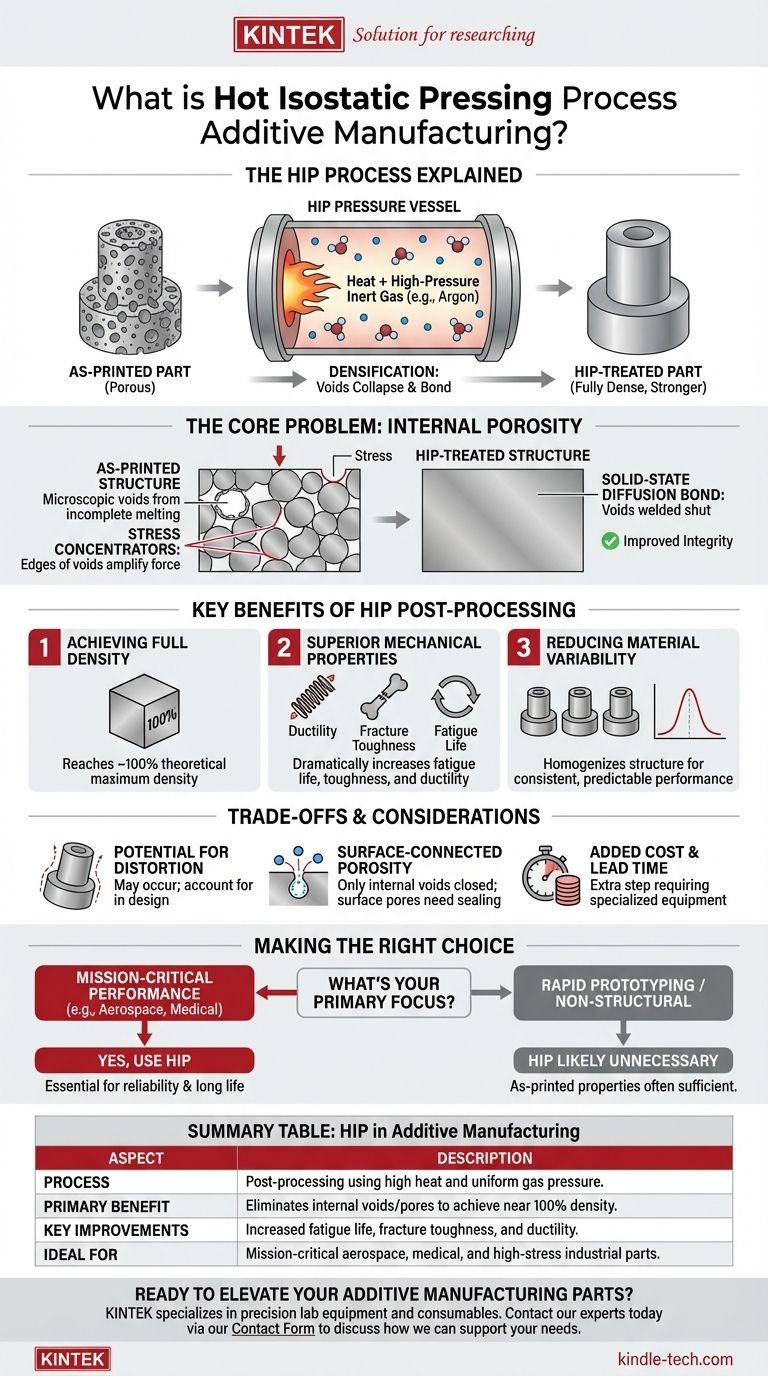
In additive manufacturing, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a post-processing method that subjects a printed metal part to intense heat and uniform, high-pressure gas. This process essentially squeezes the part from all directions at a microscopic level, eliminating internal voids and consolidating the material into a fully dense, solid state. The result is a significant improvement in the part's mechanical properties and reliability.
The core purpose of applying Hot Isostatic Pressing to an additively manufactured part is to heal internal defects. By closing microscopic pores left behind by the printing process, HIP transforms the component from a near-net shape into a fully dense part with mechanical properties comparable to, or even exceeding, those of forged or cast materials.

