In materials science, isostatic graphite represents the pinnacle of synthetic graphite performance. It is an ultra-fine grain graphite produced through a high-pressure manufacturing process called Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP). This method creates a material with exceptionally uniform properties, making it superior to other graphite grades for the most demanding technical applications.
The defining characteristic of isostatic graphite is not just its purity or fine grain, but its manufacturing process. The use of isostatic pressure creates a highly uniform, or isotropic, internal structure, which is directly responsible for its superior strength, conductivity, and resistance to thermal shock.
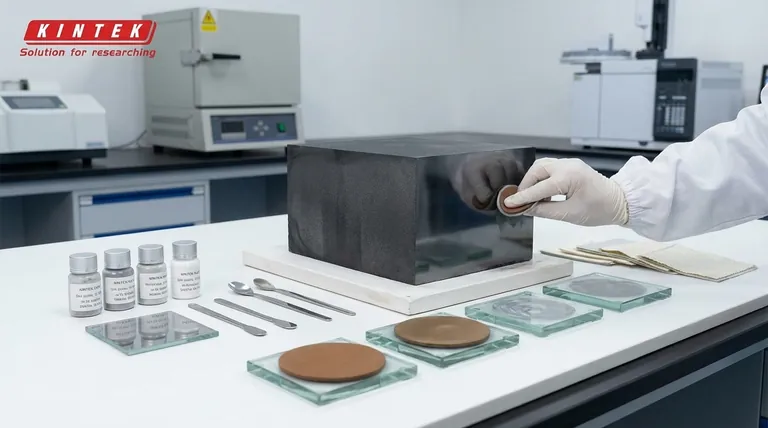

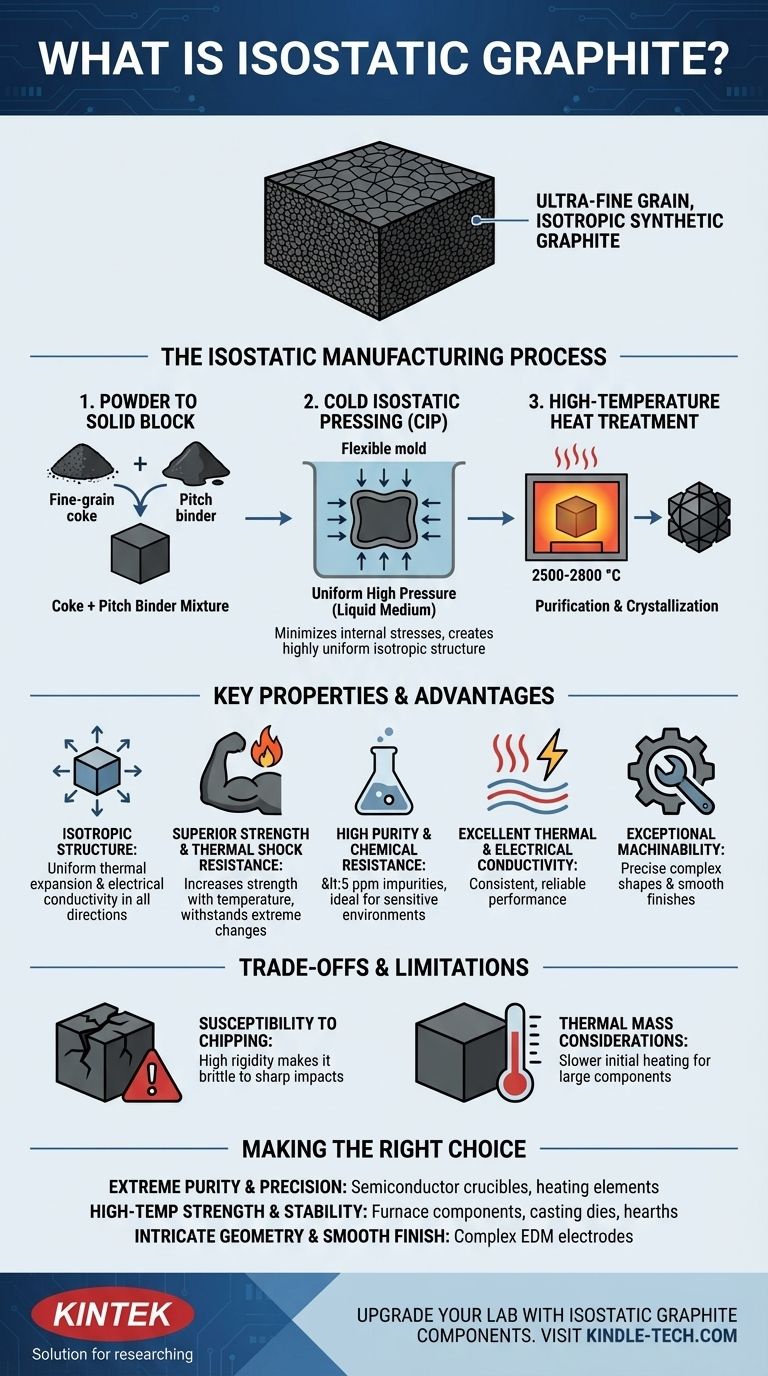
The Isostatic Manufacturing Process
To understand what makes isostatic graphite unique, you must first understand how it is made. The process is precise and designed to create a homogenous final product.
