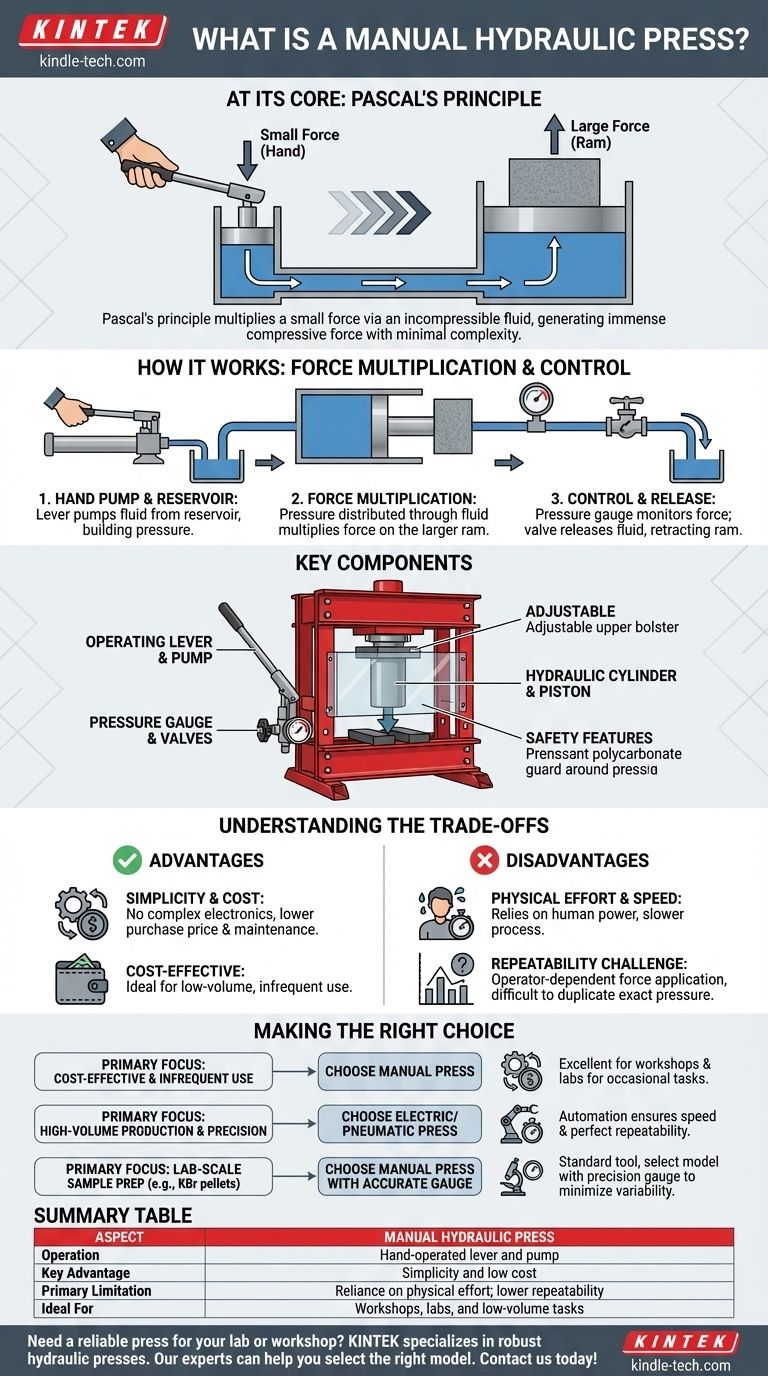
At its core, a manual hydraulic press is a machine that uses a hand-operated pump to generate immense compressive force. It works by applying Pascal's principle, where a small force exerted on a small piston via a lever is multiplied through an incompressible hydraulic fluid (typically oil) to create a much larger force on a bigger piston. This allows an operator to perform tasks like crushing, pressing, or forming materials with minimal electronic complexity.
