In essence, the MPCVD method is a highly controlled process that uses microwave energy to generate a specialized plasma for growing high-purity thin films. Short for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition, this technique is the industry standard for creating high-quality synthetic diamonds and other advanced materials by carefully depositing atoms onto a substrate from a gas state.
MPCVD's distinct advantage lies in its ability to create a non-equilibrium plasma. It uses targeted microwave energy to create hyper-energetic electrons for chemical reactions while keeping the overall gas and substrate at a much lower temperature, ensuring both high purity and process stability.

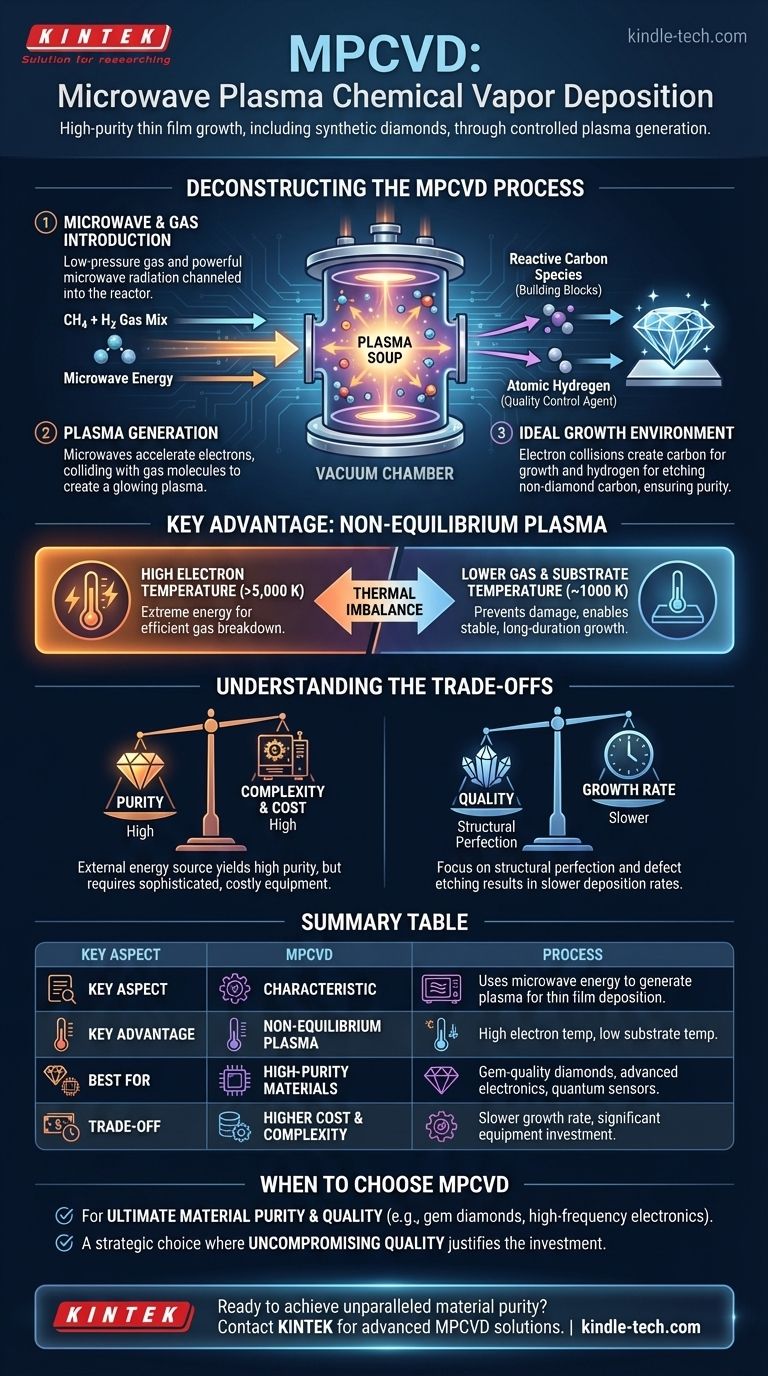
Deconstructing the MPCVD Process
To understand MPCVD, it's best to break it down into its fundamental steps. The entire process takes place within a sealed vacuum chamber where gases can be precisely controlled.
