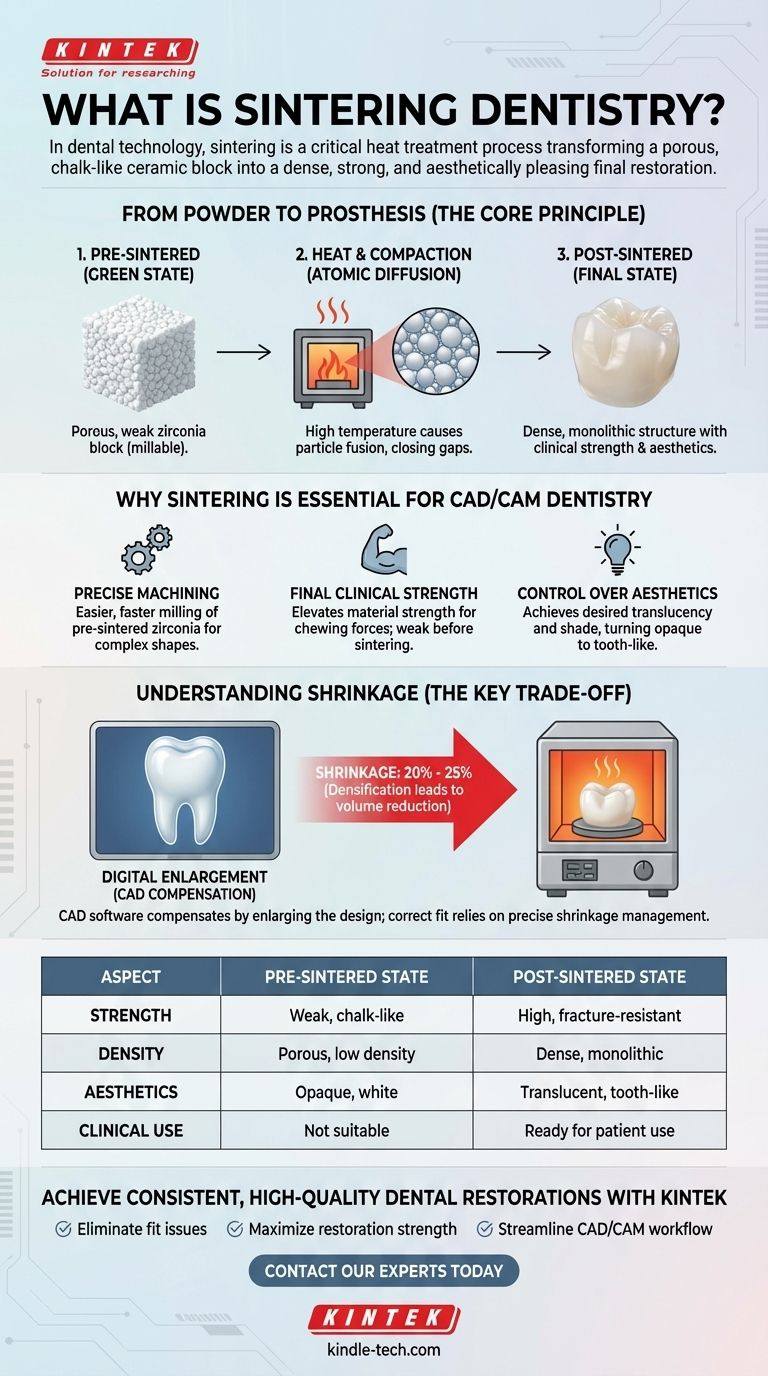
In dental technology, sintering is a critical heat treatment process that transforms a porous, chalk-like ceramic block into a dense, strong, and aesthetically pleasing final restoration. It involves heating a material, most commonly zirconia, to a high temperature—but below its melting point—which causes the individual ceramic particles to fuse together, eliminating voids and creating a solid, monolithic structure.
Sintering is not merely a heating step; it is the fundamental transformation that imparts the necessary strength, stability, and optical properties to modern ceramic dental materials. Understanding this process is key to appreciating how a soft, millable blank becomes a durable, patient-ready crown or bridge.

The Core Principle: From Powder to Prosthesis
Sintering is the essential bridge between the digital design of a dental restoration and its final physical form. The process works by fundamentally altering the material's microstructure.
What Happens at the Microscopic Level?
At its core, sintering is a process of atomic diffusion. The raw dental ceramic, such as zirconia, starts as a collection of fine particles that are lightly pressed together into a "green state" or "pre-sintered" block.
