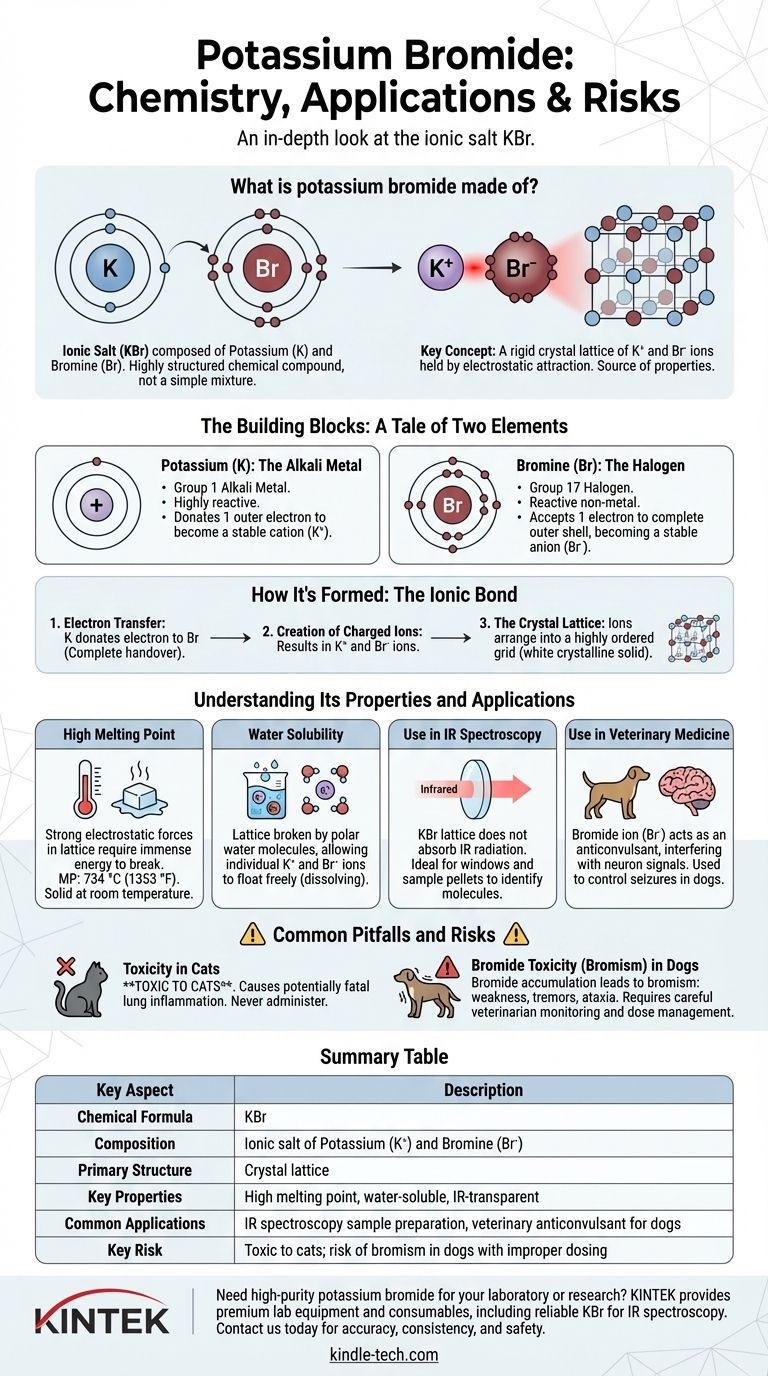
In short, potassium bromide is an ionic salt composed of the elements potassium and bromine. It is not a simple mixture but a highly structured chemical compound with the formula KBr. The potassium atom donates an electron to the bromine atom, creating charged particles (ions) that are held together by a strong electrostatic attraction.
The key to understanding potassium bromide is to see it not as a collection of atoms, but as a rigid crystal lattice of positively charged potassium ions and negatively charged bromide ions. This ionic structure is the source of its most important properties and applications.

The Building Blocks: A Tale of Two Elements
Potassium bromide's existence is a direct result of the fundamental chemical properties of its two constituent elements. Each has a strong "desire" to achieve a more stable electron configuration.
Potassium (K): The Alkali Metal
Potassium is a soft, highly reactive metal found in Group 1 of the periodic table. Its defining characteristic is having a single electron in its outermost shell.
It is far more stable energetically if it gives away this lone electron. By doing so, it becomes a positively charged ion (K⁺).
