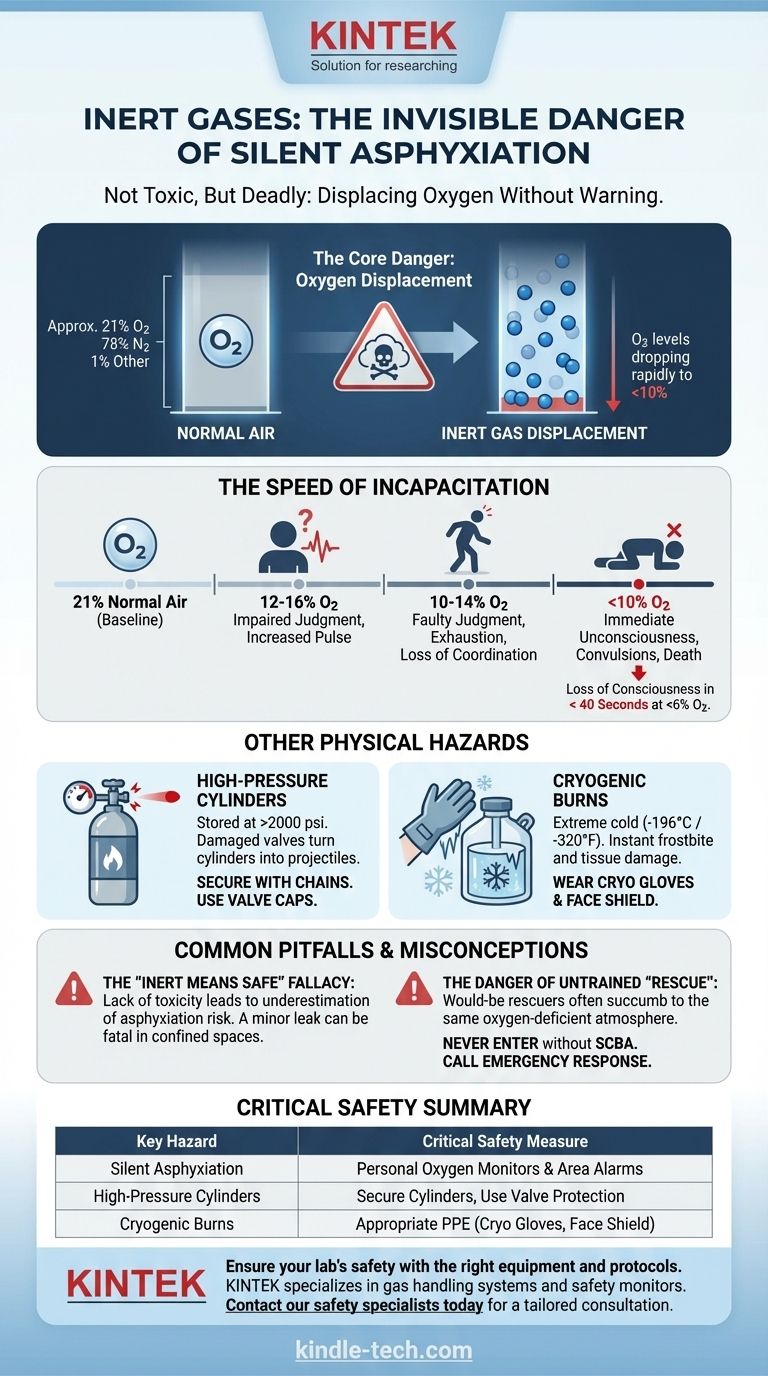
The most important thing to be aware of is that inert gases are silent asphyxiants. While they are not toxic, they displace oxygen in the air to levels that can cause rapid unconsciousness and death. Because they are colorless and odorless, you receive no sensory warning of the extreme danger until it is too late.
The core danger of inert gases is not what they are, but what they displace. Their "inert" nature makes them an invisible and insidious hazard, as they can create a fatal, oxygen-deficient atmosphere without any warning signs.

The Primary Hazard: Asphyxiation by Oxygen Displacement
The term "inert" refers to a lack of chemical reactivity, not a lack of physical hazard. The primary danger—asphyxiation—stems from the simple fact that these gases are heavier than air and will displace the oxygen necessary for life.
How Displacement Occurs
Inert gases like nitrogen, argon, and helium are often stored as compressed gases or cryogenic liquids. A small leak from a cylinder or transfer line can quickly fill a poorly ventilated room, vehicle, or confined space.