The Core Problem HIP Solves: Internal Porosity
Why Metal AM Parts Have Voids
The layer-by-layer nature of metal additive manufacturing, such as laser powder bed fusion, is not always perfect. The process can trap microscopic pockets of gas or result in incomplete melting between powder particles.
These imperfections create tiny internal voids or pores within the finished part. While the part may look solid, its internal structure can be slightly porous.
The Impact of Porosity
These internal pores are the single greatest weakness in an as-printed metal component. They act as stress concentrators, meaning any force applied to the part is amplified at the edges of these voids.
Under cyclic loading or high stress, these pores become the initiation points for cracks, leading to premature fatigue failure. This inherent variability makes as-printed parts unsuitable for many critical, load-bearing applications.
How the HIP Process Works
The Key Ingredients: Heat and Pressure
The HIP process takes place inside a specialized, high-pressure vessel. The additively manufactured component is placed inside, and the vessel is heated to a high temperature, typically below the material's melting point.
Simultaneously, the vessel is filled with a high-pressure inert gas, like argon. This gas applies uniform, isostatic pressure to every surface of the part.
The Mechanism of Densification
The high temperature makes the metal soft and malleable without melting it. The immense external pressure then causes the material to plastically deform on a microscopic level.
This pressure collapses the internal voids and pores. The surfaces of the collapsed voids are forced into intimate contact, creating a solid-state diffusion bond that permanently welds the gaps shut, effectively healing the part from the inside out.
Key Benefits for Additively Manufactured Parts
Achieving Full Density
The most immediate benefit of HIP is the elimination of internal porosity. This allows the component to reach nearly 100% of its theoretical maximum density, which is the foundation for all other property improvements.
Superior Mechanical Properties
By removing the stress-concentrating defects, HIP dramatically improves critical mechanical properties. This includes a significant increase in fatigue life, fracture toughness, and ductility, making the part far more resilient and reliable under stress.
Reducing Material Variability
The HIP process homogenizes the part's internal structure. This reduces the performance variation between different builds and different parts, leading to consistent, predictable material properties that engineers can rely on for demanding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Potential for Distortion
Subjecting a component to high temperatures can relieve residual stresses from the printing process, but it can also lead to slight distortion or changes in dimensional accuracy. This must be accounted for in the initial design, often by leaving extra material for final machining.
Surface-Connected Porosity
The HIP process can only close internal voids. If a pore is connected to the surface of the part, the high-pressure gas will simply enter the pore instead of collapsing it. Therefore, parts with surface-breaking defects are not suitable for HIP without prior sealing.
Added Cost and Lead Time
Hot Isostatic Pressing is an additional manufacturing step that requires specialized, expensive equipment. This adds both cost and time to the overall production process and must be justified by the performance requirements of the final application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Deciding whether to use HIP is a critical engineering choice based entirely on the part's intended function.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical performance: HIP is essential to eliminate internal defects and guarantee the fatigue life and fracture toughness required for aerospace, medical, or high-stress industrial parts.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or non-structural components: The added cost and time of HIP are likely unnecessary, as the as-printed mechanical properties are sufficient for form, fit, and low-stress function checks.
Ultimately, incorporating Hot Isostatic Pressing is a strategic decision to elevate an additively manufactured component from a prototype to a production-grade, highly reliable part.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Post-processing using high heat and uniform gas pressure. |
| Primary Benefit | Eliminates internal voids/pores to achieve near 100% density. |
| Key Improvements | Increased fatigue life, fracture toughness, and ductility. |
| Ideal For | Mission-critical aerospace, medical, and high-stress industrial parts. |
Ready to elevate your additive manufacturing parts to production-grade reliability?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced manufacturing processes. If you are developing critical metal components and need solutions to ensure their integrity and performance, our expertise can help.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can support your laboratory and manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance



















