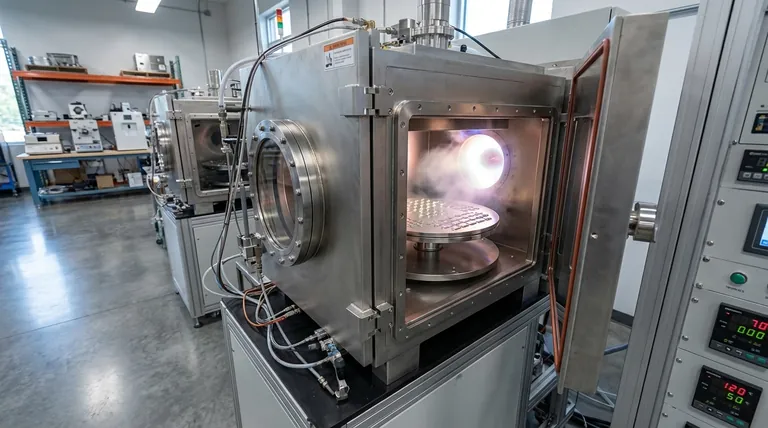
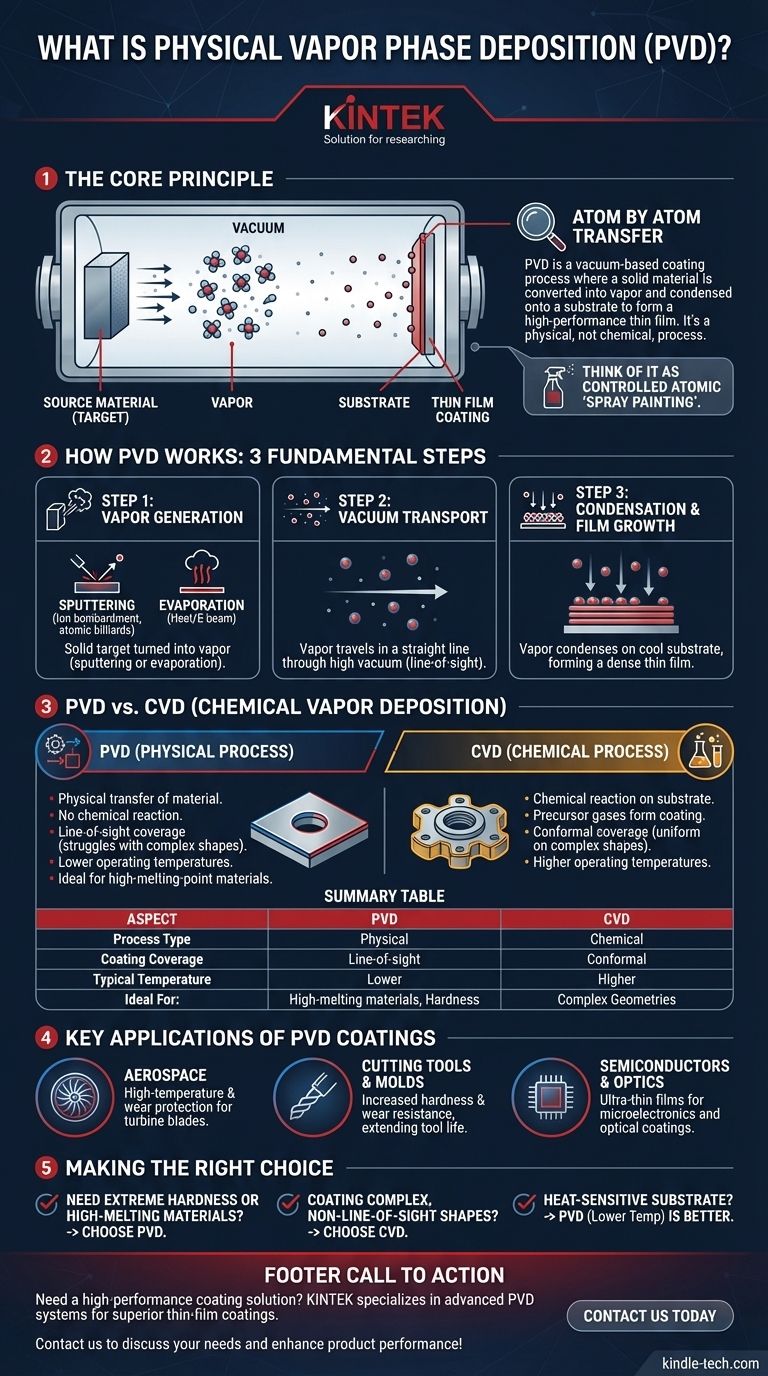
In essence, physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a vacuum-based coating process where a solid material is converted into a vapor, transported across a vacuum chamber, and condensed onto a substrate's surface to form a high-performance thin film. Unlike a chemical process, PVD is a physical one; it is fundamentally a method of transferring a material from a source to a part, atom by atom.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is best understood as a highly controlled "spray painting" process using individual atoms or molecules. Its primary advantage lies in creating extremely hard, thin, and adherent coatings from materials that are difficult to work with otherwise, but its "line-of-sight" nature presents limitations that other methods, like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), can overcome.

