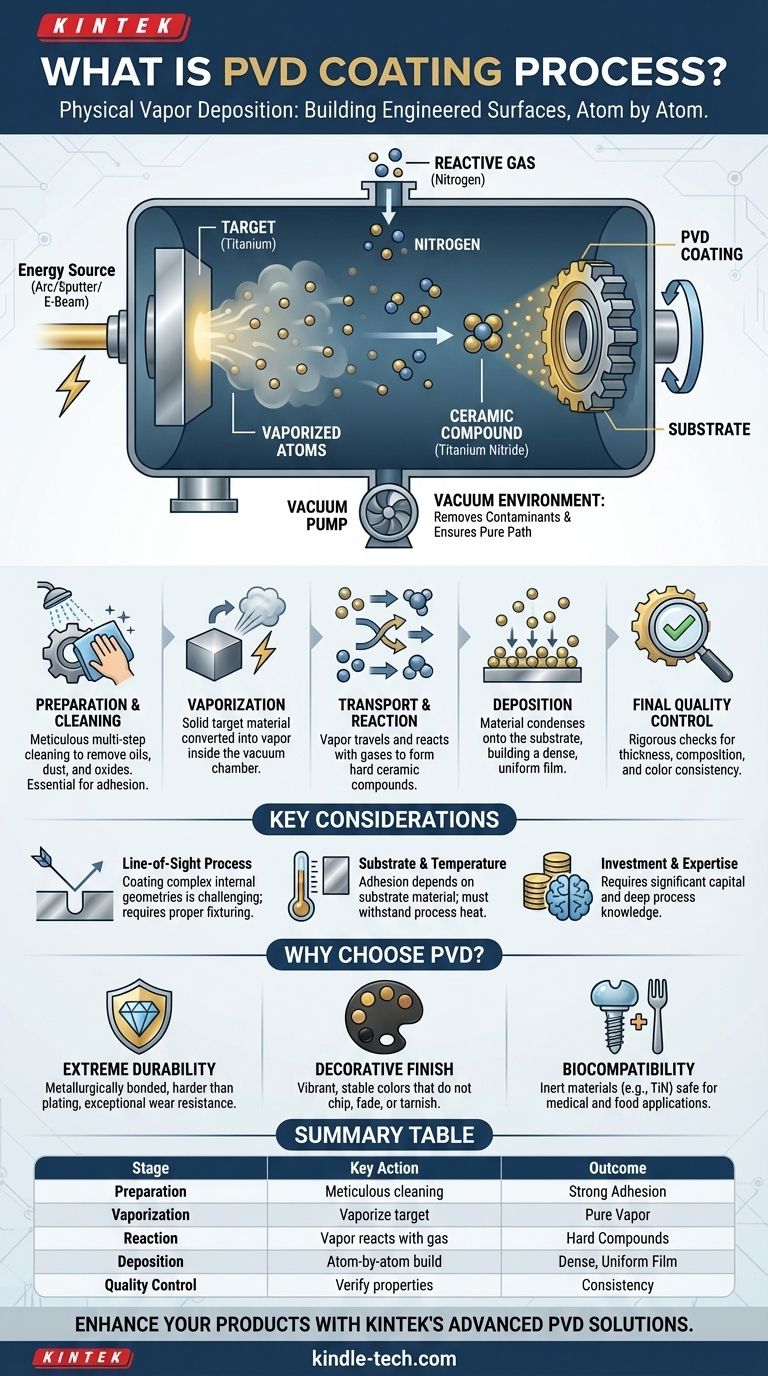
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum coating process that transfers a material on an atomic level. A solid source material, such as titanium or zirconium, is vaporized inside a vacuum chamber and then deposited as a thin, highly durable film onto the surface of a part or product. This atom-by-atom deposition creates a coating that is metallurgically bonded to the substrate, resulting in exceptional wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and hardness.
The crucial insight is that PVD is not simply applying a layer of paint or metal plating. It is a high-tech manufacturing process that builds a new, engineered surface directly on the substrate, one atom at a time, within a highly controlled vacuum environment.
The Foundation: Why a Vacuum is Essential
The entire P-V-D process—Physical Vapor Deposition—hinges on the "V" for vacuum. Understanding why this environment is non-negotiable is key to understanding the quality of the final coating.
Removing Contaminants
The primary purpose of the vacuum is to remove all other atoms and molecules from the chamber, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. If these particles were present, they would collide with the vaporized coating atoms, causing unwanted reactions and preventing a clean, strong bond with the substrate.
