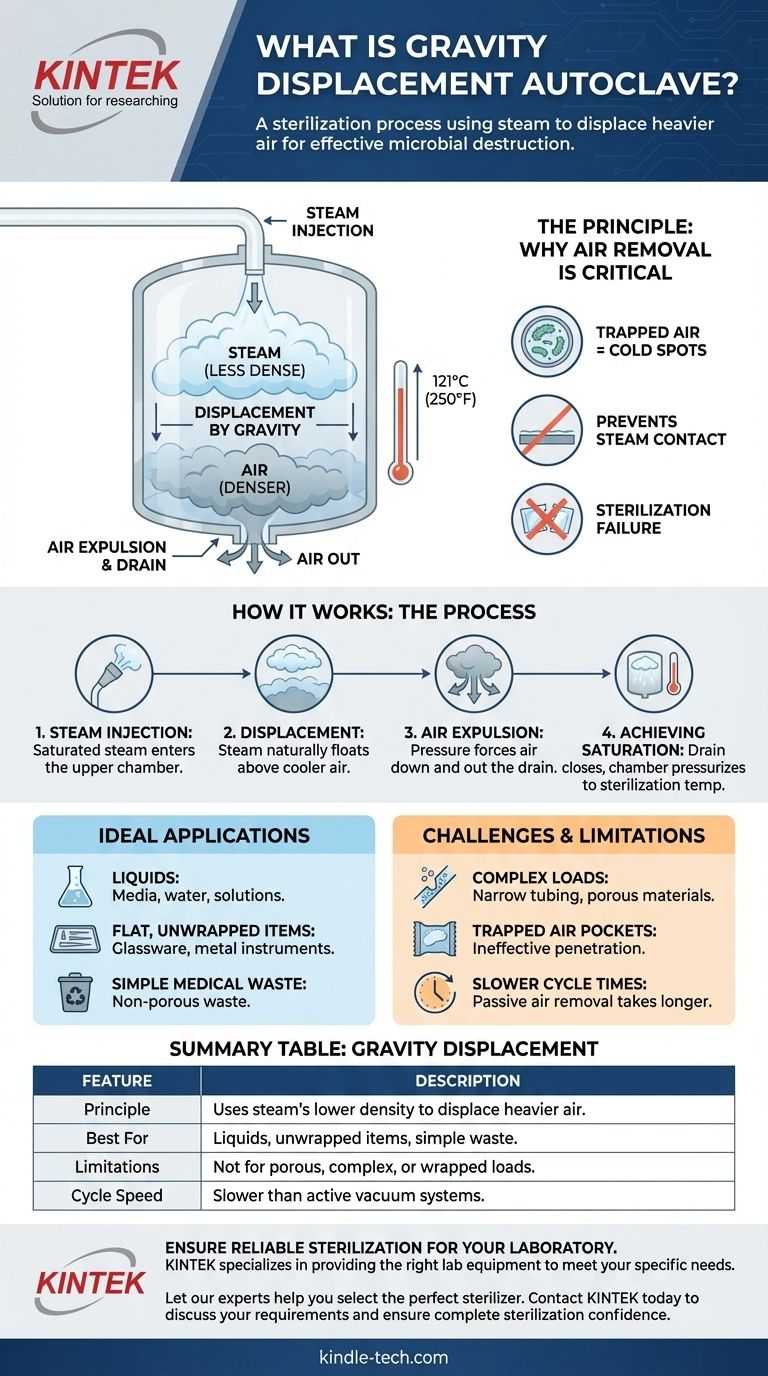
At its core, a gravity displacement autoclave is a type of sterilizer that uses steam to displace cooler, heavier air within its chamber. Steam is admitted into the top or sides of the sealed chamber, and because it is less dense than air, it forces the air down and out through a drain vent at the bottom. This process ensures the chamber becomes filled with pure, pressurized steam, which is necessary for effective sterilization.
The term "gravity displacement" describes the fundamental mechanism for removing air, which is the most critical step before sterilization can begin. This method relies on the simple physical principle that hot steam is lighter than cool air, making it a reliable but relatively slow process best suited for simple, non-porous loads.

