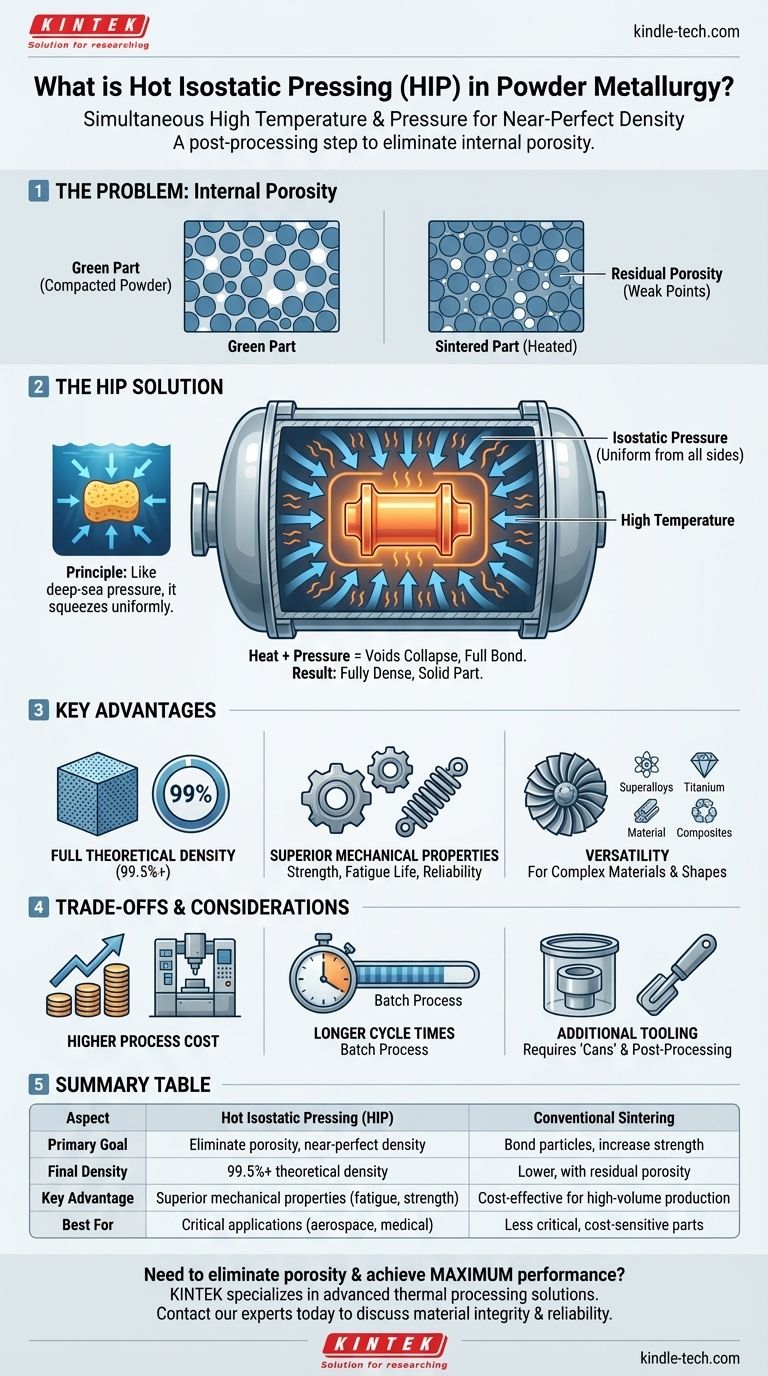
In the simplest terms, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is an advanced manufacturing process used in powder metallurgy that simultaneously applies high temperature and high-pressure gas from all directions to a component. This combination heats the metal powder to just below its melting point, making it malleable, while the uniform, all-encompassing pressure squeezes out and eliminates any internal voids or porosity. The result is a fully dense part with superior strength and a highly uniform internal structure.
The central purpose of Hot Isostatic Pressing is not merely to shape a part, but to achieve near-perfect material density. It is a post-processing or consolidation step that transforms a porous metal powder component into a solid, high-performance material free of the internal defects that limit other methods.