How PVD Works: The Core Principle
PVD processes occur under a high vacuum and generally consist of three fundamental steps. The quality of the vacuum is critical, as it prevents contamination and ensures the vaporized atoms can travel to the substrate without colliding with air molecules.
Step 1: Generation of Vapor
The first step is to turn the solid coating material, known as the "target," into a vapor. This is typically achieved through one of two main methods.
Sputtering involves bombarding the target with high-energy ions (usually an inert gas like argon), which physically knock atoms off the target's surface. Think of it as a microscopic game of atomic billiards.
Evaporation uses heat to raise the temperature of the target material until it evaporates or sublimes. This can be done with resistive heaters or, for materials with very high melting points, with a high-energy electron beam (e-beam evaporation).
Step 2: Transport Through a Vacuum
Once vaporized, the atoms or molecules of the coating material travel through the vacuum chamber. Because there is virtually no air to impede them, they travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate.
This "line-of-sight" transport is a defining characteristic of PVD.
Step 3: Condensation and Film Growth
When the vaporized atoms reach the cooler surface of the substrate (the part being coated), they condense and form a thin, solid film. This film grows layer by layer, creating a highly dense and well-adhered coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. CVD
To truly understand PVD, it is crucial to compare it with its main alternative: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Their names hint at their core difference.
The Process: Physical vs. Chemical
PVD is a physical process. It moves existing material from a source to a substrate. No fundamental chemical reaction is required to form the final film.
CVD is a chemical process. It introduces precursor gases into a chamber, which then react on the hot surface of the substrate to form a new solid material as the coating. The coating is created in situ through a chemical change.
Coverage: Line-of-Sight vs. Conformal
PVD's line-of-sight nature is both a strength and a weakness. It creates very dense coatings on surfaces directly facing the source, but it struggles to uniformly coat complex shapes, sharp corners, or the inside of holes.
CVD's use of a gas allows it to flow around the part and react on all exposed surfaces. This results in a highly conformal coating that has a uniform thickness even on intricate and complex geometries.
Operating Temperature and Materials
PVD processes can often be performed at lower temperatures than traditional CVD. This makes PVD suitable for coating materials that cannot withstand high heat.
Furthermore, PVD excels at depositing materials with extremely high melting points, such as ceramics and refractory metals, which are difficult or impossible to vaporize through chemical precursors used in CVD.
Key Applications of PVD Coatings
The unique properties of PVD coatings—high hardness, low friction, and corrosion resistance—make them invaluable across several industries.
Aerospace and High-Performance Components
Aerospace companies use PVD to apply dense, temperature-resistant coatings to components like turbine blades. These coatings protect the underlying metal from the extreme heat and stress of a jet engine, enhancing durability.
Cutting Tools and Molds
A major application for PVD is coating cutting tools, drills, and manufacturing molds. A thin layer of a material like titanium nitride can dramatically increase the tool's hardness and wear resistance, extending its life significantly.
Semiconductors and Optics
The precision of PVD makes it ideal for depositing the ultra-thin metallic and dielectric films required in semiconductor manufacturing. It is also used to apply anti-reflective and other optical films for solar panels and lenses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the fundamental difference between physical transfer (PVD) and chemical reaction (CVD) is the key to selecting the correct technology.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness or coating with refractory metals: PVD is often the superior choice due to its ability to handle high-melting-point materials and create exceptionally dense films.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-line-of-sight geometries: CVD's ability to produce a highly uniform, conformal coating is a significant and often decisive advantage.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive substrate: Lower-temperature PVD variants provide a critical advantage over many high-temperature CVD processes.
Ultimately, choosing the right deposition method requires aligning the process capabilities with the specific performance demands and geometry of your component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical transfer of material | Chemical reaction on substrate |
| Coating Coverage | Line-of-sight (limited on complex shapes) | Conformal (uniform on all surfaces) |
| Typical Temperature | Lower temperatures | Higher temperatures |
| Ideal For | High-melting-point materials, extreme hardness | Complex geometries, intricate parts |
Need a high-performance coating solution for your lab equipment or components? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including PVD systems, to help you achieve superior thin-film coatings with exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and durability. Whether you're in aerospace, tooling, or semiconductor manufacturing, our expertise ensures you get the right deposition technology for your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how our PVD solutions can enhance your product performance and longevity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- What is the difference between PECVD and sputter? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















