Levitation melting is a containerless metallurgical process that uses powerful electromagnetic fields to suspend and liquefy a metal in mid-air. By completely avoiding contact with a physical crucible, this technique prevents contamination that is common in traditional melting methods, making it essential for creating ultra-pure metals and alloys.
The core purpose of levitation melting is to achieve exceptional material purity. It solves the fundamental problem of contamination by replacing a physical container with a precisely shaped electromagnetic field that both holds and heats the metal.

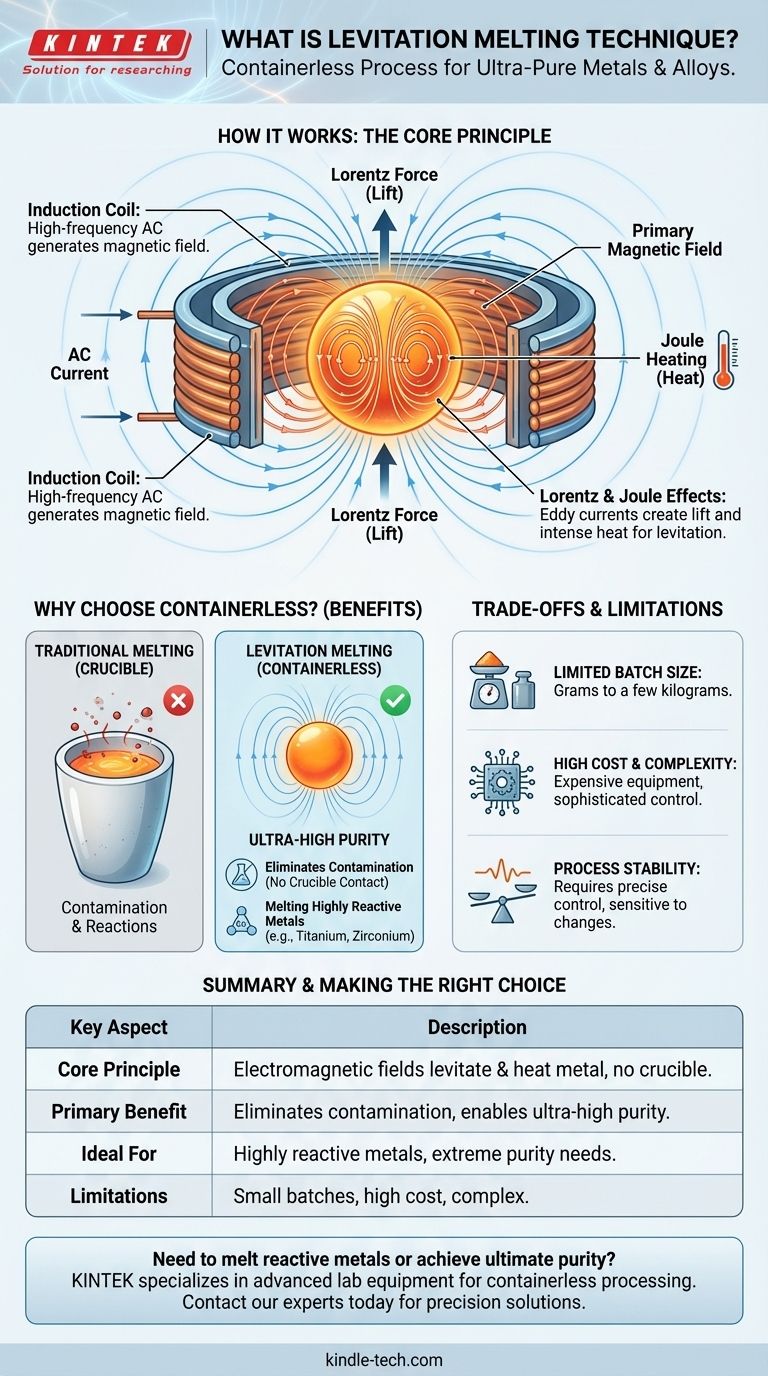
The Core Principle: How Levitation Melting Works
Levitation melting is an advanced form of induction heating that simultaneously generates two distinct effects from a single source: a lifting force and intense heat.
The Role of the Induction Coil
The process begins with a specially shaped, water-cooled copper coil. A high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil, which generates a strong and rapidly changing electromagnetic field in the space within and around it.
Generating Lift (The Lorentz Force)
This primary magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents within the conductive metal placed inside the coil. These are known as eddy currents. The eddy currents create their own secondary magnetic field, which opposes the primary field from the coil. This opposition creates a repulsive force, known as the Lorentz force, which pushes the metal upward, counteracting gravity and causing it to levitate.
Generating Heat (Joule Heating)
Simultaneously, the induced eddy currents encounter electrical resistance as they flow through the metal. This resistance converts electrical energy into thermal energy, a phenomenon called Joule heating. This effect is powerful enough to rapidly heat the metal past its melting point, turning the solid, levitating billet into a molten sphere suspended in space.
Why Choose a Containerless Process?
The decision to use a complex technique like levitation melting is driven entirely by the need to solve problems that are impossible to address with conventional crucible-based methods.
The Problem of Contamination
In traditional induction melting, the metal is held in a container, typically a ceramic or graphite crucible. At the extreme temperatures required for melting, the highly active molten metal can react with the crucible walls, leaching impurities directly into the melt.
Achieving Ultra-High Purity
For mission-critical applications in aerospace, electronics, or medical science, even minuscule levels of contamination can drastically alter a material's performance characteristics. Levitation melting eliminates the crucible, thereby removing the primary source of these impurities and enabling the production of materials with unparalleled purity.
Melting Highly Reactive Metals
Certain metals, such as titanium and zirconium, are so chemically reactive when molten that they will attack and degrade any known crucible material. For these materials, levitation melting is often one of the only viable methods to create a pure, homogenous liquid phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, levitation melting is a highly specialized technique with specific constraints that make it unsuitable for all applications.
Limited Batch Size
The strength of the levitating force is finite. Consequently, this method is only suitable for melting small quantities of material, typically grams to a few kilograms at most. It is not designed for large-scale industrial production.
High Cost and Complexity
The equipment required to generate and precisely control the powerful, high-frequency electromagnetic fields is complex and expensive. It demands sophisticated power supplies and control systems, representing a significant investment compared to standard furnace technology.
Process Stability
Maintaining the stable position and uniform temperature of a levitating molten droplet can be challenging. The process is sensitive to changes in power, frequency, and the shape of the molten mass, requiring careful monitoring and control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate melting technique depends entirely on your project's final requirements for purity, scale, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity: Levitation melting is the superior choice, as it is fundamentally designed to eliminate all sources of container-based contamination.
- If you are working with highly reactive or refractory metals: This technique is often the only practical method for melting materials that would otherwise react with a crucible.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production or cost-efficiency: Traditional crucible-based induction melting or other furnace methods are far more practical and economical.
By understanding its principles, you can identify when this advanced, containerless method is the critical tool needed to achieve exceptional material properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses electromagnetic fields to levitate and heat metal, avoiding crucible contact. |
| Primary Benefit | Eliminates contamination, enabling ultra-high purity metals and alloys. |
| Ideal For | Melting highly reactive metals (e.g., titanium) and applications requiring extreme purity. |
| Limitations | Limited batch size; high equipment cost and complexity. |
Need to melt reactive metals or achieve ultimate purity? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including solutions for containerless processing. Our expertise can help you select the right technology to meet your specific material science goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your research and development with precision laboratory solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More



















