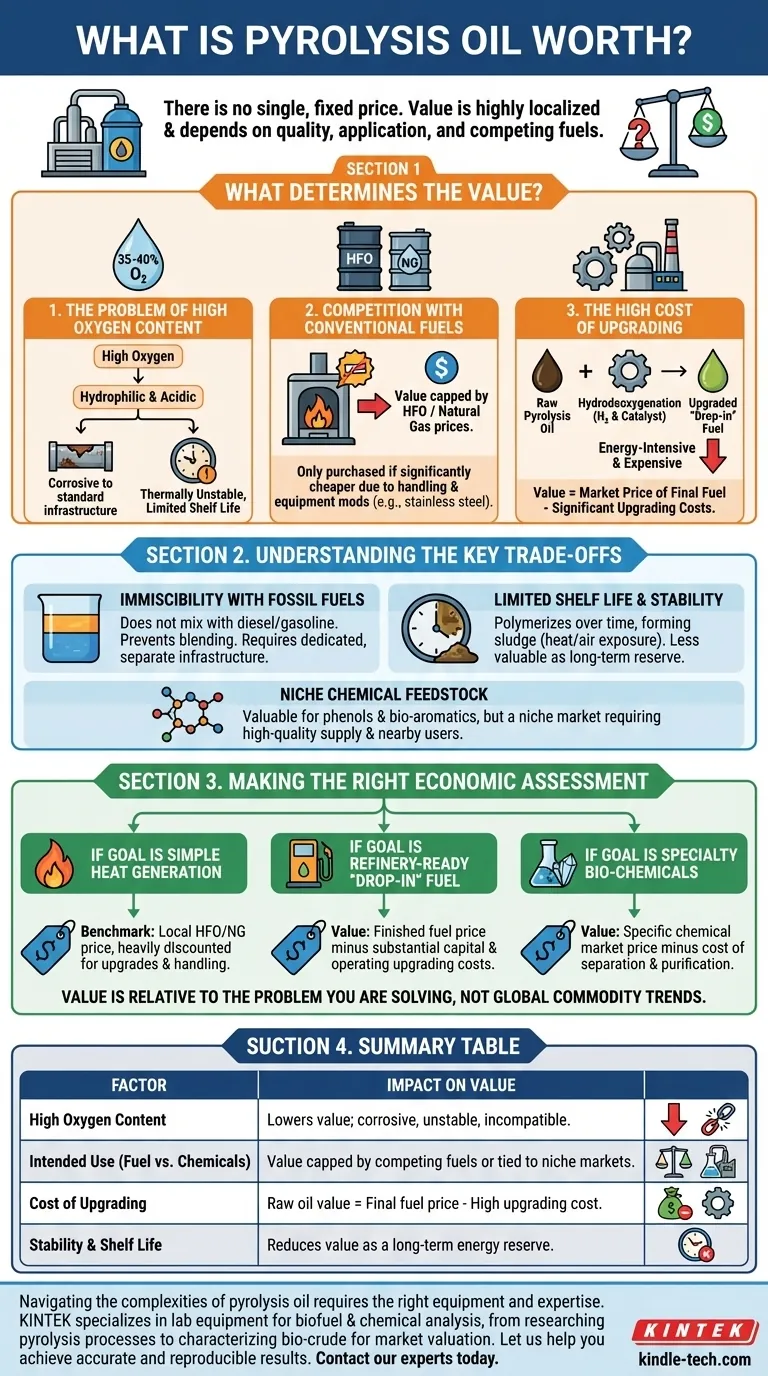
The short answer is there is no single, fixed price for pyrolysis oil. Unlike crude oil, it is not a globally traded commodity with a benchmark price. Its value is highly localized and determined by its specific quality, its intended application, and the market price of the fuels it aims to replace.
The fundamental challenge is that raw pyrolysis oil is not a direct substitute for refined petroleum. Its high oxygen content makes it unstable, corrosive, and incompatible with existing fuel infrastructure, which significantly impacts its market value.

What Determines the Value of Pyrolysis oil?
The economic worth of pyrolysis oil, often called bio-crude, is a function of its chemistry and the cost of making it usable. Several key factors dictate its price in any given scenario.
The Problem of High Oxygen Content
The single greatest technical and economic barrier is the oil's high oxygen content (often 35-40%), which is fundamentally different from crude oil's near-zero oxygen. This oxygen makes the oil hydrophilic (it contains water) and acidic.
These properties lead to severe limitations that directly lower its value, making it corrosive to standard steel pipes and tanks, and thermally unstable, meaning it can thicken and polymerize over time.