When placed in a high-temperature furnace, the particles do not melt. Instead, the heat energy excites the atoms at the contact points between particles, causing them to bond and fuse.
The Role of Heat and Compaction
This fusion process gradually closes the microscopic gaps, or pores, between the particles. As the material is held at the target temperature, the particles pull closer together, effectively compacting the structure from the inside out.
The result is a significant increase in the material's density. This densification is directly responsible for the dramatic increase in strength and fracture resistance observed in the final restoration.
From Opaque Chalk to Translucent Ceramic
The pre-sintered material is weak, porous, and chalky-white because the gaps between particles scatter light. The sintering process, by eliminating these pores, creates a more uniform structure that allows light to pass through.
This change is what gives the final zirconia restoration its desired translucency and aesthetic appearance, turning an opaque block into a material that can mimic the look of a natural tooth.
Why Sintering is Essential for CAD/CAM Dentistry
In the digital dentistry workflow, materials are specifically designed to be milled in a soft state and then sintered. This two-stage approach offers significant advantages.
Enabling Precise Machining
Milling zirconia in its pre-sintered, "chalk-like" state is far easier, faster, and less stressful on milling burs than trying to machine a fully dense ceramic block. This allows for the precise and efficient creation of complex anatomical shapes designed in CAD software.
Achieving Final Clinical Strength
The pre-sintered material is far too weak for clinical use. A crown milled from this material could be crushed with simple finger pressure. The sintering cycle is the required final step that elevates its strength to the levels needed to withstand the powerful forces of chewing.
Gaining Control Over Aesthetics
Modern dental zirconia comes in various shades and translucencies. The final aesthetic outcome is locked in during the sintering process. The specific temperature and duration of the heating cycle are carefully calibrated by the manufacturer to achieve the intended color and optical properties.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Shrinkage
The most critical factor to manage in the sintering process is the significant and unavoidable material shrinkage. This is not a flaw but a predictable consequence of densification.
The Shrinkage Factor
As the pores between the ceramic particles are eliminated, the entire restoration shrinks in volume. This shrinkage is substantial, typically ranging from 20% to 25% in all dimensions.
The Role of Software
To produce a restoration that fits the patient perfectly, the CAD software must compensate for this. The design is digitally enlarged by the exact shrinkage factor of the specific material block being used.
When the oversized restoration is milled and then sintered, it shrinks down to the precise dimensions of the original design, ensuring an accurate fit on the patient's tooth.
The Cost of Inaccuracy
Failure to account for the correct shrinkage factor is a primary source of error in dental labs. Using the wrong setting in the software will result in a crown or bridge that is either too small or too large, rendering it clinically useless.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the fundamentals of sintering directly impacts the quality and predictability of your final restorations. The key is to respect the material science and the manufacturer's validated protocols.
- If your primary focus is digital design (CAD): Always ensure you have selected the correct material profile in your software to automatically apply the precise shrinkage compensation factor for the specific blank you are using.
- If your primary focus is lab production (CAM): Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s recommended sintering cycle—including temperature, ramp-up/cool-down rates, and hold times—as even small deviations can compromise the restoration's strength and aesthetics.
- If your primary focus is clinical outcomes: Recognize that issues like fractures or a poor fit can originate from an improper sintering process, not just a flawed design, making it a critical area to review when troubleshooting cases.
Ultimately, mastering the principles of sintering is fundamental to leveraging the full potential of modern dental ceramics.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pre-Sintered State | Post-Sintered State |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Weak, chalk-like | High, fracture-resistant |
| Density | Porous, low density | Dense, monolithic |
| Aesthetics | Opaque, white | Translucent, tooth-like |
| Clinical Use | Not suitable | Ready for patient use |
Achieve Consistent, High-Quality Dental Restorations with KINTEK
Are you looking to enhance the strength, fit, and aesthetics of your zirconia crowns and bridges? The sintering process is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable dental sintering furnaces and consumables that ensure precise temperature control and consistent results, batch after batch.
Our equipment is designed for dental labs like yours, helping you:
- Eliminate fit issues with accurate, predictable shrinkage.
- Maximize restoration strength by adhering to manufacturer sintering protocols.
- Streamline your CAD/CAM workflow with user-friendly, efficient furnaces.
Don't let an inconsistent sintering process compromise your cases. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sintering solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics



