A manual hydraulic press offers a simple and cost-effective method for generating significant force. However, its main advantage—simplicity—is also the source of its primary trade-offs: a reliance on physical effort and a challenge in achieving perfectly repeatable pressure.

How It Works: The Principle of Force Multiplication
The power of a manual hydraulic press comes from a fundamental principle of fluid mechanics. Understanding this is key to appreciating both its capabilities and its limitations.
The Role of the Hand Pump
The process begins with the operator moving a hand lever. This lever operates a small piston, known as the plunger, which pumps hydraulic fluid from a reservoir into the main cylinder system. Each pump of the lever introduces more fluid and builds pressure.
Force Multiplication via Fluid
The system is comprised of two interconnected cylinders of different sizes: the small plunger cylinder and the large ram cylinder. The pressure you create in the fluid is distributed equally throughout the entire system. Because the ram has a much larger surface area than the plunger, the resulting force exerted by the ram is proportionally larger, effectively multiplying your effort.
Controlling the Force
A manual press isn't just about brute force; it requires control. Most units are equipped with a pressure gauge to monitor the applied force and a pressure release valve. Turning this valve allows the hydraulic fluid to flow back into the reservoir, releasing the pressure and retracting the piston.
Key Components of a Manual Press
While designs vary, nearly all manual hydraulic presses share a common set of core components that enable their function.
The Hydraulic Cylinder and Piston
This is the heart of the press. It is a robust cylinder containing the main piston (the ram) that moves to apply force to the workpiece. The quality of its seals is critical to preventing leaks and maintaining pressure.
The Operating Lever and Pump
This is the user's interface. It is a simple mechanical lever connected to the plunger pump. The length of the lever provides mechanical advantage, making it easier for the operator to generate the initial high pressure in the fluid.
Pressure Gauges and Valves
An accurate pressure gauge is essential for knowing how much force is being applied. This is especially critical in scientific applications like sample preparation. Likewise, the release valve provides the necessary control to complete a task and reset the press.
Safety Features
Modern presses incorporate essential safety features. These often include strong polycarbonate safety guards to protect the operator from material failure under pressure and an adjustable upper bolster (the pressing block) to accommodate workpieces of different sizes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a manual press involves weighing its distinct advantages against its inherent limitations. Your specific application will determine if these trade-offs are acceptable.
Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
With no electronic components, motors, or complex wiring, a manual press is mechanically simple. This leads to a lower purchase price and reduced maintenance requirements compared to automated alternatives.
Disadvantage: Physical Effort and Speed
The most obvious drawback is the reliance on human power. Achieving high tonnage requires significant physical effort from the operator. This makes the process slower and less suitable for high-volume production environments.
Disadvantage: The Challenge of Repeatability
Because the force is entirely operator-dependent, it is very difficult to apply the exact same pressure across multiple samples. One operator might apply a slightly different force than another, or even differ from one press cycle to the next. This lack of precision can be a critical issue in quality-controlled manufacturing or scientific research.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use a manual hydraulic press depends entirely on your project's priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and infrequent use: A manual press is an excellent, straightforward choice for workshops or labs that need occasional high-force capability.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and precision: An electric or pneumatic press is a better investment, as automation ensures speed and perfectly repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale sample preparation (e.g., KBr pellets): A manual press is often the standard tool, but select a model with a clear, accurate pressure gauge to minimize variability.
By understanding its core principles and trade-offs, you can confidently determine if a manual hydraulic press is the right tool for your specific task.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Manual Hydraulic Press |
|---|---|
| Operation | Hand-operated lever and pump |
| Key Advantage | Simplicity and low cost |
| Primary Limitation | Reliance on physical effort; lower repeatability |
| Ideal For | Workshops, labs, and low-volume tasks |
Need a reliable press for your lab or workshop? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment, including robust hydraulic presses perfect for sample preparation and material testing. Our experts can help you select the right model to ensure cost-effective and efficient operation. Contact us today to find the perfect press for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hydraulic hot press machine? A Guide to Force and Heat for Material Transformation
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing



