From Powder to Solid Block
The journey begins with a raw material mixture of fine-grain coke and a pitch binder. This mixture is the fundamental building block of the final graphite.
The Role of Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP)
The powder mixture is placed in a flexible mold and subjected to extremely high, uniform pressure from all directions using a liquid medium. This isostatic pressing is the key step.
Unlike conventional pressing, which applies force from one or two directions, CIP ensures the material compacts evenly. This minimizes internal stresses and creates the most isotropic (uniform in all directions) structure possible in artificial graphite.
High-Temperature Heat Treatment
After pressing, the solid block is heat-treated at extremely high temperatures, typically between 2500-2800 °C. This final step converts the raw materials into a pure, crystalline graphite structure.
Key Properties and Their Advantages
The manufacturing process directly translates to a set of highly desirable material properties that make isostatic graphite essential for advanced equipment.
Isotropic and Ultra-Fine Grain Structure
The uniform pressure from CIP results in an ultra-fine grain material where properties like thermal expansion and electrical conductivity are the same regardless of the direction measured. This predictability is critical for precision components.
Superior Strength and Thermal Shock Resistance
Isostatic graphite has high mechanical strength that, uniquely, increases with temperature. Its uniform structure allows it to withstand extreme and rapid temperature changes without cracking, giving it excellent thermal shock resistance.
High Purity and Chemical Resistance
The production process allows for purification to exceptionally high levels, with impurity content as low as < 5 parts per million (ppm). This, combined with its inherent chemical inertness, makes it ideal for environments like semiconductor manufacturing that cannot tolerate contamination.
Excellent Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Like all graphites, this material exhibits high thermal and electrical conductivity. Its consistency ensures reliable performance in applications such as heating elements, hearths, and electrodes.
Exceptional Machinability
The fine-grain, homogenous structure allows isostatic graphite to be machined to very precise and complex shapes with smooth surface finishes, which is impossible with lesser grades of graphite.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly capable, isostatic graphite is not without practical considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging its potential downsides.
Susceptibility to Chipping
The material's high rigidity and hardness, which contribute to its strength, can also make it brittle. Components like furnace hearth rails made from isostatic graphite can be prone to chipping if subjected to sharp impacts during the loading and unloading of parts.
Thermal Mass Considerations
Although its thermal conductivity is excellent, a large or heavy component made of isostatic graphite has a high thermal mass. This can lead to slower initial heating rates at lower temperatures compared to a lighter component, though its high conductivity helps minimize this effect as temperatures rise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting isostatic graphite is a decision driven by the need for ultimate performance where other materials fail.
- If your primary focus is extreme purity and precision: This material is the standard for semiconductor production, including crucibles and heating elements, where contamination is not an option.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength and stability: Its ability to get stronger at higher temperatures makes it ideal for furnace components, casting dies, and hearths that must maintain their shape under extreme thermal stress.
- If your primary focus is intricate geometry and smooth finish: The unmatched machinability is essential for producing complex EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) electrodes.
Ultimately, choosing isostatic graphite is an investment in performance, reliability, and precision under the most demanding operational conditions.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Isotropic Structure | Uniform strength & conductivity in all directions |
| High Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid temperature changes |
| Ultra-High Purity (<5 ppm) | Ideal for contamination-sensitive processes |
| Excellent Machinability | Allows for complex, precise components |
| High-Temperature Strength | Gets stronger under extreme heat |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with isostatic graphite components from KINTEK.
As a leading supplier of high-performance lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK provides isostatic graphite solutions for the most demanding applications. Whether you need crucibles for semiconductor processing, EDM electrodes for precision machining, or furnace components for high-temperature research, our materials deliver unmatched purity, thermal stability, and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how isostatic graphite can solve your specific challenges and enhance your process efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of electrolytic polishing and electrolytic cells in FeCrAl sample prep? Reveal true structures.
- What is the purpose of alumina polishing powder in GCE pretreatment? Master Surface Prep for Electrochemistry
- How long does it take to solder? A guide to timing and technique for perfect joints
- What is the step-by-step process for polishing, testing, and cleaning an electrode? A Pro Guide for Precision Results
- What is the recommended polishing sequence for a disk electrode that has scratches? Restore Your Surface to a Mirror Finish



















