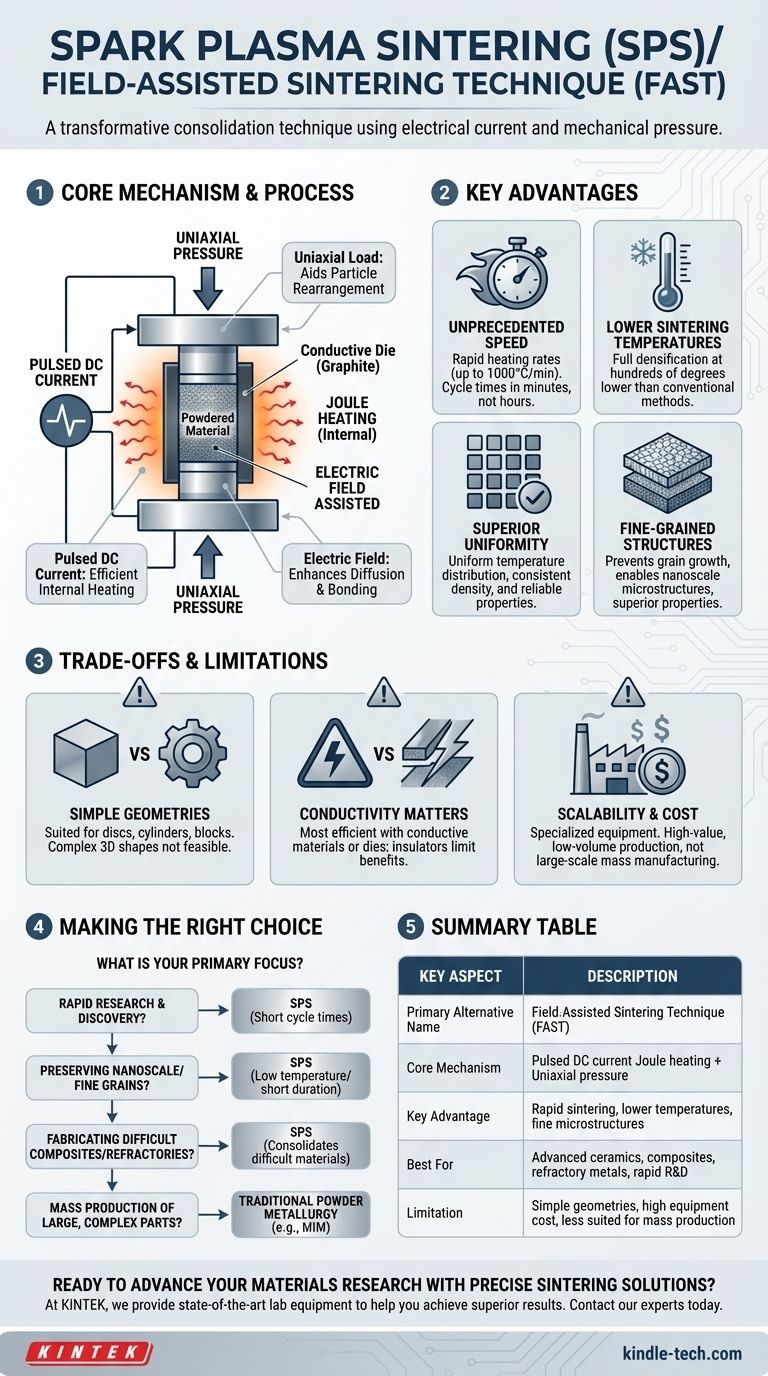
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is also known as Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST). This alternative name more accurately describes the process, which uses an electrical current and mechanical pressure to rapidly consolidate powders into dense solid materials. Unlike conventional furnaces that slowly heat a sample from the outside, SPS passes a current directly through the mold and sometimes the material itself, enabling incredibly fast heating and shorter processing times.
The critical takeaway is that SPS is not merely a faster heating method; it is a fundamentally different consolidation technique. By simultaneously applying pressure, a direct electrical current, and the resulting thermal field, it creates highly dense, fine-grained materials at lower temperatures and in a fraction of the time required by traditional sintering.

