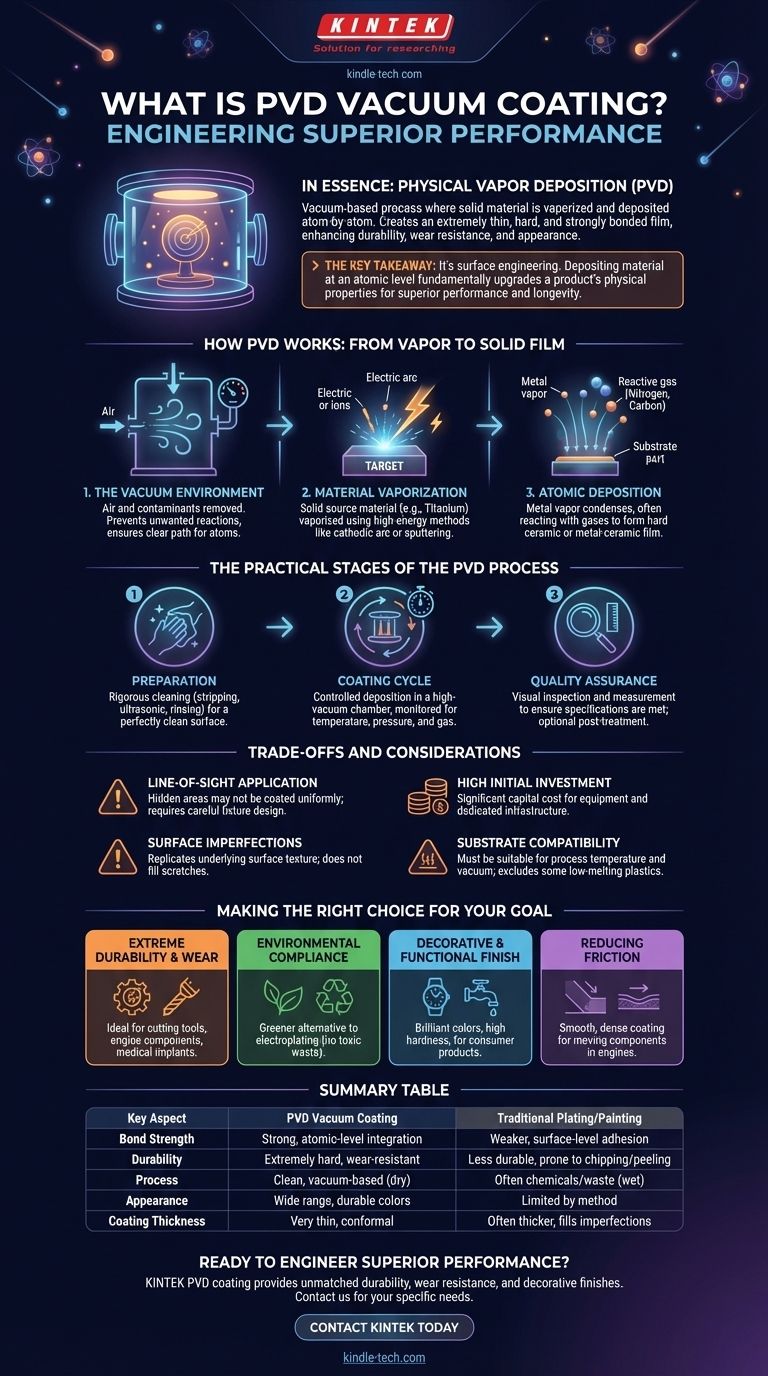
In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum-based coating process where a solid material is vaporized, and then deposited atom by atom onto a target object. This creates an extremely thin, hard, and strongly bonded film that enhances the part's durability, wear resistance, and appearance. Unlike traditional painting or plating, the coating becomes an integral part of the surface itself.
The key takeaway is that PVD is not merely a surface layer; it's a surface engineering technique. By depositing material at an atomic level in a vacuum, it fundamentally upgrades a product's physical properties, offering superior performance and longevity that conventional methods cannot match.