As the inert gas concentration increases, the oxygen concentration decreases proportionally.
The Insidious Nature of the Threat
Humans have no natural alarm system for a lack of oxygen. You cannot smell, see, or taste the presence of an inert gas leak.
The initial symptoms of oxygen deficiency—dizziness or light-headedness—can be misinterpreted as simply feeling unwell, leading to a fatal lack of urgency.
The Speed of Incapacitation
The effects of oxygen deprivation are swift and severe.
- At 12-16% oxygen: Breathing and pulse rate increase, and judgment becomes impaired.
- At 10-14% oxygen: Faulty judgment, exhaustion, and loss of coordination occur.
- Below 10% oxygen: Unconsciousness is nearly immediate, followed by convulsions and death.
A person entering an area with less than 6% oxygen can lose consciousness in under 40 seconds.
Other Critical Physical Hazards
Beyond asphyxiation, the physical state of inert gases presents two other significant risks.
High-Pressure Cylinders
Inert gases are stored in cylinders at extremely high pressures, often exceeding 2000 psi. If a cylinder valve is damaged or broken, the cylinder can become a projectile with enough force to penetrate concrete walls.
Proper handling, securing cylinders with chains or straps, and using valve protection caps are non-negotiable.
Cryogenic Burns
Gases like liquid nitrogen and liquid argon are stored at extremely low temperatures (-196°C / -320°F).
Direct contact with these liquids or uninsulated equipment can cause severe frostbite and tissue damage instantly. Splashes can cause permanent eye damage.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Trust in your procedures, not your senses. The most common incidents occur when workers become complacent or misunderstand the nature of the risk.
The "Inert Means Safe" Fallacy
This is the single most dangerous misconception. The lack of toxicity leads people to underestimate the physical hazards of asphyxiation, high pressure, and cryogenic temperatures.
Underestimating Small Leaks
A seemingly minor leak from a fitting in a small, unventilated room (like a storage closet or an elevator) can create a fatal atmosphere in minutes. Always treat every leak as a serious event until proven otherwise.
The Danger of Untrained "Rescue"
A tragic and common pattern in asphyxiation incidents is the death of would-be rescuers. Seeing a collapsed colleague, a person's first instinct is to rush in, only to succumb to the same oxygen-deficient atmosphere.
Never enter a suspected oxygen-deficient area to perform a rescue unless you are trained and equipped with a Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA). Your first action should always be to call for an emergency response.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your safety protocols must be built around the absolute assumption that an invisible hazard could be present at any time.
- If your primary focus is handling and storing gas cylinders: Ensure every cylinder is properly secured with chains, valve caps are on when not in use, and storage areas have adequate ventilation.
- If your primary focus is working in an area where inert gas is used: Mandate the use of a personal oxygen monitor and ensure the area has functioning mechanical ventilation and fixed gas detection alarms.
- If your primary focus is emergency preparedness: Establish and drill a clear procedure that prohibits entry without SCBA and prioritizes calling for trained emergency responders.
Always treat inert gases with the respect their invisible hazards demand.
Summary Table:
| Key Hazard | Description | Critical Safety Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Silent Asphyxiation | Inert gases displace oxygen, causing rapid unconsciousness and death with no warning. | Use personal oxygen monitors and area gas detection alarms. |
| High-Pressure Cylinders | Cylinders store gas at over 2000 psi; damage can turn them into dangerous projectiles. | Always secure cylinders with chains and use valve protection caps. |
| Cryogenic Burns | Liquefied gases like LN2 are extremely cold (-196°C), causing instant frostbite on contact. | Wear appropriate PPE (cryo gloves, face shield) when handling. |
Ensure your lab's safety with the right equipment and protocols. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, including gas handling systems and safety monitors. Our experts can help you select the right solutions to mitigate the risks of working with inert gases. Don't leave safety to chance—contact our safety specialists today for a consultation tailored to your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Lab Infrared Press Mold
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How do Teflon (PTFE) baskets facilitate glass thin-film leaching? Enhance Accuracy with Chemical Inertness
- How does the combination of PTFE tape and ceramic washers function in crevice corrosion modeling? Expert Analysis
- What are the specific applications of PTFE in micro-batch slug flow systems? Enhance Your Microfluidic Reaction Purity
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car



















