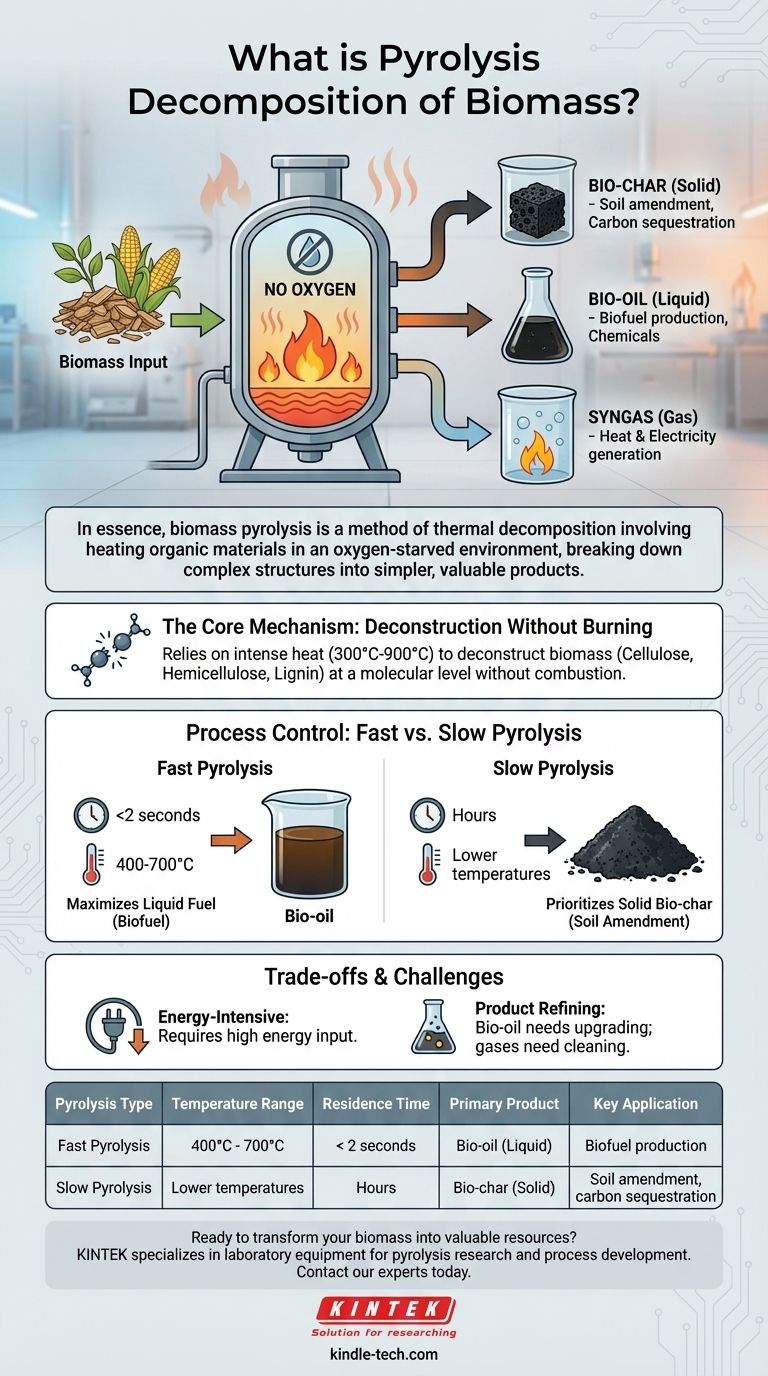
In essence, biomass pyrolysis is a method of thermal decomposition. The process involves heating organic materials, such as wood, agricultural waste, or manure, to high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen. This lack of oxygen prevents combustion and instead causes the material’s complex chemical structures to break down into simpler, more valuable products: a solid (bio-char), a liquid (bio-oil), and a gas (syngas).
