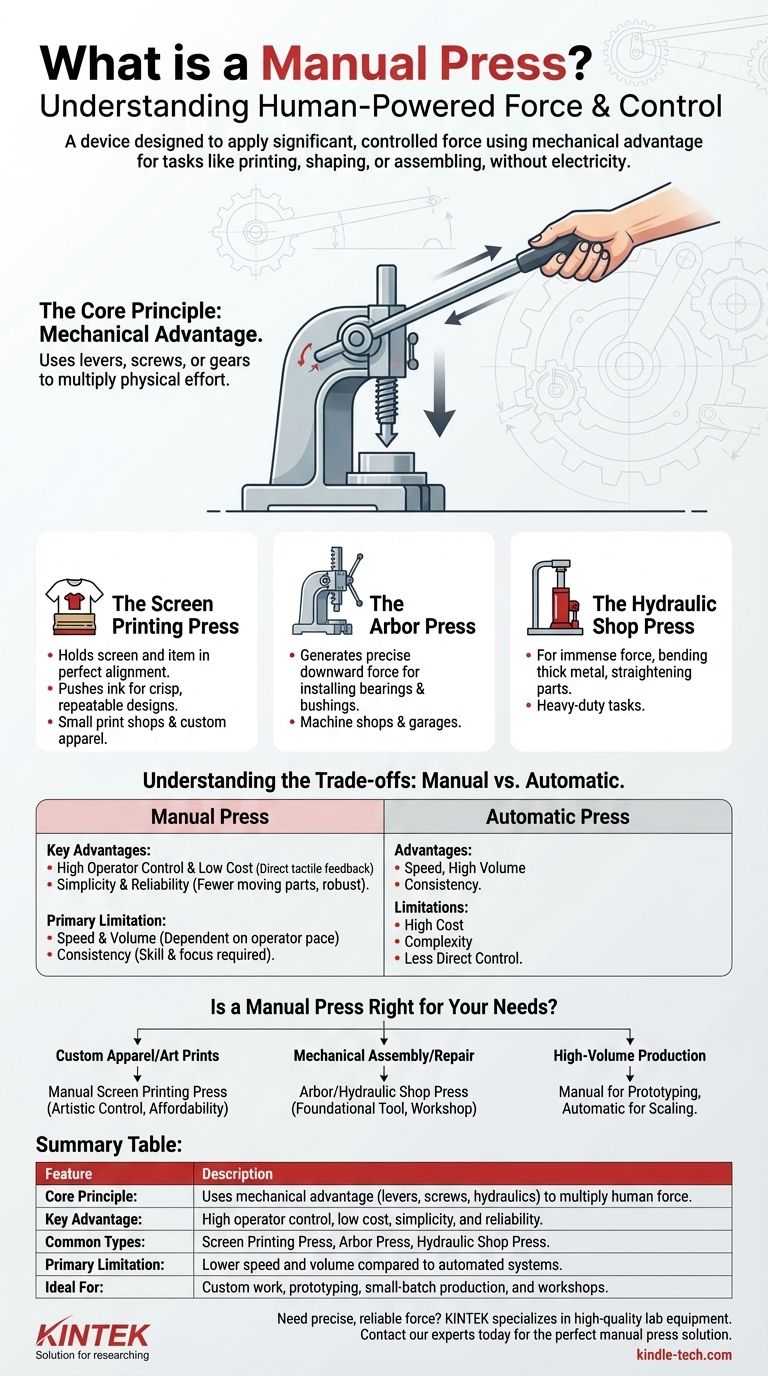
In simple terms, a manual press is any human-powered device designed to apply significant and controlled force to a specific area. It uses mechanical advantage—through levers, screws, or gears—to multiply the operator's physical effort, allowing for tasks like printing, shaping materials, or assembling components without the need for electricity or automation.
The core concept of a manual press is leverage. It's a foundational tool that translates modest human energy into powerful, precise force, making it essential for everything from small-scale manufacturing and art creation to workshop repairs.
