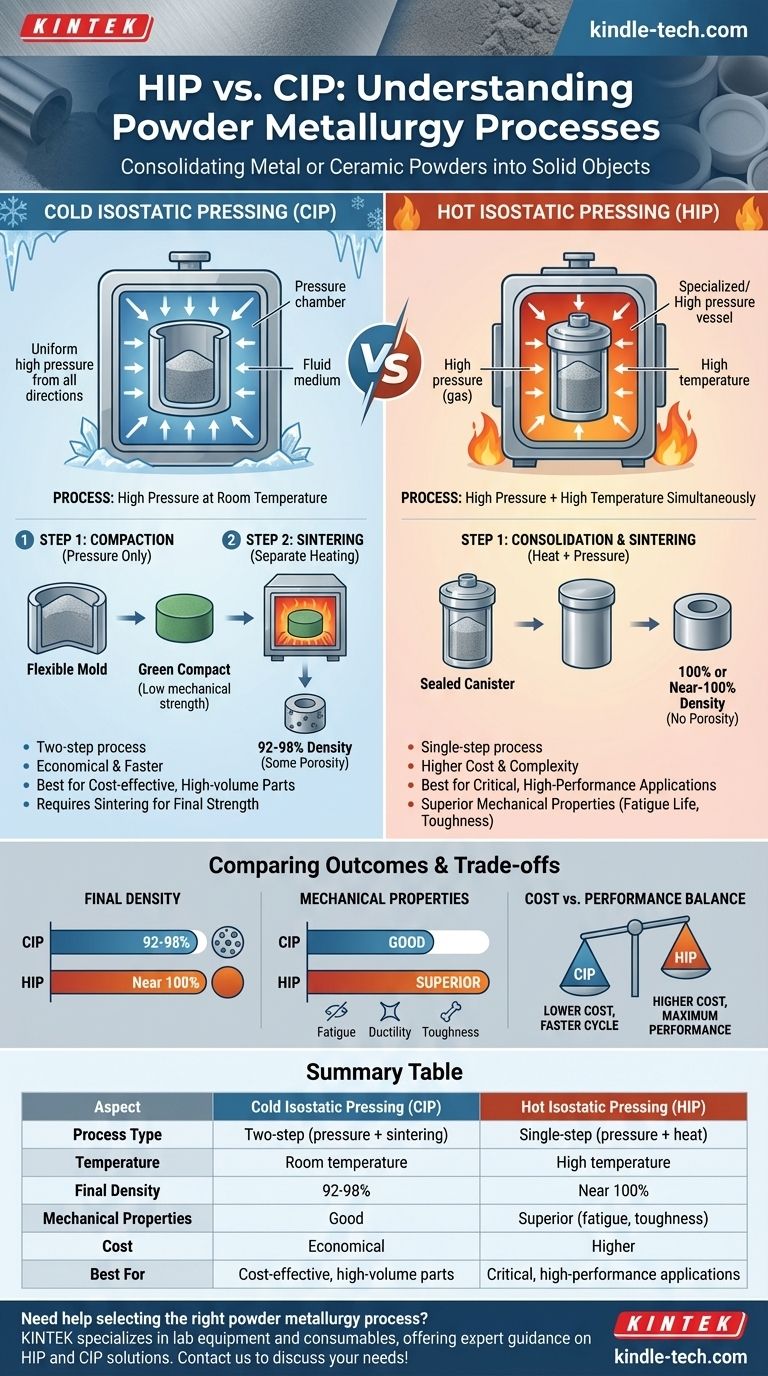
In powder metallurgy, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) and Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) are two distinct methods for consolidating metal or ceramic powders into a solid object. HIP uses both high pressure and high temperature simultaneously to create a fully dense part in a single step. In contrast, CIP uses only high pressure at room temperature to form a preliminary shape, which must then be heated in a separate process called sintering to achieve its final strength.
The core difference lies in their approach to achieving density and strength. HIP is a single-step, high-performance process combining heat and pressure for maximum density, while CIP is a two-step, more economical process that separates initial compaction (pressure only) from final strengthening (heat only).

