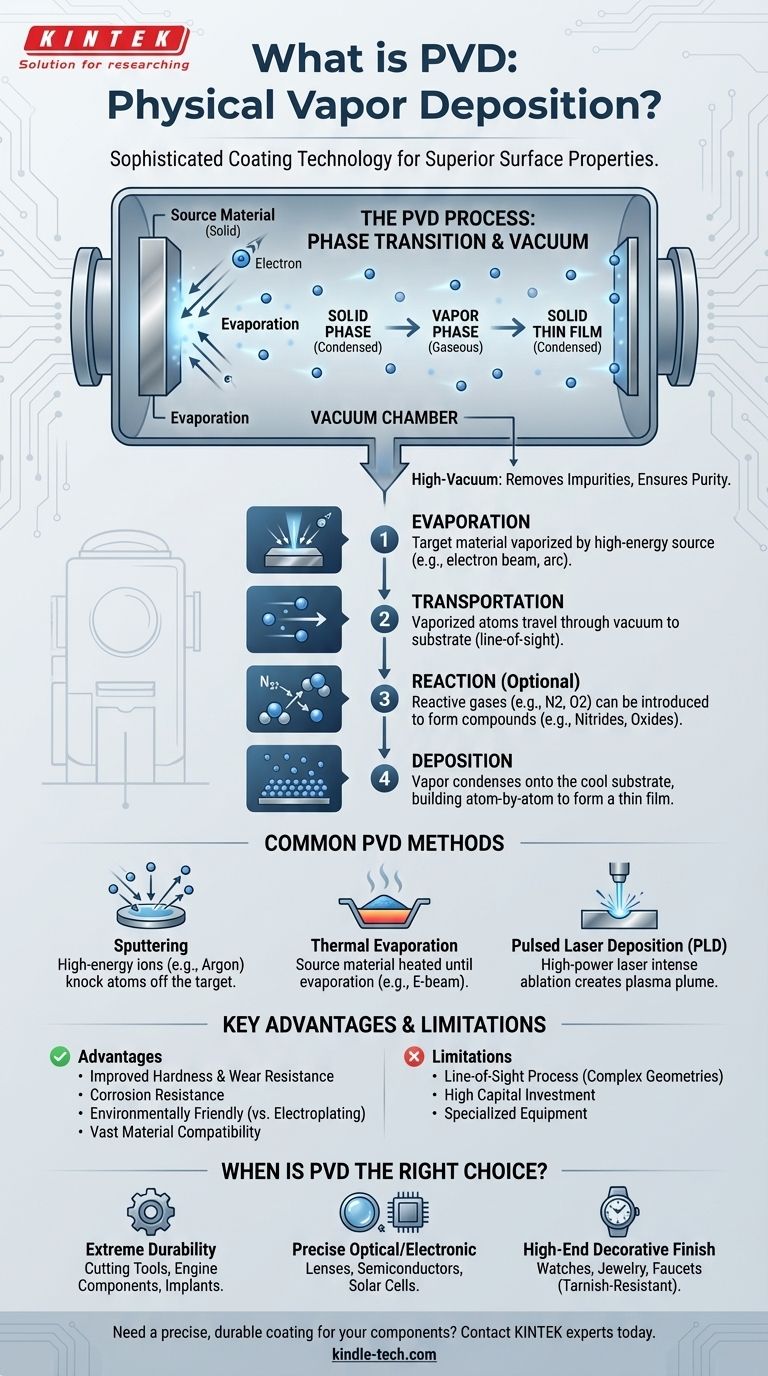
In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a sophisticated coating technology used to apply an extremely thin, high-performance film onto a surface. The process involves taking a solid source material, vaporizing it in a vacuum, and then allowing those vaporized atoms or molecules to condense onto a target object, forming the desired coating.
PVD is not a single technique but a family of vacuum-based processes that physically transfer material atom-by-atom from a source to a substrate. This method allows for the creation of ultra-thin films with properties—such as hardness or conductivity—that are often superior to the base material itself.

How PVD Fundamentally Works
The Core Principle: Phase Transition
The PVD process is defined by a material's journey through different physical states.