How PVD Works: From Vapor to Solid Film
To understand PVD's benefits, you must first understand its core mechanism. The entire process takes place within a high-vacuum chamber, a controlled environment that is critical to the outcome.
The Vacuum Environment
The process begins by creating a vacuum to remove virtually all air and other gaseous contaminants. This is crucial because it prevents any unwanted reactions with the vaporized coating material and ensures the atoms have a clear path to the substrate.
Material Vaporization
A solid source material, known as a 'target' (often a pure metal like titanium, zirconium, or chromium), is then vaporized. This is typically achieved through high-energy methods like cathodic arc vaporization, where an electric arc strikes the target, or sputtering, where the target is bombarded with ions.
Atomic Deposition
The resulting metal vapor travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses on the parts being coated. Often, a reactive gas like nitrogen or a carbon-based gas is introduced. The vaporized metal atoms react with this gas as they deposit, forming an extremely hard and durable ceramic or metal-ceramic film on the surface.
The Practical Stages of the PVD Process
Achieving a flawless PVD coating is a multi-step industrial process that demands precision at every stage.
Preparation is Paramount
Before entering the vacuum chamber, parts undergo rigorous cleaning and pre-treatment. This may involve stripping old coatings, ultrasonic cleaning, and rinsing to remove any oils, dust, or oxides. A perfectly clean surface is non-negotiable for proper adhesion.
The Coating Cycle
Parts are securely mounted on fixtures to ensure uniform exposure. Once inside the chamber, the PVD cycle begins, depositing the thin film over a period of time. This stage is highly controlled for temperature, pressure, and gas composition.
Quality Assurance and Finishing
After coating, parts undergo quality control. This includes visual inspection and often thickness measurements to ensure they meet specifications. Depending on the application, some parts might receive a final post-treatment to achieve a specific finish.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Line-of-Sight Application
The deposition process is fundamentally "line-of-sight." Areas that are hidden or deep within complex internal geometries may not receive a uniform coating. This must be considered during the part design and fixturing phase.
High Initial Investment
PVD equipment—including vacuum chambers, power supplies, and control systems—represents a significant capital investment. This is not a workshop process but an industrial one that requires dedicated infrastructure.
Surface Imperfections are Replicated
PVD creates an extremely thin, conformal film. It will not hide or fill in scratches, tool marks, or other surface defects. On the contrary, it will precisely replicate the underlying surface texture, making substrate quality critical.
Substrate Compatibility
While PVD works on almost any inorganic material, the process temperature, although lower than many heat treatments, must be suitable for the substrate. Certain low-melting-point plastics or tempered materials may not be compatible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD is a strategic choice used to achieve specific performance goals. Use these points to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: PVD is the superior choice for extending the functional life of cutting tools, engine components, or medical implants.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: PVD is a high-performance, greener alternative to traditional electroplating methods like hard chrome, as it produces no toxic waste.
- If your primary focus is a decorative, yet functional finish: PVD provides a wide range of brilliant colors with a hardness that paint cannot match, ideal for consumer products like watches, faucets, and firearms.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: The smooth, dense nature of PVD coatings creates a low-friction surface, making it ideal for moving components in engines and machinery.
Ultimately, understanding PVD allows you to move beyond simple surface treatments and engineer superior product performance from the atomic level up.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | PVD Vacuum Coating | Traditional Plating/Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Bond Strength | Strong, atomic-level integration | Weaker, surface-level adhesion |
| Durability | Extremely hard, wear-resistant | Less durable, prone to chipping/peeling |
| Process | Clean, vacuum-based (dry process) | Often involves chemicals/waste (wet process) |
| Appearance | Wide range of durable, decorative colors | Limited by method, less durable finishes |
| Coating Thickness | Very thin, conformal film | Often thicker, can fill/hide imperfections |
Ready to engineer superior performance into your products?
PVD coating from KINTEK can transform your components, providing unmatched durability, wear resistance, and brilliant decorative finishes. Our expertise in lab and industrial equipment ensures you get the right coating solution for your specific needs—whether for cutting tools, medical devices, or consumer goods.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PVD vacuum coating services can enhance your product's longevity and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