Competition with Conventional Fuels
The most common use for raw pyrolysis oil is as a fuel for industrial boilers and furnaces. In this context, its value is directly capped by the price of the fuels it competes with, such as heavy fuel oil (HFO) or natural gas.
A buyer will only purchase pyrolysis oil if it is significantly cheaper than these alternatives to compensate for its difficult handling properties and the required equipment modifications (like stainless steel tanks).
The High Cost of Upgrading
To be used as a true "drop-in" fuel for refineries, pyrolysis oil must be upgraded, primarily through a process called hydrodeoxygenation. This process uses hydrogen and a catalyst to remove oxygen.
This upgrading step is energy-intensive and expensive. Therefore, the value of raw pyrolysis oil is often calculated by taking the market price of a desirable fuel (like diesel or jet fuel) and subtracting the significant cost of this upgrading process.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Evaluating pyrolysis oil requires a clear-eyed view of its inherent limitations. These are not minor inconveniences; they are core economic factors.
Immiscibility with Fossil Fuels
Because of its unique chemistry, pyrolysis oil does not mix with hydrocarbon fuels like diesel or gasoline. This prevents it from being easily blended, which is a common practice in the conventional fuel industry.
This lack of fungibility means it requires its own dedicated and separate infrastructure, from storage to transport, adding cost and complexity.
Limited Shelf Life and Stability
The oil's tendency to polymerize means it has a limited shelf life. Over time, it can form sludge and solids, especially when exposed to heat or air.
This instability complicates storage and makes it less valuable as a long-term energy reserve compared to highly stable fossil fuels.
Value as a Niche Chemical Feedstock
In some specialized cases, pyrolysis oil can be more valuable as a source of renewable chemicals, such as phenols and other bio-based aromatics.
However, this is not a bulk market. It requires a consistent, high-quality supply and a nearby industrial user who can extract and utilize these specific chemical compounds, making it a niche opportunity rather than a broad commodity play.
Making the Right Economic Assessment
To determine what pyrolysis oil is worth, you must first define your goal. Its value is not intrinsic; it is relative to the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is simple heat generation: Your benchmark is the local price of heavy fuel oil or natural gas, discounted heavily to account for the necessary capital upgrades and handling costs.
- If your primary focus is creating a refinery-ready "drop-in" fuel: The raw oil's value must be calculated by working backward from the price of finished fuels, subtracting the substantial capital and operating costs of the required upgrading facility.
- If your primary focus is producing specialty bio-chemicals: The value is tied to the specific market price of the chemicals you can extract, minus the cost of separation and purification.
Ultimately, the worth of pyrolysis oil is defined not by global commodity trends, but by the specific industrial process it can integrate into economically.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Value |
|---|---|
| High Oxygen Content | Lowers value; makes oil corrosive, unstable, and incompatible with standard fuel infrastructure. |
| Intended Use (Fuel vs. Chemicals) | Value is capped by competing fuel prices (e.g., HFO) or tied to niche chemical markets (e.g., phenols). |
| Cost of Upgrading | Raw oil value is the price of the final fuel (e.g., diesel) minus the high cost of hydrodeoxygenation. |
| Stability & Shelf Life | Limited shelf life and instability reduce its value as a long-term energy reserve compared to fossil fuels. |
Navigating the complexities of pyrolysis oil requires the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced biofuel and chemical analysis. Whether you are researching pyrolysis processes, optimizing oil quality, or characterizing bio-crude for market valuation, our precise and reliable tools are designed to meet your laboratory's needs.
Let us help you achieve accurate and reproducible results. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your specific pyrolysis and biofuel research challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- How does RF sputtering work? Deposit Thin Films on Insulating Materials
- What is the function of a laboratory heater? Achieve Precise, Safe, and Controlled Heating
- Why is a laboratory oven essential in the catalyst impregnation workflow? Secure Your Material's Structural Integrity
- What are the safety issues with vacuum pumps? Avoid Chemical, Mechanical, and Implosion Risks
- Why is a laboratory oven required for pre-drying zeolite-titanate photocatalysts? Ensure Structural Integrity
- Why are ultrasonic cleaners or homogenizers required for electrocatalyst inks? Ensure Uniform Dispersion Today
- What is the use of drying oven in laboratory? Achieve Uniform Heat for Drying, Sterilizing, and Curing
- Why only KBr is used in IR spectroscopy? The Truth About the Best Material for Your Sample