Deconstructing the Isostatic Pressing Process
The term "isostatic" is key to understanding both processes. It means that pressure is applied to the powder uniformly from all directions.
This is typically achieved by placing the powder, contained within a flexible mold or sealed canister, into a vessel filled with a fluid or gas. When the vessel is pressurized, the pressure medium exerts equal force on all surfaces of the part, resulting in a highly uniform density.
How Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) Works
In CIP, a flexible mold is filled with powder, sealed, and submerged in a fluid-filled pressure chamber at ambient temperature.
The chamber is pressurized to extremely high levels, compacting the powder into a solid shape known as a "green compact."
This green compact has good handleability and uniform density but possesses very low mechanical strength because the powder particles are only mechanically interlocked, not metallurgically bonded. It requires a subsequent thermal treatment—sintering—to fuse the particles together and develop its final properties.
How Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Works
In HIP, the powder is sealed in a gas-tight metallic or glass container, often called a "can." This canister is placed inside a specialized furnace that is also a high-pressure vessel.
The vessel is filled with an inert gas (like argon) and is simultaneously heated to high temperatures and pressurized.
Through a combination of plastic deformation, creep, and diffusion bonding at the particle level, HIP produces a fully dense part with a fine-grained, uniform microstructure. It consolidates and sinters the material in a single operation, eliminating the need for a separate heating step.
Comparing the Outcomes: Density, Properties, and Application
The choice between CIP and HIP is driven by the final requirements of the component, as each process yields significantly different results.
Final Density and Porosity
CIP followed by sintering typically results in a part that is 92-98% of its theoretical maximum density, leaving some residual porosity.
HIP is capable of achieving 100% or near-100% theoretical density, effectively eliminating all internal voids and porosity.
Mechanical Properties
Because of its full density, a HIP-processed component generally exhibits superior mechanical properties. This includes significantly better fatigue life, ductility, and fracture toughness compared to a part made via CIP and sintering.
Shape Complexity and Size
Both methods are excellent for producing complex, near-net-shape parts that would be difficult or wasteful to create using traditional subtractive machining. HIP, in particular, can be used to produce very large components, weighing several tons.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
Your decision must balance the required performance against the economic realities of each process.
The Cost Factor
CIP is a significantly less expensive and faster process than HIP. The equipment is simpler, cycle times are shorter, and it avoids the high costs associated with high-temperature, high-pressure vessels and inert gas systems.
The Performance Mandate
HIP is a more complex and expensive process. However, its cost is justified for critical, high-performance applications where material integrity is paramount and failure could be catastrophic, such as in aerospace turbine disks, medical implants, or deep-sea components.
Sintering as a Necessary Partner
It is crucial to remember that CIP is not a standalone process for producing a final part. It is the first step in a "press-and-sinter" workflow. HIP, by consolidating and bonding in one cycle, offers a more streamlined, albeit more intensive, production path.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Application
To select the correct method, you must first define the non-negotiable requirements for your component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for high-volume parts where some porosity is acceptable: CIP followed by sintering is the logical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance, reliability, and failure elimination in a critical application: HIP is the required process to achieve superior material properties.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex shape while minimizing machining: Both are excellent candidates, with the final decision determined by your specific performance and budget constraints.
Ultimately, the choice between these processes is a strategic decision balancing economic feasibility against engineering necessity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Two-step (pressure + sintering) | Single-step (pressure + heat) |
| Temperature | Room temperature | High temperature |
| Final Density | 92-98% | Near 100% |
| Mechanical Properties | Good | Superior (fatigue, toughness) |
| Cost | Economical | Higher |
| Best For | Cost-effective, high-volume parts | Critical, high-performance applications |
Need help selecting the right powder metallurgy process for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance on HIP and CIP solutions to enhance your material performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is a cold isostatic press? Achieve Uniform Powder Compaction for Complex Parts
- What is cold isostatic pressing examples? Achieve Uniform Density in Powder Compaction
- What are the disadvantages of powder metallurgy? Key Limitations in Strength and Size
- Why is cold working better than hot working? A Guide to Choosing the Right Metal Forming Process
- How much does an isostatic press cost? A Guide to Lab vs. Industrial Pricing



