### The Role of Microwaves
The process begins with the introduction of low-pressure gas into the reactor, typically a mixture of a carbon source (like methane) and a large excess of hydrogen. Microwave radiation, similar to that in a kitchen oven but far more powerful and focused, is then channeled into the chamber.
### Generating the Plasma
This intense microwave energy does not heat the gas directly. Instead, it energizes the free electrons within the gas, accelerating them to extreme speeds. These high-energy electrons collide with the neutral gas molecules (methane and hydrogen), stripping them of their own electrons and breaking them apart.
The result is a plasma: a glowing, ionized gas soup consisting of electrons, ions, and highly reactive molecular fragments.
### Creating the Ideal Growth Environment
This plasma is the engine of MPCVD. The electron collisions create two critical components:
- Reactive Carbon Species: These are the broken-down fragments of the methane molecules, which serve as the fundamental building blocks for the diamond film.
- Atomic Hydrogen: This is the quality control agent. It selectively etches away any non-diamond carbon (like graphite) that might form, ensuring the growing film has a pure, crystalline diamond structure.
The Key Advantage: Non-Equilibrium Plasma
The true elegance of MPCVD is its ability to create a thermal imbalance. The different components inside the plasma exist at radically different temperatures, which is the key to its success.
### High Electron Temperature
The electrons, directly absorbing the microwave energy, can reach temperatures exceeding 5,000 K. This extreme energy makes them incredibly effective at breaking down the precursor gases, far more efficient than simple thermal heating.
### Lower Gas Temperature
Simultaneously, the bulk gas and the substrate upon which the diamond grows remain much cooler, often around 1000 K. This lower temperature is crucial as it prevents damage to the substrate and the reactor itself, allowing for stable, long-duration growth runs essential for thick, high-quality films.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No method is perfect. The precision of MPCVD comes with specific considerations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
### Purity vs. Complexity
MPCVD is renowned for producing some of the purest materials possible because the energy source (microwaves) is external. There are no internal heating elements, like the hot filaments in other CVD methods, that can degrade and introduce contaminants into the film.
The trade-off for this purity is complexity and cost. MPCVD systems require sophisticated microwave generators, waveguides, and vacuum technology, making the initial equipment investment significantly higher than simpler methods.
### Quality vs. Growth Rate
The highly controlled nature of the MPCVD environment, especially the role of atomic hydrogen in etching away defects, often results in a slower deposition rate compared to other techniques. The focus is squarely on structural perfection, not speed.
When to Choose MPCVD
Your choice of deposition method should be driven entirely by your end goal. MPCVD is a specialized tool for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity and quality: MPCVD is the undisputed choice for applications like gem-quality diamonds, high-frequency electronics, quantum sensors, and durable optical windows.
- If your primary focus is rapid growth or lower initial cost: A simpler method like Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD) may be more appropriate, provided you can tolerate a higher potential for contamination and slightly lower material quality.
Ultimately, selecting MPCVD is a strategic choice for applications where uncompromising material quality justifies the investment in its sophisticated and highly controlled process.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | MPCVD Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses microwave energy to generate plasma for thin film deposition |
| Key Advantage | Non-equilibrium plasma: high electron temperature, low substrate temperature |
| Best For | High-purity materials, gem-quality diamonds, advanced electronics |
| Trade-off | Higher equipment cost and complexity, slower growth rate |
Ready to achieve unparalleled material purity in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment like MPCVD systems, providing the precision and reliability needed for high-quality diamond synthesis and material research. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the CVD process diamond? A Guide to Lab-Grown Diamonds for Industrial Use
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- Is synthetic the same as lab grown? Yes, and here's why it matters for your diamond choice.
- What is the structure of DLC film? A Tunable Amorphous Mix of Diamond and Graphite Bonds
- What is MP CVD? Unlock the Power of Microwave Plasma for High-Purity Diamond Synthesis
- Are all lab grown diamonds CVD? Understanding the Two Main Methods
- What are synthetic diamonds used for in industry? Powering High-Tech Tools and Electronics
- What is the process of MPCVD? Grow High-Purity Diamond & Advanced Films



