Bromine (Br): The Halogen
Bromine is a reactive non-metal from Group 17, the halogens. Its defining feature is having seven electrons in its outer shell, just one short of a full, stable set of eight.
It readily accepts one electron to complete this shell, becoming a negatively charged ion (Br⁻), known as a bromide ion.
How It's Formed: The Ionic Bond
The formation of potassium bromide is a classic example of an ionic bond, which is defined by the transfer, not the sharing, of electrons.
The Electron Transfer
When potassium metal and bromine react, each potassium atom donates its single outer electron to a bromine atom. This is not a gentle sharing but a complete handover.
Creation of Charged Ions
This electron transfer results in two stable, but now charged, particles: the potassium cation (K⁺) and the bromide anion (Br⁻). Because opposite charges attract, they are powerfully drawn to one another.
The Crystal Lattice
These positive and negative ions do not form simple pairs. Instead, they arrange themselves into a highly ordered, repeating three-dimensional grid called a crystal lattice. This strong, rigid structure is what makes potassium bromide a white, crystalline solid at room temperature.
Understanding Its Properties and Applications
The ionic nature of potassium bromide directly explains its physical and chemical behavior, which in turn dictates its uses.
High Melting Point
The powerful electrostatic forces holding the K⁺ and Br⁻ ions together in the crystal lattice require a tremendous amount of energy to break. This is why KBr is a solid with a high melting point of 734 °C (1353 °F).
Water Solubility
While the lattice is strong, it can be broken apart by polar molecules like water. The water molecules surround the individual K⁺ and Br⁻ ions, neutralizing their charge and allowing them to float freely, which we perceive as the salt dissolving.
Use in IR Spectroscopy
The KBr crystal lattice does not absorb infrared radiation. This transparency makes it an ideal material for creating windows and sample pellets used in IR spectroscopy, a technique that helps chemists identify molecules.
Use in Veterinary Medicine
The bromide ion (Br⁻) can act as an anticonvulsant by interfering with chloride ion transport in the neurons of the central nervous system. For this reason, KBr is used in veterinary medicine to control seizures in dogs.
Common Pitfalls and Risks
While useful, potassium bromide is not without its risks, which are critical to understand in its practical applications.
Toxicity in Cats
The primary risk is in veterinary use. Potassium bromide is toxic to cats, causing a potentially fatal inflammatory lung condition. It should never be administered to them.
Bromide Toxicity (Bromism) in Dogs
Even in dogs, where it is used therapeutically, the bromide ion can accumulate in the body over time. If levels become too high, it can lead to a condition called bromism, with symptoms like weakness, tremors, and ataxia. This requires careful dose management and monitoring by a veterinarian.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Your perspective on potassium bromide will depend entirely on your goal.
- If your primary focus is chemistry: See this as the quintessential example of an ionic bond formed between a Group 1 alkali metal and a Group 17 halogen.
- If your primary focus is laboratory analysis: Recognize that its IR transparency and ability to be pressed into a solid pellet are the key properties making it invaluable for sample preparation.
- If your primary focus is veterinary health: Understand that its therapeutic effect comes from the bromide ion, but this is inseparable from the serious risk of toxicity, especially in cats.
Ultimately, knowing that KBr is built from ions transferred between a metal and a non-metal is the foundation for understanding its every use and limitation.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | KBr |
| Composition | Ionic salt of potassium (K⁺) and bromine (Br⁻) |
| Primary Structure | Crystal lattice |
| Key Properties | High melting point, water-soluble, IR-transparent |
| Common Applications | IR spectroscopy sample preparation, veterinary anticonvulsant for dogs |
| Key Risk | Toxic to cats; risk of bromism in dogs with improper dosing |
Need high-purity potassium bromide for your laboratory or research? KINTEK specializes in providing premium lab equipment and consumables, including reliable KBr for IR spectroscopy and other applications. Our products ensure accuracy, consistency, and safety for your work. Contact us today to learn how we can support your laboratory needs with the right materials and expertise.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Stirring Bar Recovery Rod
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- How do you remove sputter coating? A Guide to Safe, Selective Removal
- What function do magnetic stirrers and high-shear homogenizers serve? Optimize Core-Shell PCM Synthesis
- What environmental conditions should be avoided when operating or storing a carbon fiber brush? Protect Your Investment from Damage
- What are the applications of semiconductor thin films? Powering the Core of Modern Electronics
- What is the correct procedure for post-use handling and cleaning of an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Ensure Purity and Longevity



