It begins with the coating material in a solid, condensed phase. It is then converted into a gaseous, vapor phase. Finally, it returns to a condensed phase as it deposits onto the substrate, forming a solid thin film.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
This entire process occurs within a high-vacuum chamber.
The vacuum is essential because it removes air and other particles that could otherwise react with or impede the vaporized material as it travels from the source to the substrate, ensuring a pure and uniform coating.
The Four Key Stages of the PVD Process
While specific methods vary, they all follow a general four-step sequence.
1. Evaporation
The process begins by turning the solid source material (known as the "target") into a vapor.
This is accomplished by bombarding the target with a high-energy source, such as an electron beam, an electrical arc, or ions, which dislodges atoms from its surface.
2. Transportation
Once vaporized, these atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum chamber.
Because there is little to no air to interfere, they travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate, which is the object being coated.
3. Reaction (Optional)
In some applications, reactive gases like nitrogen, oxygen, or acetylene are introduced into the vacuum chamber.
The vaporized metal atoms react with these gases during their journey to form new compounds, such as nitrides or oxides, which can give the final coating specific properties like extreme hardness or a particular color.
4. Deposition
Finally, the vaporized material reaches the cooler surface of the substrate and condenses, building up atom by atom to form a thin, dense, and highly adherent film.
Common PVD Methods Explained
PVD is a category of techniques, each with a different way of creating the initial vapor.
Sputtering
In sputtering, the target is bombarded with high-energy ions (typically of an inert gas like argon). This acts like a subatomic sandblaster, knocking atoms off the target material, which then deposit onto the substrate.
Thermal Evaporation
This is one of the simplest methods. The source material is heated in the vacuum chamber until it evaporates, creating a vapor cloud that condenses on the substrate. E-beam evaporation is a more precise version that uses a focused electron beam to heat the material.
Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD)
In this technique, a high-power laser is aimed at the target material. The intense energy of the laser pulse instantly ablates (vaporizes) a small amount of the material, creating a plasma plume that then deposits onto the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
Key Advantages of PVD
PVD is chosen for its significant benefits. It can deposit coatings with improved properties, such as enhanced hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
The range of usable materials is vast, covering almost any inorganic material and even some organic ones. Furthermore, it is considered more environmentally friendly than traditional processes like electroplating, which often involve hazardous chemicals.
PVD vs. CVD: A Key Distinction
PVD is often compared to Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The primary difference is that PVD is a physical process (vaporizing a solid), while CVD is a chemical process.
In CVD, precursor gases are introduced into a chamber and react on the surface of the hot substrate to form the film. PVD is typically a lower-temperature, "line-of-sight" process, whereas CVD can often coat more complex geometries but requires higher temperatures.
Common Limitations
The "line-of-sight" nature of most PVD processes means they are excellent for coating flat or gently curved surfaces but can struggle to uniformly coat the inside of complex shapes or hidden areas. The equipment is also highly specialized and represents a significant capital investment.
When is PVD the Right Choice?
Choosing PVD depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final product.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: PVD is the standard for creating hard, protective coatings on cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants.
- If your primary focus is precise optical or electronic properties: PVD is used to deposit anti-reflective coatings on lenses, conductive layers in semiconductors, and transparent electrodes on solar cells.
- If your primary focus is a high-end decorative finish: PVD provides a brilliant, tarnish-resistant finish for watches, faucets, and jewelry that is far more durable than traditional plating.
Ultimately, Physical Vapor Deposition is a powerful tool for engineering surfaces at the atomic level to achieve performance that the underlying material alone cannot provide.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (vacuum-based) |
| Common Methods | Sputtering, Thermal Evaporation, Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) |
| Key Advantage | Creates hard, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant coatings |
| Typical Applications | Cutting tools, medical implants, semiconductors, decorative finishes |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight process, can struggle with complex geometries |
Need a precise, durable coating for your components? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including PVD systems, to help you achieve superior surface properties for your R&D or production needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your product's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating



















