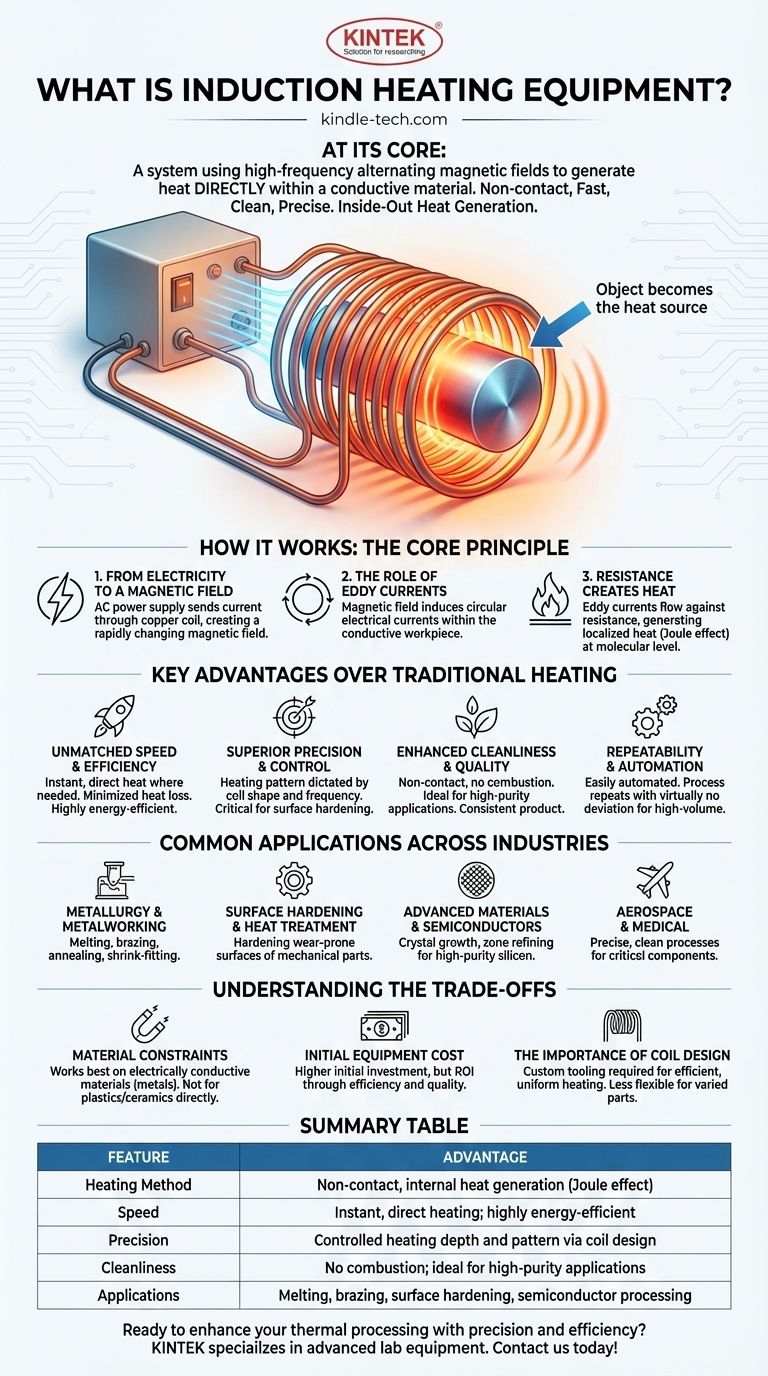
At its core, induction heating equipment is a system that uses a powerful, high-frequency alternating magnetic field to generate heat directly within a conductive material. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats the outside of an object, induction heating turns the object itself into the heat source. This process is entirely non-contact, making it exceptionally fast, clean, and precise.
Induction heating is not just another way to apply heat; it is a fundamental shift in thermal technology. By generating heat inside the object itself, it offers unparalleled speed, precision, and cleanliness, solving critical challenges in modern manufacturing, metallurgy, and material science.
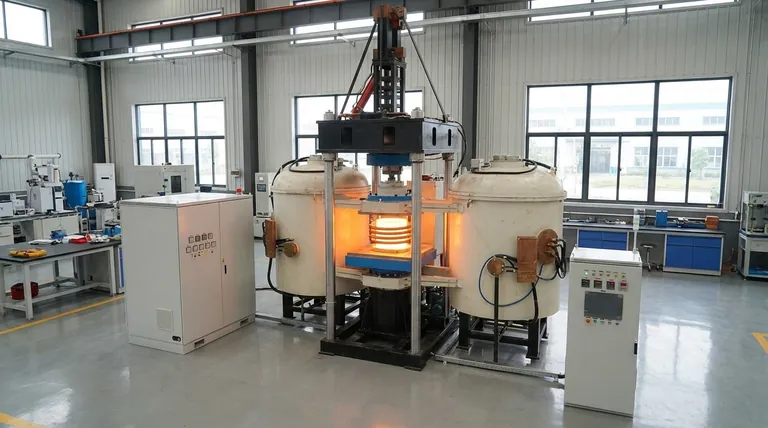

The Core Principle: How It Works
Induction is a sophisticated process, but its principle is based on fundamental laws of electromagnetism. It works by converting electrical energy into heat energy through a two-step process.