The Core Problem HIP Solves: Internal Porosity
In conventional powder metallurgy, metal powder is first compacted into a preliminary shape called a "green part." This part holds its shape but is filled with microscopic voids between the individual powder particles.
The Limits of Sintering Alone
The next traditional step is sintering, where the green part is heated in a furnace. This heat causes the particles to bond or "neck" together, increasing the part's strength.
However, sintering alone often fails to close every single internal pore. This residual porosity acts as a microscopic defect, becoming a potential point of failure that can compromise the material's strength, fatigue life, and overall reliability.
The Isostatic Solution
Hot Isostatic Pressing directly targets this residual porosity. The key is the term "isostatic," which means the pressure is applied equally and simultaneously from every direction.
Imagine squeezing a sponge with your hand—you apply pressure primarily from two sides. Now, imagine submerging that sponge deep in the ocean. The water pressure acts on its entire surface uniformly, compressing it evenly from all directions. This is the principle of isostatic pressure.
The Synergy of Heat and Pressure
During the HIP process, a component is placed inside a sealed, high-pressure vessel. The vessel is filled with an inert gas (typically argon), which is then heated and pressurized.
The high temperature softens the metal particles without melting them. The intense, uniform gas pressure then collapses the internal voids, forcing the particles to bond on a metallurgical level and creating a fully dense, solid object.
Key Advantages of the HIP Process
By eliminating internal defects, HIP delivers significant performance gains that are often unattainable with other powder metallurgy techniques.
Reaching Full Theoretical Density
The primary benefit of HIP is its ability to produce parts that are 99.5%+ of their theoretical maximum density. This near-perfect consolidation is the foundation for all other property improvements.
Superior and Predictable Mechanical Properties
Because there are no internal voids to initiate cracks, HIPed components exhibit dramatically improved mechanical properties. This includes higher tensile strength, ductility, and especially resistance to fatigue failure. The properties are also highly uniform throughout the part.
Versatility for Complex Materials
HIP is exceptionally effective for consolidating materials that are difficult to sinter through conventional means. This includes high-performance superalloys, titanium alloys, and metal matrix composites used in demanding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, HIP is a specialized process that involves clear trade-offs against more conventional methods.
Higher Process Cost
The equipment required to safely generate extreme heat and pressure is highly specialized and expensive. This translates to a higher per-part cost compared to traditional press-and-sinter operations.
Longer Cycle Times
HIP is a batch process. The cycles for loading, heating, pressurizing, holding at temperature, and cooling can take several hours. This makes it less suitable for the kind of high-volume production where conventional pressing excels.
Additional Tooling Requirements
In many cases, the metal powder must be sealed within a disposable metal or ceramic container (often called a "can") before being placed in the HIP vessel. This container forms the part's final shape and must be removed after the cycle, adding steps and costs to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on the component's performance requirements and economic constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and reliability: HIP is the superior choice for critical components in aerospace, medical implants, or defense where material failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes with uniform density: HIP overcomes the limitations of uniaxial pressing, which can create density variations in parts with intricate geometries.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-sensitive production: Conventional press-and-sinter methods are almost always more economical for parts where good, but not perfect, material properties are acceptable.
Ultimately, Hot Isostatic Pressing is a strategic investment in material integrity, chosen when the application demands performance that justifies the cost.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Eliminate internal porosity, achieve near-perfect density | Bond particles, increase strength |
| Final Density | 99.5%+ theoretical density | Lower, with residual porosity |
| Key Advantage | Superior mechanical properties (fatigue life, strength) | Cost-effective for high-volume production |
| Best For | Critical applications (aerospace, medical implants) | Less critical, cost-sensitive parts |
Need to eliminate porosity and achieve maximum part performance?
KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions for demanding laboratory and industrial applications. Our expertise can help you determine if Hot Isostatic Pressing is the right strategic investment for your high-performance components.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can meet your specific needs for material integrity and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance



