How SPS Redefines the Sintering Process
To understand the value of SPS, you must first understand how it diverges from conventional furnace-based methods. The process leverages a unique synergy between electrical, thermal, and mechanical forces.
The Core Mechanism: Joule Heating
In conventional sintering, heat is transferred slowly via radiation from an external heating element.
SPS generates heat internally through Joule heating. A pulsed direct current (DC) is passed through a conductive die (typically graphite) and, if the material is conductive, through the powder compact itself. This resistance heating is incredibly efficient and uniform.
The Role of Uniaxial Pressure
Similar to hot pressing, the powdered material is contained within a die and compressed by punches under a uniaxial mechanical load.
This constant pressure aids in particle rearrangement and plastic deformation, closing up porosity and accelerating the densification process far beyond what heat alone could achieve.
The Electric Field's Contribution
The "field-assisted" aspect of its alternative name is crucial. Beyond just generating heat, the electric field itself is believed to enhance material transport and bonding at the particle surfaces.
This unique combination of factors allows for full densification at temperatures often hundreds of degrees lower than required for conventional sintering.
The Key Advantages of SPS
The unique mechanism of SPS translates into several significant advantages for materials development and manufacturing.
Unprecedented Speed
The direct, internal heating allows for extremely rapid heating rates, sometimes as high as 1000°C per minute.
This drastically shortens the entire sintering cycle from many hours or even days to just a few minutes, accelerating research and development cycles.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
By activating sintering mechanisms with pressure and an electric field, SPS achieves densification at much lower peak temperatures.
This is critical for preventing undesirable grain growth, allowing for the creation of materials with fine-grained or even nanoscale microstructures, which often leads to superior mechanical properties.
Superior Material Uniformity
The rapid and direct heating method results in a highly uniform temperature distribution throughout the sample.
This minimizes thermal gradients and ensures the final product has a consistent density and microstructure, leading to more reliable and predictable performance. It's particularly effective for fabricating advanced ceramics, refractory metals, and composite materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its practical constraints.
Sample Geometry Limitations
The reliance on a rigid uniaxial die-and-punch setup means that SPS is primarily suited for producing simple geometries, such as discs, cylinders, or rectangular blocks.
Fabricating parts with complex, three-dimensional shapes is not feasible with standard SPS equipment.
Material Conductivity Matters
The process is most efficient when the material being sintered has at least some electrical conductivity, allowing the current to pass through it directly.
While insulating materials like many ceramics can still be sintered by heating the conductive graphite die, the full benefits of the field-assisted mechanism are not realized.
Scalability and Cost
SPS equipment is specialized and generally more expensive than conventional furnaces.
Furthermore, the process is typically used for smaller, high-value components rather than high-volume, large-scale industrial production, where the costs and geometric constraints can be prohibitive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct sintering technique depends entirely on your end goal. SPS is a specialized tool designed for specific, demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is rapid research and materials discovery: SPS is an unparalleled tool due to its extremely short cycle times.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanoscale or fine-grained structures: The low temperatures and short duration of SPS are essential to prevent grain growth and maintain desired microstructural features.
- If your primary focus is fabricating dense, high-performance composites or refractory metals: SPS excels at consolidating materials that are notoriously difficult or impossible to sinter using conventional methods.
- If your primary focus is mass production of large, complex parts: You should explore traditional powder metallurgy routes like press-and-sinter or metal injection molding.
Ultimately, Spark Plasma Sintering is a transformative technology that enables the creation of a new generation of advanced materials with precisely controlled microstructures and superior properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Alternative Name | Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST) |
| Core Mechanism | Uses pulsed DC current for internal Joule heating, combined with uniaxial pressure |
| Key Advantage | Rapid sintering (up to 1000°C/min), lower temperatures, fine-grained microstructures |
| Best For | Advanced ceramics, composites, refractory metals, and rapid R&D cycles |
| Limitation | Primarily for simple geometries (discs, cylinders); less suited for mass production |
Ready to advance your materials research with precise sintering solutions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment, including advanced sintering systems, to help you achieve superior material properties with controlled microstructures. Whether you're developing next-generation ceramics, composites, or refractory metals, our expertise can accelerate your R&D cycle and enhance your results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application



