The core purpose of pyrolysis is not merely to dispose of biomass, but to strategically transform it. By carefully controlling temperature and time, pyrolysis acts as a versatile conversion platform, turning low-value organic matter into distinct streams of high-value energy and material products.

The Core Mechanism: Deconstruction Without Burning
Pyrolysis is fundamentally different from burning. It relies on intense heat to deconstruct biomass at a molecular level without the presence of an oxidizer, which unlocks the raw materials trapped within.
The Role of Heat and Oxygen Deprivation
When biomass is heated without oxygen, it cannot combust. Instead of releasing its energy as fire and smoke, the thermal energy breaks the long-chain polymers that make up the biomass.
Temperatures for this process typically range from 300°C to 900°C. The specific temperature is a critical control parameter that dictates the final product distribution.
Decomposing the Building Blocks
Biomass is primarily composed of three main components: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Pyrolysis targets these structures, breaking them down into a variety of smaller molecules.
The different rates at which these components decompose allow operators to fine-tune the process to favor the production of either liquid, solid, or gaseous outputs.
The Three Primary Outputs
The decomposition results in three distinct product streams:
- Bio-char (Solid): A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It is widely used as a soil amendment to improve fertility and water retention or as a method for long-term carbon sequestration.
- Bio-oil (Liquid): A dark, dense liquid also known as pyrolysis oil. While it requires refining and upgrading to remove impurities, it can be processed into transportation biofuels and other valuable chemicals.
- Syngas (Gas): A mixture of combustible gases, primarily carbon monoxide and hydrogen. This gas can be burned directly to generate heat and electricity, often used to power the pyrolysis process itself.
Process Control: Fast vs. Slow Pyrolysis
The ratio of bio-char, bio-oil, and syngas produced is not fixed. It is determined by the speed and temperature of the pyrolysis process.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Liquid Fuel
This method uses high temperatures (400-700°C) and extremely short residence times—often less than two seconds.
This rapid heating and cooling cycle vaporizes the biomass quickly, maximizing the yield of liquid bio-oil. It is the preferred method for biofuel production.
Slow Pyrolysis: Prioritizing Solid Bio-char
In contrast, slow pyrolysis involves lower temperatures and much longer residence times, sometimes lasting for hours.
This gradual heating process favors the formation of a stable carbon lattice, maximizing the yield of solid bio-char. This method is ideal for producing agricultural soil amendments or for carbon sequestration.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While pyrolysis is a powerful technology, it is not without its practical limitations and complexities. An objective assessment requires acknowledging these factors.
Energy Input vs. Energy Output
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process. Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required consumes a significant amount of energy, which can impact the overall net energy gain of the system.
Efficient designs often capture and reuse the heat from the syngas output to help power the operation, but the initial energy investment remains a key consideration.
Product Quality and Contamination
The raw outputs of pyrolysis are not immediately ready for use. Bio-oil, in particular, is acidic, unstable, and contains water and impurities like tar.
It requires significant and often costly upgrading and refining before it can be used as a drop-in transportation fuel. Likewise, gases may need cleaning before use in engines or turbines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis strategy depends entirely on the desired end product. The process is a flexible tool, and the operating conditions must be aligned with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels: Fast pyrolysis is the necessary approach, but you must account for the significant downstream costs of refining the bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is creating stable carbon for soil amendment or sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the most effective and efficient path to maximize bio-char yield and quality.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction with on-site energy generation: Either process can work, as the co-produced syngas can be combusted to generate heat and power for your facility.
Pyrolysis provides a technological pathway to unlock the value embedded in organic waste, turning a disposal problem into a resource opportunity.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature Range | Residence Time | Primary Product | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | 400°C - 700°C | < 2 seconds | Bio-oil (Liquid) | Biofuel production |
| Slow Pyrolysis | Lower temperatures | Hours | Bio-char (Solid) | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment for pyrolysis research and process development. Whether you're focusing on biofuel production, soil enhancement, or waste-to-energy solutions, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you optimize your pyrolysis process. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory and research needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time

