Ensuring a Pure Coating Path
A vacuum creates an unimpeded, "line-of-sight" path for the vaporized material to travel from its source (the target) to the product being coated (the substrate). This ensures the deposition is controlled and the resulting film is dense and uniform.
Deconstructing the PVD Process: A Step-by-Step Analysis
While the exact parameters vary by application, the process follows a consistent and logical sequence. It moves from meticulous preparation to atomic deposition and final quality assurance.
Step 1: Meticulous Preparation and Cleaning
The process begins long before the part enters the vacuum chamber. The substrate must be flawlessly clean. Any oils, dust, or oxides on the surface will prevent the coating from adhering properly. This stage often involves multi-step ultrasonic cleaning, chemical baths, and drying. For parts with existing coatings, a stripping process may be required first.
Step 2: Vaporization (Ablation)
Once inside the sealed vacuum chamber, the solid source material, known as a 'target', is converted into a vapor. This is the "Physical Vapor" part of the name.
Common methods for this include:
- Arc Discharge: A high-current electric arc is applied to the target, creating a localized hot spot that evaporates the material.
- Sputtering: The target is bombarded with high-energy ions (usually argon) from a plasma, which physically knocks atoms off its surface.
- Electron Beam: A powerful beam of electrons is focused on the target in a crucible, heating it to its boiling point.
Step 3: Transportation and Reaction
The vaporized metal atoms travel through the vacuum toward the substrate. At this stage, a reactive gas (such as nitrogen, carbon, or oxygen) is often precisely introduced into the chamber.
These gases react with the metal vapor to form a new ceramic compound. For example, titanium vapor reacting with nitrogen gas forms titanium nitride (TiN), a very hard, gold-colored ceramic. This reaction step is what determines the coating's final color, hardness, and chemical properties.
Step 4: Deposition
The vaporized material (now often a metal-gas compound) condenses onto the cooler surface of the substrate. This deposition happens atom by atom, building a thin, dense, and highly structured film. The parts are often rotated on fixtures to ensure the coating is applied evenly across all surfaces.
Step 5: Final Quality Control
After the process, which can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours, the parts are cooled and removed. Rigorous quality control checks are performed to ensure consistency and adherence to specifications. This typically involves using an X-ray fluorescent (XRF) machine to verify the coating's elemental composition and thickness, and a spectrophotometer to measure its exact color.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
PVD is a powerful technology, but it's important to understand its operational realities.
It Is a Line-of-Sight Process
Because the vaporized atoms travel in straight lines, coating complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes can be challenging. Proper fixturing and rotation of the parts are critical to achieving uniform coverage on complex shapes.
Substrate and Temperature Matter
The adhesion and performance of the PVD coating depend heavily on the substrate material it's being applied to. The process also generates heat, so the substrate must be able to withstand the temperatures inside the chamber without deforming or losing its properties.
Investment and Expertise
PVD coating requires significant capital investment in vacuum chambers, power supplies, and quality control equipment. It is not a simple process and relies on deep process expertise to manage the variables of temperature, pressure, gas mixtures, and power levels correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the PVD process allows you to specify it effectively for your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability: Leverage the fact that PVD creates a metallurgically bonded ceramic layer that is far harder and more wear-resistant than traditional plating or painting.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish: Specify the correct reactive gas to achieve a wide range of stable, vibrant colors (like gold, black, or bronze) that will not chip, fade, or tarnish.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility or chemical resistance: Choose inert PVD materials like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), which are safe for medical implants and food-grade applications.
By understanding that PVD is fundamentally a process of building a new surface from individual atoms, you can better leverage its unique capabilities for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| PVD Process Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Meticulous substrate cleaning | Ensures strong coating adhesion |
| Vaporization | Solid target material is vaporized in a vacuum | Creates a pure vapor for deposition |
| Transport & Reaction | Vapor reacts with gases (e.g., Nitrogen) | Forms hard ceramic compounds (e.g., TiN) |
| Deposition | Atoms condense on the substrate | Builds a dense, uniform, metallurgically bonded film |
| Quality Control | Coating thickness and composition verified | Guarantees consistency and performance |
Ready to enhance your products with a superior PVD coating?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise PVD coating processes. Whether you need to improve durability, achieve specific decorative finishes, or ensure biocompatibility, our solutions are designed to meet the exacting demands of laboratory and industrial applications.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you leverage PVD technology for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















