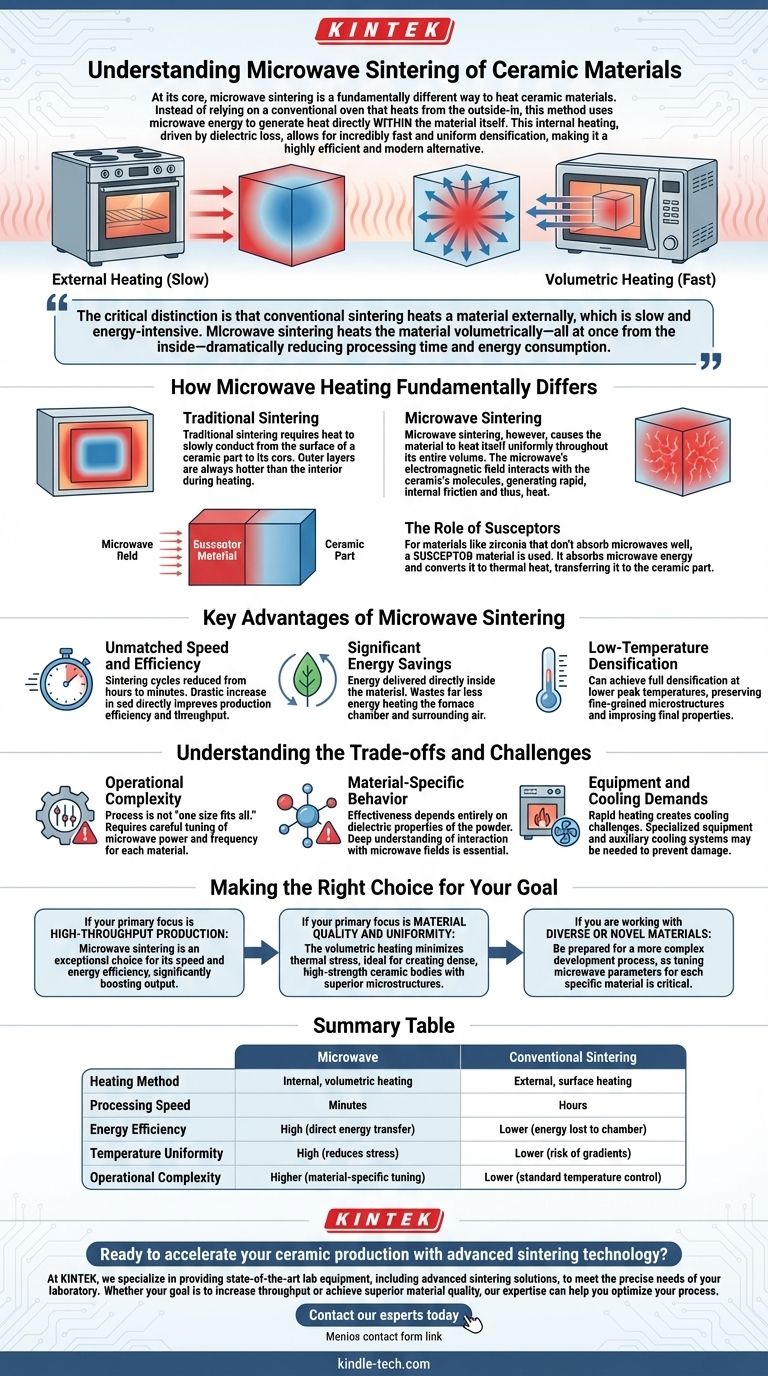
At its core, microwave sintering is a fundamentally different way to heat ceramic materials. Instead of relying on a conventional oven that heats from the outside-in, this method uses microwave energy to generate heat directly within the material itself. This internal heating, driven by a property called dielectric loss, allows for incredibly fast and uniform densification, making it a highly efficient and modern alternative.
The critical distinction is that conventional sintering heats a material externally, which is slow and energy-intensive. Microwave sintering heats the material volumetrically—all at once from the inside—dramatically reducing processing time and energy consumption.

How Microwave Heating Fundamentally Differs
Traditional sintering requires heat to slowly conduct from the surface of a ceramic part to its core. Microwave sintering bypasses this limitation entirely, leading to a more controlled and efficient process.
The Principle of Volumetric Heating
In a conventional furnace, the outer layers of the ceramic are always hotter than the interior during the heating phase.
Microwave sintering, however, causes the material to heat itself uniformly throughout its entire volume. This is achieved as the microwave's electromagnetic field interacts with the ceramic's molecules, generating rapid, internal friction and thus, heat.
Uniform Temperature, Reduced Stress
This uniform heating minimizes the internal temperature gradients that can cause stress, warping, or cracking in ceramic components. The result is often a more densified and structurally sound final product.
The Role of Susceptors
Some ceramic materials, like certain forms of zirconia, do not respond effectively to microwave energy on their own.
In these cases, a susceptor material is used. The susceptor is a different material that readily absorbs microwave energy and converts it to thermal heat, which is then transferred to the ceramic part. It effectively acts as an internal heating element powered by microwaves.
Key Advantages of Microwave Sintering
The shift from external to internal heating provides several significant advantages in ceramic manufacturing.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because the material heats so quickly and uniformly, sintering cycles can be reduced from many hours to mere minutes. This drastic increase in speed directly improves production efficiency and throughput.
Significant Energy Savings
By delivering energy directly where it is needed—inside the material—microwave sintering wastes far less energy heating the furnace chamber and surrounding air. This results in substantial energy savings compared to conventional methods.
Low-Temperature Densification
The unique heating mechanism can often achieve full densification at lower peak temperatures than traditional sintering. This can help preserve fine-grained microstructures and improve the final properties of the ceramic.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, microwave sintering is not a universally simple solution and comes with its own set of technical considerations.
Operational Complexity
The process is not "one size fits all." Different ceramic materials require careful tuning of the microwave power and frequency to achieve optimal results. This makes the operation more complex than setting a temperature on a conventional furnace.
Material-Specific Behavior
The effectiveness of microwave sintering is entirely dependent on the dielectric properties of the powder being used. A deep understanding of your material's interaction with microwave fields is essential for success.
Equipment and Cooling Demands
The rapid heating cycles can also create challenges for cooling. Specialized equipment, sometimes with auxiliary cooling systems, may be required to manage the thermal cycle effectively and prevent damage to the furnace or the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use microwave sintering depends on balancing its clear benefits in speed and efficiency against its operational complexity.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: Microwave sintering is an exceptional choice for its speed and energy efficiency, capable of significantly boosting output.
- If your primary focus is material quality and uniformity: The volumetric heating minimizes thermal stress, making it ideal for creating dense, high-strength ceramic bodies with superior microstructures.
- If you are working with diverse or novel materials: Be prepared for a more complex development process, as tuning microwave parameters for each specific material is critical to success.
Ultimately, microwave sintering represents a powerful evolution in ceramic processing, offering a path to faster, more efficient, and often superior material outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Microwave Sintering | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal, volumetric heating | External, surface heating |
| Processing Speed | Minutes | Hours |
| Energy Efficiency | High (direct energy transfer) | Lower (energy lost to chamber) |
| Temperature Uniformity | High (reduces stress) | Lower (risk of gradients) |
| Operational Complexity | Higher (material-specific tuning) | Lower (standard temperature control) |
Ready to accelerate your ceramic production with advanced sintering technology?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment, including advanced sintering solutions, to meet the precise needs of your laboratory. Whether your goal is to increase throughput or achieve superior material quality, our expertise can help you optimize your process.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can bring unmatched speed, efficiency, and performance to your ceramic manufacturing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations



