The Principle: Why Air Removal is Critical
The entire purpose of an autoclave is to use moist heat (saturated steam) to sterilize items. However, any air trapped within the chamber acts as an insulator, preventing the steam from making direct contact with all surfaces of the load.
The Problem with Trapped Air
Air pockets create cold spots where the temperature does not reach the required 121°C (250°F). These spots will not be sterilized, leading to a complete failure of the process even if the autoclave's sensors report a successful cycle. Effective air removal is non-negotiable for true sterilization.
How Gravity Displacement Works
This method is an elegant, passive solution to the air removal problem.
- Steam Injection: The cycle begins by injecting saturated steam into the upper part of the sealed chamber.
- Displacement by Gravity: The hot, low-density steam naturally floats above the cooler, high-density air already in the chamber.
- Air Expulsion: As more steam is added, it creates pressure that pushes the layer of cool air downwards, forcing it out through a temperature-sensitive drain at the chamber's floor.
- Achieving Saturation: The drain remains open until a sensor detects that all the air has been purged and only pure steam is passing through. At this point, the drain closes, and the chamber can be pressurized to reach sterilizing temperature.
Reaching Sterilization Temperature
Once the air is removed and the chamber is filled with pure steam, the pressure is increased. Based on physical laws, as the pressure on a gas increases, so does its temperature. The autoclave targets a pressure that raises the steam's temperature to at least 121°C (250°F) for a set duration, typically 15-20 minutes, which is sufficient to coagulate proteins and destroy all microorganisms.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While effective, the gravity displacement method is not a universal solution. Its passive nature creates specific limitations that are critical to understand.
Ideal Applications
Gravity displacement autoclaves excel at sterilizing loads where air can be removed easily. This includes:
- Liquids: Laboratory media, water, and other pharmaceutical solutions.
- Flat, Unwrapped Items: Glassware, trays, and simple, non-porous metal instruments.
- Medical Waste: Certain types of regulated waste that do not contain large air pockets.
The Challenge of Complex Loads
This method is poorly suited for items with complex geometries or porous materials where air can become trapped.
Air struggles to escape from inside narrow tubing, wrapped surgical packs, dense textiles, or animal cages. The passive force of gravity displacement is often insufficient to penetrate these pockets, making sterilization unreliable for such loads. For these applications, a dynamic air removal method (like a pre-vacuum cycle) is required.
Slower Cycle Times
The passive displacement of air is a gradual process. Compared to autoclaves that use a vacuum pump to actively pull air out of the chamber, gravity displacement cycles are significantly longer. This can be a major drawback in high-throughput environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct type of autoclave cycle is a matter of matching the technology to the load you need to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids, glassware, or unwrapped instruments: A gravity displacement cycle is a reliable, simple, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing porous materials or wrapped surgical kits: Gravity displacement is not recommended, as its inability to remove trapped air can lead to sterilization failure.
- If your primary focus is high-speed throughput: The slower nature of the gravity cycle makes it less suitable than autoclaves with active air removal systems.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental role of air removal is the key to ensuring successful and reliable sterilization.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Principle | Uses steam's lower density to displace heavier air out of a drain vent. |
| Best For | Liquids, unwrapped glassware/metal instruments, simple medical waste. |
| Limitations | Not suitable for porous materials, wrapped packs, or complex loads with trapped air. |
| Cycle Speed | Slower than autoclaves with active vacuum systems. |
Ensure reliable sterilization for your laboratory.
Gravity displacement autoclaves are a cornerstone of effective lab sterilization for straightforward loads. KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment, including autoclaves, to meet your specific needs—whether you're processing liquids, glassware, or require a more advanced system for complex materials.
Let our experts help you select the perfect sterilizer for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's requirements and ensure complete sterilization confidence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer Lab Microcomputer Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory autoclave play in the separation of lignin? High-Purity Extraction for Biomass Research
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise



