From Electricity to a Magnetic Field
The heart of an induction system is a power supply that sends an alternating current (AC) through an induction coil, which is typically made of copper. When this current flows, it generates a concentrated and rapidly changing magnetic field around and within the coil.
The Role of Eddy Currents
When a conductive workpiece (like a steel gear or a crucible of metal) is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circular electrical currents within the material. These are known as eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat
The workpiece material has a natural electrical resistance. As the induced eddy currents flow against this resistance, they generate immense friction at a molecular level, resulting in rapid and localized heat. This phenomenon is known as the Joule effect, and it's the same principle that makes a stove's heating element glow red, but it happens inside the part itself.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Heating
The "inside-out" nature of induction heating provides distinct advantages over traditional methods like gas furnaces or resistance ovens, which rely on slow, external heat transfer.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Heat is generated instantly and directly where it is needed. There is no need to heat a chamber or wait for thermal conduction. This minimizes heat loss to the environment, making the process highly energy-efficient and significantly faster than conventional methods.
Superior Precision and Control
The heating pattern is dictated by the shape of the induction coil and the frequency of the alternating current. This allows for precise control over which part of the object gets hot, how hot it gets, and to what depth. This is critical for processes like surface hardening, where only the outer layer of a part needs to be treated.
Enhanced Cleanliness and Quality
Because the process is non-contact and involves no combustion, the workpiece is never contaminated by flames or pollutants. This is essential in high-purity applications like medical device manufacturing, aerospace, and melting precious metals. The result is a higher quality, more consistent end product.
Repeatability and Automation
Induction heating systems can be easily automated. Once the power, frequency, and cycle time are set, the process can be repeated thousands of times with virtually no deviation. This reliability is a cornerstone of modern, high-volume manufacturing.
Common Applications Across Industries
The unique benefits of induction heating make it the technology of choice for a wide range of demanding industrial and specialized processes.
Metallurgy and Metalworking
Induction is widely used for melting aluminum, copper, and specialty alloys in foundries. It is also the preferred method for brazing, annealing (softening), and shrink-fitting components together with extreme precision.
Surface Hardening and Heat Treatment
Perhaps one of its most valuable applications is the surface hardening of mechanical parts like gears, shafts, and bearings. Induction can harden the wear-prone surface to a specific depth while leaving the core of the part tough and ductile, creating a component with a superior lifespan.
Advanced Materials and Semiconductors
In the semiconductor industry, induction heating is used for Czochralski crystal growth and zone refining. Its pure, controlled environment is essential for creating the high-purity single-crystal silicon that forms the basis of microchips.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Material Constraints
Induction works best on electrically conductive materials, primarily metals. Non-conductive materials like plastics and most ceramics cannot be heated directly and require a different approach, such as using a conductive crucible to hold them.
Initial Equipment Cost
The initial investment for an induction power supply, cooling system, and custom coil can be higher than for a simple gas-fired furnace. The return on this investment comes from higher throughput, lower energy costs, and improved product quality over time.
The Importance of Coil Design
The induction coil is not a generic part; it is a piece of custom tooling. It must be carefully designed to match the geometry of the workpiece to ensure efficient and uniform heating. This requires expertise and can make the system less flexible for small runs of varied parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing a heating technology depends entirely on your project's critical success factors.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with strict quality control: The repeatability, speed, and automation potential of induction heating are likely your best solution.
- If your primary focus is precision and cleanliness: For applications like medical devices, semiconductors, or aerospace brazing, induction's contactless nature is a significant and often necessary advantage.
- If your primary focus is rapid, efficient melting of metals: The speed and uniform stirring action of an induction furnace offer clear operational and energy-saving benefits over traditional furnaces.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, low-volume, or heating non-conductive materials: A simpler resistance oven or gas furnace may be a more practical and cost-effective choice.
Ultimately, understanding induction heating empowers you to move beyond simply applying heat and start precisely engineering thermal outcomes for your product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Non-contact, internal heat generation (Joule effect) |
| Speed | Instant, direct heating; highly energy-efficient |
| Precision | Controlled heating depth and pattern via coil design |
| Cleanliness | No combustion; ideal for high-purity applications |
| Applications | Melting, brazing, surface hardening, semiconductor processing |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with precision and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for high-volume production, material science, and metallurgy. Our solutions deliver unmatched speed, control, and cleanliness for your most demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your heating processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace improve the density of Ti2AlN ceramics? Achieve 98.5%+ Density & Superior Strength
- How does the mechanical pressure from a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of B4C/Al composites?
- Why is the vacuum system of a Vacuum Hot Pressing furnace critical for ODS ferritic stainless steel performance?
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity
- How does the degassing stage in a vacuum hot press (VHP) optimize diamond/aluminum composite performance?



