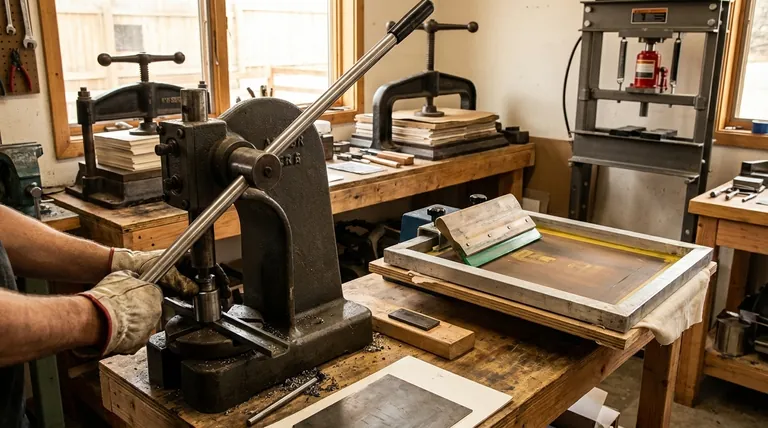

The Core Principle: Mechanical Advantage
A manual press is a direct application of physics. Its design is centered on making a difficult task physically manageable and repeatable.
How It Works: Levers, Screws, and Hydraulics
The "magic" of a manual press lies in its mechanism. A long handle, a finely threaded screw, or a hand-pumped hydraulic cylinder multiplies the force you apply.
This allows an operator to generate hundreds or even thousands of pounds of pressure with minimal physical strain.
The Goal: Precision and Repeatability
Beyond raw power, a press provides a rigid frame that ensures the force is applied consistently to the exact same spot, every single time.
This is critical for tasks like screen printing, where perfect alignment is necessary, or for pressing a bearing into a housing without damaging it.
The Human Element
With a manual press, the operator is in complete control. They can feel the pressure being applied and can adjust the speed and force in real-time, providing tactile feedback that automated systems lack.
Common Types of Manual Presses and Their Uses
The term "manual press" covers a wide range of tools, each tailored to a specific function. The context is key to understanding which type is being discussed.
The Screen Printing Press
This is one of the most common applications. A manual screen printing press holds a screen, a squeegee, and the item being printed (like a t-shirt or poster) in perfect alignment.
Operators use it to push ink through the screen's mesh, creating crisp, repeatable designs. They are the backbone of small print shops and custom apparel businesses.
The Arbor Press
Found in machine shops and garages, an arbor press uses a rack-and-pinion lever system to generate precise downward force.
Its primary use is for installing or removing bearings, bushings, and other interference-fit parts that require a steady, controlled press.
The Hydraulic Shop Press
For tasks requiring immense force, a manual hydraulic press is used. The operator pumps a handle, which pressurizes fluid in a cylinder to drive a ram.
These are used for bending thick metal, straightening parts, or forming materials—tasks that would be impossible by hand alone.
Other Familiar Examples
The principle extends to many other tools, including a drill press for controlled drilling, a book press for bookbinding, and even a French press for making coffee. Each uses a manual mechanism to apply controlled force.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Manual vs. Automatic
Choosing a manual press involves weighing its distinct advantages and limitations against automated alternatives.
Key Advantage: Control and Low Cost
Manual presses are significantly less expensive to purchase and maintain than their automatic counterparts. They offer direct, tactile feedback that many artisans and technicians value for custom or delicate work.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Reliability
With fewer moving parts and no reliance on electricity or compressed air, manual presses are incredibly robust and reliable. They are simple to understand, operate, and repair.
The Primary Limitation: Speed and Volume
The obvious downside is production speed. A manual press is entirely dependent on the operator's pace and stamina, making it unsuitable for high-volume mass production.
The Challenge of Consistency
While a press ensures alignment, consistency in pressure and speed over a long production run depends entirely on the operator's skill and focus. Operator fatigue can lead to variations that an automatic machine would avoid.
Is a Manual Press Right for Your Needs?
The right choice depends entirely on your specific goal, budget, and required production volume.
- If your primary focus is custom apparel or art prints: A manual screen printing press offers the perfect balance of artistic control and affordability for small-to-medium batches.
- If your primary focus is mechanical assembly or repair: An arbor or hydraulic shop press is an essential, foundational tool for any professional or hobbyist workshop.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: A manual press is an excellent tool for prototyping, but you should investigate automatic alternatives for scaling your output.
Ultimately, understanding the function of a manual press is about recognizing the power of controlled, human-directed force.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses mechanical advantage (levers, screws, hydraulics) to multiply human force. |
| Key Advantage | High operator control, low cost, simplicity, and reliability. |
| Common Types | Screen Printing Press, Arbor Press, Hydraulic Shop Press. |
| Primary Limitation | Lower speed and volume compared to automated systems. |
| Ideal For | Custom work, prototyping, small-batch production, and workshops. |
Need precise, reliable force for your lab or workshop? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables. Whether you're pressing samples, assembling components, or creating custom prints, the right manual press is key to your success. Contact our experts today to find the perfect manual press for your specific application and enhance your productivity with KINTEK's reliable solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy



















